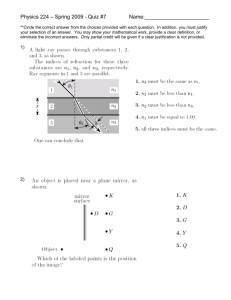
Section 19-4 Wave Properties of Light
advertisement
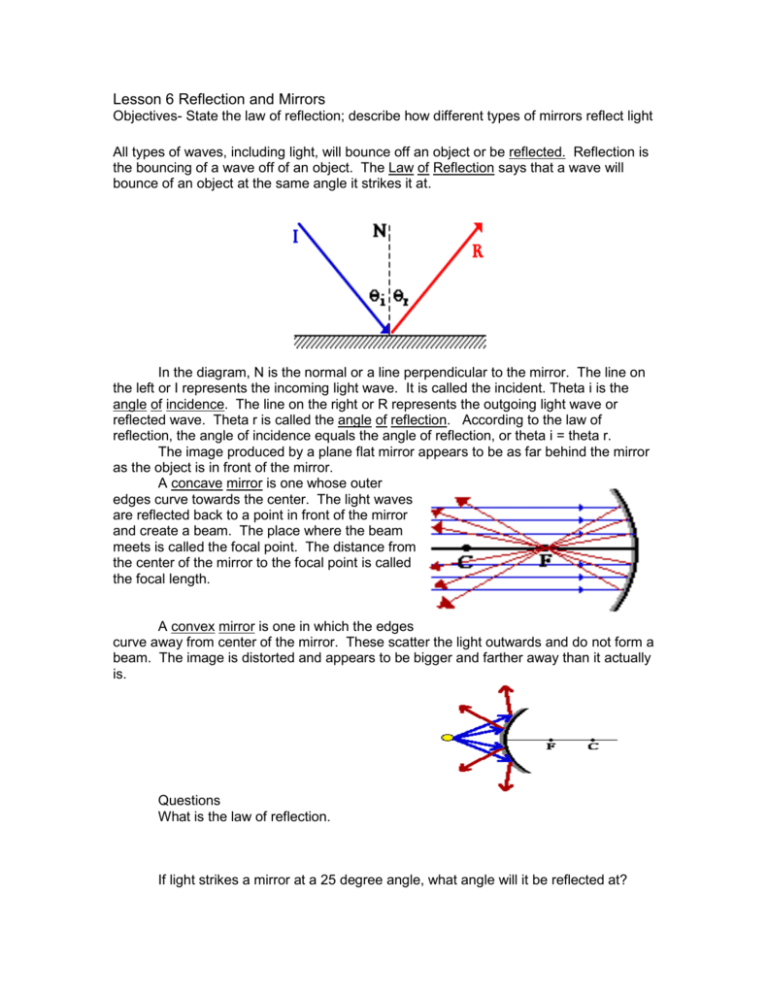
Lesson 6 Reflection and Mirrors Objectives- State the law of reflection; describe how different types of mirrors reflect light All types of waves, including light, will bounce off an object or be reflected. Reflection is the bouncing of a wave off of an object. The Law of Reflection says that a wave will bounce of an object at the same angle it strikes it at. In the diagram, N is the normal or a line perpendicular to the mirror. The line on the left or I represents the incoming light wave. It is called the incident. Theta i is the angle of incidence. The line on the right or R represents the outgoing light wave or reflected wave. Theta r is called the angle of reflection. According to the law of reflection, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, or theta i = theta r. The image produced by a plane flat mirror appears to be as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror. A concave mirror is one whose outer edges curve towards the center. The light waves are reflected back to a point in front of the mirror and create a beam. The place where the beam meets is called the focal point. The distance from the center of the mirror to the focal point is called the focal length. A convex mirror is one in which the edges curve away from center of the mirror. These scatter the light outwards and do not form a beam. The image is distorted and appears to be bigger and farther away than it actually is. Questions What is the law of reflection. If light strikes a mirror at a 25 degree angle, what angle will it be reflected at? Define angle of incidence. Define angle of reflection. Define focal point. What happens to the light that is reflected off a concave mirror? Give an example where a concave mirror is used. What happens to the light that is reflected off a convex mirror? Give an example where a convex mirror is used.