IV. Hazardous Materials and Waste Management Plan
advertisement

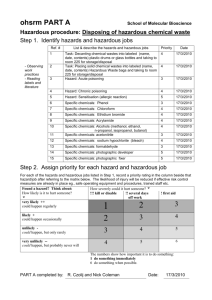
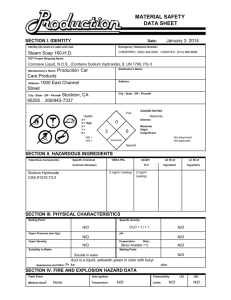
IV. Hazardous Materials and Waste Management Plan Goal—The goal of the Hazardous Materials and Waste Management Plan is to establish and maintain procedures to safely control hazardous materials and wastes generated by the organization. Scope—The scope of this plan includes the selecting, handling, storing, transporting, using and disposing of hazardous materials from receipt or generation through use and/or disposal. This also takes into consideration staff orientation, education and monitoring. Hazard Communication Program The Hazard Communication Standard (HCS), established by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), requires that the hazards of all chemicals, produced or imported, be evaluated, and that information concerning their hazards, if any, be transmitted to employees who may be exposed to those chemicals under normal operating conditions or in foreseeable emergencies. This Hazard Communication Program policy statement has been prepared to assist the clinic in complying with the Hazard Communication Standard. The Hazard Communication Program will provide all personnel with the means to understand the nature of any chemical hazard to which they may be exposed during the course of their employment so that they will be better able to protect themselves. The purpose of the program is to educate all personnel in the proper use, storage and disposal of toxic substances and chemical agents to improve employee protection from chemical hazards and thereby reduce illnesses and injuries caused by exposure to such substances and agents. The program includes: 1. Identifying and listing all hazardous chemicals present in the workplace; 2. Labeling all containers of hazardous chemicals in the workplace; 3. Obtaining and maintaining Material Safety Data Sheets; 4. Providing information about hazardous chemicals in the workplace; 5. Training employees regarding hazards of chemicals present in the workplace and the use of appropriate protective measures 6. Reporting and investigating all hazardous materials or waste spills, exposures, and other incidents; and 7. Monitoring and disposing of hazardous gases and vapors. Responsibilities The Infection Control Officer or designee for this organization is responsible for the communication and implementation of our program With all employees. The Infection Control Officer will compile a list of all hazardous chemicals used in each clinic and will update that list if new chemicals are obtained. The 1 chemical list will be placed in the Exposure Control Manual. The hazard determination will be based on information contained in the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) supplied by the manufacturer of each chemical. If a new chemical or material arrives without an accompanying MSDS, the Infection Control Officer will immediately contact the manufacturer or the supplier and request the appropriate MSDS. If the Infection Control Officer is unable to get the MSDS form the manufacturer or supplier, he/she will contact the local OSHA office for assistance. If a MSDS is unavailable because the material is "not hazardous," the supplier must provide a written statement to that effect and the statement will be filed with the other MSDS sheets. Identification and Listing of Hazardous Chemicals All hazardous chemicals will be identified on this list in the same manner as those chemicals are identified on the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheets. This list will be maintained in the clinic Policy and Procedure Manual. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) The clinic designee will maintain Material Safety Date Sheets for each product containing hazardous chemicals known to be present in the workplace. Each Material Safety Data Sheet will contain the following minimal information: The name, address and telephone number of the chemical's manufacturer, importer or distributor 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Hazardous ingredients/identity of the chemical Physical/chemical characteristics Fire and explosive hazard data Reactivity data Health hazard data Precautions for safe handling and use Control measures. Labels and Other Warnings The Infection Control Officer will take all necessary and appropriate measures to ensure that all hazardous chemicals present in the work area are labeled, tagged or marked as required under the applicable regulations. Labels and other warnings will include the identity of the product contained therein and appropriate hazard warning(s). Labels and other warnings will be legible, in English, and be prominently displayed on the container or readily available in the workplace throughout the work shift. Labels and other warnings may be repeated in languages other than English in appropriate circumstances. No employee will remove or deface existing labels or other warnings, unless the container is immediately thereafter marked with the required label or other warning. Employees will not be required to work with hazardous chemicals from unlabeled containers, except if portable containers are used, and the user knows the contents of the containers that are intended for immediate use. 2 Information The Infection Control Officer or designee will take all necessary and appropriate measures to ensure that all employees are informed of hazardous chemicals in their work area at the time of their initial assignment to that work area. Whenever a new hazard is introduced into their work area or significant changes occur in the data provided, additional training will be conducted. Non routine Tasks Management and personnel anticipating non routine tasks will consult with the Infection Control Officer/Employee Health Nurse before beginning these tasks. Any employee assigned to these tasks will be informed of the chemical hazards associated with the performance of these tasks and will be informed of the appropriate protective measures. Hazard Communication Training The Infection Control Officer or designee will take all necessary and appropriate measures to ensure that all employees are trained in the proper use, storage, transportation and disposal of hazardous chemicals in their work area at the time of their initial assignment in the work area and thereafter whenever a new hazard is introduced into their work area. Employees will be trained annually and be able to recall fundamental health and physical hazards associated with the specific chemicals to which they are exposed in their job, All employees will be given an opportunity for questions and answers during the training program. Employees should be able to verbally recall hazardous chemicals they work with, where the chemicals are stored, the effect on the body, detection, protection, disposal and other pertinent information. Written records of the training will be maintained. The Infection Control Officer and/or consultants will provide training. Training may include seminar presentations, videos, written materials, tests and demonstrations. Time will be allotted for employee questions. Training will be provided by this organization, as required by OSHA, at the following times and under the following conditions. • • • • • • • During normal working hours and at no cost to the employee. For all employees, full or part time, who have an actual or potential risk for contact with hazardous chemicals. When new hazardous materials and associated materials are received. Whenever safe handling and emergency procedures are modified. Annually as refresher training for all employees. For all new employees within their probationary period. For contract workers. Employee training shall include the following: 1. The Hazardous Communication Standard provides a "right-to-know" law for employees. 2. Hazardous chemicals are used and stored in the clinic. 3. A Material Safety Data Sheet Manual is located in the clinic and contains information on each particular chemical used in the clinic. 3 4. Reading for comprehension of Material Safety Data Sheets is required, and a glossary of terms is provided. 5. Employees may file complaints with the Department of Health and may not be discharged or discriminated against in any manner for the exercise of any rights provided by this act. Employees and citizens may make written requests to the Department of Health to require listing of small quantities of certain highly hazardous chemicals. 6. Records for any employee with an actual occupational exposure will be kept. Records will be kept confidential and will include the employee's name; social security number; hepatitis B vaccination status and dates; results of examinations, medical testing and follow-up procedures; a copy of the health care professional's written opinion; and a copy of information provided to the healthcare professional rendering the opinion. 7. Prior to being assigned to tasks or job responsibilities requiring a potential exposure or occupational hazard of exposure, employees must review the OSHA component during new employee orientation and must successfully complete the Hazard Communication Training program. Chemical/Mercury Spill Kits This organization will maintain both a chemical and mercury spill kit at each clinical location, replacing components as they are consumed. Employees will be trained on how to properly clean up spills, whether of chemical or biological origin. In case of a chemical spill the staff member will page "CODE GREEN... NAME OF Department. (location of spill by giving zone)" over the system if possible or out loud for assistance. The staff member will not leave the spill unattended. If the spill is in a patient care area, patients will be evacuated immediately. All employees must refer to the MSDS for proper cleanup procedures of a chemical spill. The spill kit should be used for cleanup of ALL chemical spills and biohazardous spills of more than 15ml. Mercury spill tits must be used to remove mercury. Mercury cannot enter the general waste stream. PPEs (gowns, glove, masks, eyeshields) should be used when cleaning up the spill. If the spill involves blood or other potentially infectious materials, then the spill bag or container must be placed in a biohazardous waste container. (See also Infection Control). Eyewash Stations Each clinical site will have an eyewash station that is easily accessible to employees who are performing those tasks, which may result in splashes of hazardous chemicals to the eye. Eyewash stations will be inspected monthly to ensure that they are in good working order. Handling of Disposable Waste Disposable waste may be grossly contaminated with infectious materials and therefore should be handled with care. Contaminated disposable waste would include but is not limited to: 4 -Any dressing used on phlebotomy sights -Paper tissues containing sputum -Wound dressings -Any other item not mentioned above contaminated with blood or body fluids -Disposable speculums -Cotton tipped applicators -Urine cups -Culture paddles Red bags are placed in trash containers in each room. All above items should be placed in red bags. Wound Dressings are to be disposed of in a manner to confine and contain any blood/body fluids that may be present. • Small dressings can be enclosed in the disposable glove used to remove the dressing. Pull the glove off inside out containing the dressing. The dressing and gloves can then be discarded into the red bag lined trash container in each exam room. • Larger dressings should be removed using gloved hands and placed into a red bag and then closed and deposited into the Bio-Hazardous cardboard box stored in the specified area of each clinic. Stericycle, Inc. Biomedical Waste, Enserv and BFI Services will pick up all red bag waste on a regular basis and as needed when notified. Disposal of Laboratory Specimens Laboratory specimens of blood and urine shall be disposed of by flushing them into the public sewer system in accordance with local sewage treatment or red bags. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) It is the policy of the clinic to protect employees from occupational exposure. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is one means of protection from potentially infectious materials. The purpose of the policy is to investigate instances when personal protective equipment is not used by an employee on his/her own judgment. There may be instances when, under rare and extraordinary circumstances it is the employee's professional judgment that the use of personal protective equipment would prevent the delivery of health care or public safety services or would pose an increased hazard to the safety of the worker or co worker. Needle Recapping 1. Recapping is permitted on clean needles when needles are to be changed, or during the process of drawing up medication 2. Contaminated needles should not be cut, bent or broken. 3. Contaminated needles are not to be recapped unless it is the only means for providing safe transport to the needle disposal container. If it is necessary to recap a contaminated needle, the onehanded technique is to be used. Under no circumstances are needles to be recapped using a twohanded technique. 4. Recapping is only to be done by using a one-handed recapping method in a safe manner or by a needle-to-syringe cork. 5 Procedure 1. Needle/Syringe/Cap • Place lid on a flat surface. Holding the syringe in one hand, slide the needle into the cap as far as it will go. • Using the opposite hand, carefully take the top of the cap between the forefinger and the thumb and secure the lid onto the syringe. 2. Needle/Syringe/Cork • • • Place cork on a flat surface standing upright. Holding the syringe in one hand, place the needle in the center of the cork and insert carefully. Keep your opposite hand away from the cork and needle. Handling of Contaminated Needles and SharpsPolicy Appropriate work practice controls will be followed in the handling and disposal of sharps in accordance to OSHA'S Blood Borne Pathogens Standard. Waste will be disposed of in a safe, efficient, environmentally sound and cost-effective manner. Purpose The purpose of outlining a procedure for the safe handling of contaminated sharps is to prevent needle stick injuries and cuts. If such an injury should occur, the incident should be reported immediately and protocol should be followed as outlined earlier in this manual. Disposal of Sharps 1. All sharps are to be placed in appropriate receptacles for disposal. 2. The containers are to meet the requirements as outlined in the OSHA Blood Bourne Pathogen Standard section that addresses the Regulations for Engineering Controls. These requirements are: a) The container must be puncture resistant and leak-proof on the sides and bottom. b) The container must be labeled or color-coded so that they can be readily identified by staff. c) The container must be located as close as possible to the places where sharps are used and be easily accessible. d) If reusable containers are used, the container must be designed so that they can be emptied without risk to the person emptying them. 3. Sharps containers are not to be filled over % full. The sharps container is to be closed tightly and discarded in the area designated for disposal waste at each site when it reaches the % full level. 4. Stericycle, Inc., Biomedical Waste, Enserve or BFI Services will pick up all closed and bagged sharps in the same manner in which they pick up red bag waste; on a regular basis and as needed when notified. 5. Employees will be trained on these procedures during their orientation period. Evaluation 6 A summary of the Hazardous Waste Management Plan which evaluates the program's objectives, scope, performance, and effectiveness will be prepared annually by the President/CEO for review by the Board of Directors. 7