Readers Notebook Pages
advertisement

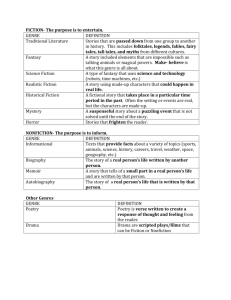
Marilyn Amey Reader’s Notebook (Gr. 2 – 8) (Fountas and Pinnell, 2006) Consider tabs in a notebook (spiral thick version) for: 1. Reading List 2. Books to Read 3. Letters 4. Guided Reading / Book Club Why use a reader’s notebook as a reflection tool? Helps students organize their thinking and collect it in one place Each section of notebook supports the reading process Students engage in meaningful opportunities to collect and organize their thinking about books *See attached pages for possible templates and/or explanations. Attachment are placed in book as follows: Front Cover - glue in “Guidelines for Reading Workshop” sheet Back Cover – glue in “How to Give a Book Talk” sheet Reading List – in the front of divider glue, “Reading Requirements” and on the back glue, “Genres at a Glance” Books to Read - in the front of divider glue, “Reading Interests” and on the back glue, “Books to Read” Letters - in the front of divider glue, “Form for a Friendly Letter” and on the back glue, “Guidelines for Proofreading Your Letter” Guided Reading / Book Club - in the front of divider glue, “Preparing for Book Discussion” and on the back glue, “Ways to Have a Good Discussion” Guidelines for Reading Workshop 1. Read a book or write your thoughts about your reading. 2. Work silently so that you and your classmates can do your best thinking. 3. Use a soft voice when conferring with a teacher. 4. Choose books that you think you’ll enjoy and abandon books that aren’t working for you after you’ve given them a chance. 5. List the book information when you begin and record the date when you finish. 6. Always do your best work. How to Give a Book Talk 1. Purpose Get readers excited about a book, author, series or genre. 2. Prepare Make sure you’ve read the book. Choose a book other readers will like. Think about what is interesting about your book. Think about the lead – how you will capture the readers’ interest. Write page numbers and a few notes on a sticky. 3. Present Show the book. Start with a good lead. Tell the author, title, genre. Explain why you choose to share the book. Tell a little about the book, but don’t give away secrets. Mention other books by the same author or other books in the series. 4. Remember Look at everyone. Speak clearly. Show your enthusiasm. Keep it short! Reading Requirements Book Minimum: ______ Requirement Genre Traditional Literature Realistic Fiction Historical Fiction Fantasy Science Fiction Informational Biography Choice Tally Genres at a Glance FICTION Code Genre Definition TL Traditional Literature Stories that are passed down from one group to another in history. This includes folktales, legends, fables, fairy tales, tall tales, and myths from different cultures. F Fantasy A story including elements that are impossible such as talking animals or magical powers. Make-believe is what this genre is all about. SF Science Fiction A type of fantasy that uses science and technology (robots, time machines, etc.) RF Realistic Fiction A story using made-up characters that could happen in real life. HF Historical Fiction M Mystery A fictional story that takes place in a particular time period in the past. Often the setting is real, but the characters are made up from the author’s imagination. A suspenseful story about a puzzling even that is not solved until the end of the story. R Romance A Action/Adventure H Horror A story that focuses on the love and attraction of two people and usually has a happy ending. A story that features physical action and violence, often around a quest or military-style mission set in exotic or forbidding locations. A story that aims to create fear in its readers. NONFICTION Code I Genre Informational B Biography AB Autobiography Code Genre P Poetry Definition Texts that provide facts about a variety of topics (sports, animals, science, history, careers, travel, geography, space, weather, etc.) The story of a real person’s life written by another person. The story of a real person’s life that is written by that person. OTHER GENRE Definition Poetry is verse written to create a response of thought and feeling from the reader. It often uses rhythm and rhyme to help convey its meaning. READING Title Author Genre Done? Pages Completed Date LOG Reading Interests Topics That Interest Me Genre / Types of Books That Interest Me Authors That Interest Me Books to Read Title Author Check When Completed Form for a Friendly Letter Date Greeting, Paragraph 1 Paragraph 2 Paragraph 3 Closing, Signature Body Guidelines for Proofreading Your Letter 1. Reread your letter to be sure it makes sense. 2. Be sure you have included 3 well-developed paragraphs (one may be a brief summary of what you read). 3. Did you include the date? 4. Check the greeting and closing. 5. Check your spelling, capitalization, and punctuation. Letters Letters between you and your students are a collection of thoughts over time as students develop as readers. They’re like written conversations about books. You can help children better communicate their thinking in several ways: 1. Model and demonstrate ways of expressing thinking through minilessons. 2. Talk with students about their letters during conferences giving specific feedback. 3. You can scaffold student’s thinking thorough ongoing written exchanges with them. Letters exchanged in a reader’s notebook have many advantages in helping students learn to write about their reading: Transition easily from talking to conversing about reading in writing Writing to an authentic audience for an authentic purpose Content is open-ended. Students usually focus on any kind of thinkng about reading that is meaningful to them. Expectation is for them to reflect on their reading Organize and present their thinking in continuous text (i.e. as compared to short-answer questions) Format is easily learned Receive authentic feedback that can extend their thinking Can ask questions and receive a response Can follow up or build on thinking Weekly opportunities to write about thinking Build-in audience (have in mind another reader who is listening and responding) Record of their thinking over time Gain vast amounts of practice organizing and presenting their thinking Teachers can analyse and assess the letters using a rubric and/or through anecdotal comments of their ability to read within, beyond and about the text. Preparing for Book Discussion Read and think about . . . . what you find interesting or surprising how the author makes you feel what you like/dislike about the writing what the author is trying to say and how you feel about it what the book makes you think your reaction to the characters how the book reminds you of your life how the book reminds you of other books how the book is similar to or different from other books by this author or other books in this genre what you don’t understand, finding confusing, or have questions about what you notice about the illustrations what you want to remember about the book places where the author gives good descriptions why you think the author wrote the book what the author is really trying to say what you notice about the author’s craft how the author used time examples of stereotypes or other biases what you notice about the author’s language, word choice, or style what you learned Ways to Have a Good Discussion 1. Be prepared. 2. Sit so everyone can see everyone else. 3. Get started right away. 4. Look at the person who is talking. 5. Listen to understand. 6. Ask questions to understand better. 7. Speak clearly but not too loudly. 8. Wait for the speaker to finish. 9. Use language that invites the opinions of others. 10. Be sure everyone gets a turn. 11. Build on one another’s ideas. 12. Respect one another’s ideas. 13. Stay on the topic. 14. Provide evidence from your experience or from the text to support your thinking. Example of a Reader’s Notebook (Fountas and Pinnell) READER’S NOTEBOOK Contents: A/ Reading Log and Books to Read List Record the title, author and other information about your reading selections. B/ Letters Letters are written to either a classmate or teacher. The letter should follow the friendly letter format and include a one paragraph summary about your selection (without giving too much away). The other paragraphs should develop 2 (different) formal responses to the reading (see response ideas, sample paragraph and rubric). Letters are to be written neatly. C/ Reading Workshop Students will explore skills/concepts presented in mini-lessons and then develop responses to a variety of texts. Reading workshops will also often include time for sharing (for example, Book Talks).