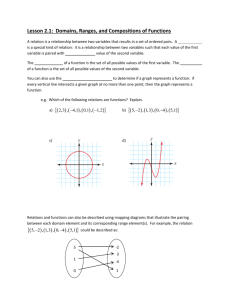
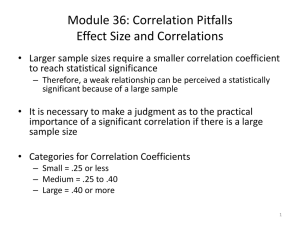
here - Maryland State Department of Education
advertisement
Maryland Model for School Readiness Fall 2010 Kindergarten Assessment Data Reliability Analysis Prepared by: Alicia Singleton, Research Analyst Maryland State Department of Education, Division of Early Childhood Development Office of the Asst. State Superintendent Introduction: This document is designed to provide an in depth analysis of the Maryland Model for School Readiness (MMSR) Kindergarten Assessment. The analysis interprets various relationships between the assessment items (the 30 indicators), each subject matter (the seven domains), and the overall test score (composite score). Below is a synopsis of each area of analysis that was performed, followed by a more descriptive illustration of the topics of interest. Correlation Analysis of the Composite Scores with the Seven Domains This process shows the results of the correlation of each of the seven domains with respect to the composite score. Using the Sum of Squares Method, the Correlation Coefficient is calculated and provides the percentage of variance between the variables. When the Correlation Coefficient is high, the relationship between the domain and the composite score are high. Analysis of Variance between local school systems (LEA) and schools within each system For the analysis of variance, the composite score (dependent variable) is measured under the independent variable classifications of local school system (LEA) and individual schools in each local system. The variation in the responses is assumed to be due to the effects of these factors. The remaining variation is accounted for with random error. The analysis of variance investigates whether there are significant differences between the groups and which groups have the most significant differences. Measurement of the Inner Consistency of the Work Sampling System Indicators Chronbach’s Alpha (α) Interrelated items may be summed to obtain an overall score for each participant. Cronbach's coefficient alpha estimates the reliability of this type of scale by determining the internal consistency of the test or the average correlation of items within the test. Chronbach’s Alpha generally increases when the correlations between the items increase. The 95% confidence interval for alpha is also determined. The reliability coefficient is then used to estimate the range of the true percentage of Fully Ready Kindergarten Students. Item Properties: Difficulty and Discrimination The Difficulty Index analyzes the proportion of students who rated proficient on an indicator. The Discrimination Index compares how the overall high scorers rated on an indicator compared to overall low scorers. The greater the value of the discrimination index, the stronger the relationship between overall test performance and performance on that item. Items with a higher difficulty index will have a higher discrimination index. Frequency Distribution of Composite Scores This table displays the occurrence of all possible composite scores and the percentage of the population. General Statistical Description: Composite Score by LEA This is a table that provides basic statistic information on the composite score for each Local School System. A description of the assessments overall general statistics is provided as well. Rating Percentages of Domain Indicators A detailed breakdown of the number and percent of “Proficient”, “In Process”, and “Needs Development” ratings for each domain’s indicators are provided.