Mineral Notes 1
advertisement
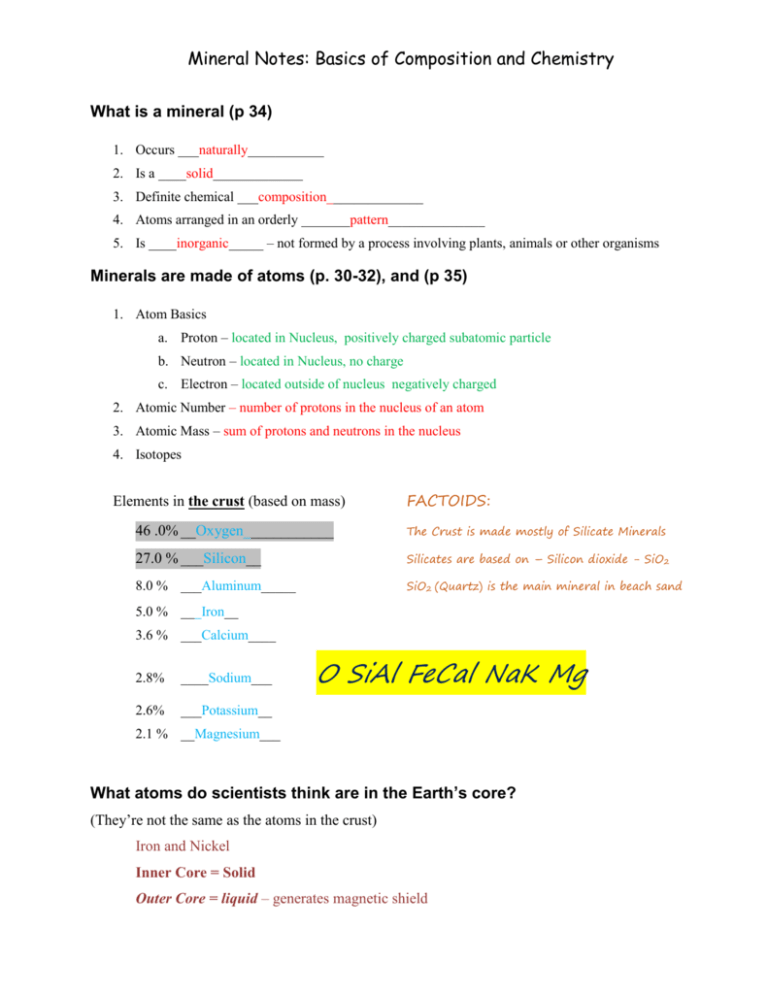
Mineral Notes: Basics of Composition and Chemistry What is a mineral (p 34) 1. Occurs ___naturally___________ 2. Is a ____solid_____________ 3. Definite chemical ___composition______________ 4. Atoms arranged in an orderly _______pattern______________ 5. Is ____inorganic_____ – not formed by a process involving plants, animals or other organisms Minerals are made of atoms (p. 30-32), and (p 35) 1. Atom Basics a. Proton – located in Nucleus, positively charged subatomic particle b. Neutron – located in Nucleus, no charge c. Electron – located outside of nucleus negatively charged 2. Atomic Number – number of protons in the nucleus of an atom 3. Atomic Mass – sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus 4. Isotopes Elements in the crust (based on mass) FACTOIDS: 46 .0% __Oxygen____________ The Crust is made mostly of Silicate Minerals 27.0 % ___Silicon__ Silicates are based on – Silicon dioxide - SiO2 8.0 % ___Aluminum_____ SiO2 (Quartz) is the main mineral in beach sand 5.0 % ___Iron__ 3.6 % ___Calcium____ 2.8% ____Sodium___ 2.6% ___Potassium__ O SiAl FeCal NaK Mg 2.1 % __Magnesium___ What atoms do scientists think are in the Earth’s core? (They’re not the same as the atoms in the crust) Iron and Nickel Inner Core = Solid Outer Core = liquid – generates magnetic shield Atoms can combine to form minerals in different ways Atoms combine by “bonding” with one another. All bonding between atoms involves the sharing or transfer of the outermost __electrons_______. Bonding (p 35 – 36) 1. Atoms bond in order to maximize the spread of energy. The most “comfortable” arrangement for an atom is when it has eight electrons in its outermost shell. Atoms will often transfer or share electrons so that they can obtain exactly eight electrons in the valence shell. An atom with eight electrons in the shell is said to have an _octet___. Interesting fact – atoms that already have an octet are relatively unreactive, and are called “noble gases” because they don’t associate with other atoms (light bulb demo) 2. Atoms can obtain an octet by “BONDING” with other atoms in two general ways: a. by transferring electrons. b. by ___sharing___ electrons. 3. Four general types of bonds are listed below: a. M_etallic b. C_ovalent__ c. I__onic___ d. P_olyatomic__ Ions METALLIC BONDS: A. Valence electrons wander freely through metal. Metal consist of a clump of positive atom nuclei held together by negativelycharged electron "glue" between them. B. Electrons can move rapidly in response to electric fields, hence metals are good conductors of electricity. C. Electrons can transmit kinetic energy rapidly; hence metals are good conductors of thermal energy. D. The layers of atoms in metal are hard to pull apart because of the electrons holding them together, so metals are tough. But individual atoms are not held to any other specific atom, and can slip easily past one another, so metals are ductile. COVALENT BONDS: When two Nonmetal atoms share electrons they create __covalent_ Bonds. Atoms bonded by sharing electrons are called molecules. The most common mineral with covalent bonds is silicon dioxide (quartz). Diamond is one of the hardest minerals. Diamond is composed of carbon atoms held together by covalent bonds Graphite is one of the softest minerals. Graphite is composed of carbon atoms held together by covalent bonds. What do you see that is different between the structure of graphite and diamond that might account for their different hardness? In diamond all the bonds between carbon atoms are strong (covalent), but in graphite the bonds between atoms of different layers are weak (not covalent) IONIC BONDS: When a Metal and a Nonmetal atoms get together the atoms will gain or lose electrons to achieve an octet, creating __ionic_ Bonds. Sodium and Chlorine; valence electron transfer: NaCl. The Positive and Negative ions attract one another: Na+ and Cl- Count the electrons and examine the charge in the valence shells for the sodium and chlorine before and after forming the ionic bond: Electrons in Valence Shell Charge on the atom BEFORE BONDING Sodium Chloride AFTER BONDING Sodium Chloride After the bonds have formed, the sum of all positive and negative charges must be __zero___ in an ionic compound Most minerals have a combination of many types of bonds. The properties of minerals are totally related to the type and number of bonds between the atoms: 1. What is the Mohs hardness number for the softest minerals? 2. What are three very soft minerals? 3. What bonding characteristics do the softest minerals have in common? 4. What is the Mohs hardness number for the hardest minerals? 5. What are three very hard minerals? 6. What bonding characteristics do the hardest minerals have in common? 7. What is unique about the bonds in pure metals that make their hardness between 2 and 5 on Mohs scale? 8. What type of bonds do the hardest minerals have?






