A-CODE-FOR-TRAITS
advertisement

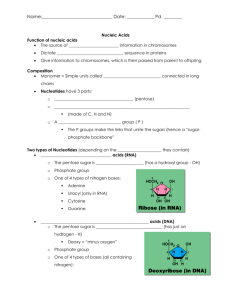
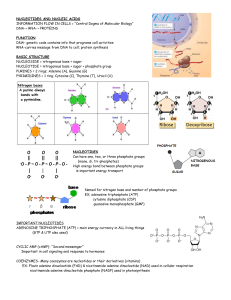
A CODE FOR TRAITS: DNA STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION NAME______________________________________________DATE_______________PERIOD____ INTRODUCTION Just as an architect uses a blueprint to construct a building, an organism’s DNA is a blueprint for its traits. The blueprints for the White House are different from the blueprints for the Washington Monument, making these two buildings different on a structural level. It makes sense, therefore, that organisms with different traits must have different DNA; but how is their DNA different? In today’s lab, you will investigate how differences in DNA can produce differences in human red blood cells. OBJECTIVE After completing this investigation, you will be able to explain how a genetic trait is determined by the code in a DNA molecule. PROCEDURES _____ 1. CUT out your 12 nucleotides along the solid lines. _____ 2. WRITE “Gene From (Mother or Father)” at the top of the plain white paper. _____ 3. FIND the numbered nucleotides – there should be six. GLUE these nucleotides in numerical order, beginning with number 1, down the LEFT side of your paper. The tab of one nucleotide should fit into the notch of the nucleotide before it. _____ 4. CONSTRUCT the complementary strand of DNA to complete your gene. This step models the anti-parallel nature of a DNA molecule – one side is “right-side-up” on a molecular level while the other side is “upside-down” _____ 5. LABEL your gene as either “normal hemoglobin” or “sickle hemoglobin” according to the key below. COMPARE your gene sequence to those in the key. RECORD the label to the right of your gene or at the bottom of your paper. Label your gene with one of the following: “N” (normal hemoglobin) if it has the following sequence G G C T T A “S” (sickle hemoglobin) if it has the following sequence G G C A T A _____ 6. DRAW the product of your gene on your white paper, according to the information below. Normal Hemoglobin Sickle Hemoglobin _____ 7. SIMULATE sexual reproduction with your partner. COMPLETE the data table below. MOTHER FATHER OFFSPRING Gene(s) (use N and/or S) Type of red blood cells (draw and label) _____ 8. COMPLETE the Analysis Questions. ANALYSIS QUESTIONS 1. Describe the shape of a real DNA molecule. Be as specific as possible. 2. How many base pairs does your gene have? 3. If a DNA molecule has 8436 Ts, how many As will it have? Justify your answer. 4. Use the template DNA molecule below to construct its complementary strand. template gene = A T C G C G A T A A G G C T A G C T G A C complement = . 5. Will your fictitious child be healthy or have sickle cell anemia? Explain your answer using information from your data table and incorporating your knowledge of how DNA is a code for traits. NUCLEOTIDES FOR MOTHER 1 deoxyribose adenine thymine phosphate group phosphate group adenine guanine phosphate group deoxyribose thymine phosphate group phosphate group adenine deoxyribose guanine 3 guanine phosphate group phosphate group deoxyribose phosphate group 2 deoxyribose deoxyribose 4 6 deoxyribose deoxyribose deoxyribose cytosine phosphate group 5 deoxyribose phosphate group thymine deoxyribose phosphate group cytosine deoxyribose phosphate group cytosine NUCLEOTIDES FOR FATHER 1 4 deoxyribose adenine deoxyribose thymine phosphate group phosphate group deoxyribose guanine phosphate group 6 deoxyribose adenine deoxyribose thymine phosphate group phosphate group adenine deoxyribose 3 guanine phosphate group phosphate group guanine phosphate group 2 deoxyribose deoxyribose deoxyribose cytosine phosphate group 5 deoxyribose phosphate group thymine deoxyribose phosphate group cytosine deoxyribose phosphate group cytosine