DI-Chest-consolidation
advertisement

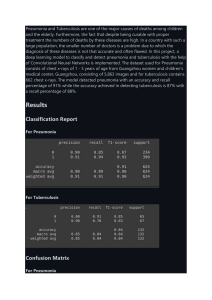
RADIOLOGY CASE REPORT Patient ID: OH# 3451423-2 Date of Study: July 13, 2008 Type of Study: CHEST X-RAY PA and LAT 1. Clinical Indication: Twenty year old female of African descent. Presents with chest pain. Past Medical history of sickle cell anemia and ? Active TB. 2. Picture: 2. Describe the radiological findings: The X-rays are PA and lateral of a 20 year old female. The PA is of adequate inspiration, exposure and minimal rotation. There is a Right Upper Lobe consolidation seen on the PA and Lateral films. A central cavitation can be seen in the lesion. There is improvement of the consolidation when compared to previous x-ray dated June 30, 2008. There is no evidence of pleural effusion as both costophrenic angles are well defined. The heart and mediastinum are within normal limits. There is no soft tissue swelling subcutaneous emphysema or fractures. 3. Provide possible diagnosis(es): Cavitary lesion located in the RUL will have a high suspicion of Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Bacterial pneumonia, fungal pneumonia, abscess, and tumor processes must be ruled out. Tb prefers the upper lobes due to the higher ventilation:perfusion ratio. 4. What would you recommend next for this patient? Clinical correlation with detailed history and physical examination is required. The patient will have to be placed on droplet precautions. Further testing for Tuberculosis would have to be done including a TB skin test, and acid-fast staining. Sputum culture can also help diagnose a bacterial pneumonia. Proper antiobiotic/antiTB treatment must then be administered based on previous test results. 5. Is the use of this test/procedure appropriate? This is an appropriate test for diagnosing a pulmonary consolidation. 6. Is(are) there any alternate test(s)? Alternate imaging tests would include a CT scan. This will better define the exact extent of the consolidation. 7. How would you explain to the patient about the possible risks and benefits of this test? The risk of a chest x-ray is due to radiation exposure. However, this risk is very low. There are natural x-rays in the environment which have higher doses of radiation such as radon from rocks and soil. The smallest dose of radiation is given, and a protective apron is provided. A pregnancy test should be done for all women of child bearing age. 8. What is the cost of this test? Chest X-ray is considered a relatively cheap test. I have been unable to find an exact cost, however, have been told it ranges from 10-20 dollars. As compared to a CT scan (500 dollars), MRI (1000 dollars), it is a very cheap test. References: Ouellette, H., & P. Tetreault. (2007). Clinical Radiology made ridiculously simple 2nd Edition. Miami: Medmaster Inc. James, L., & D. Brainard. (2006, March 13). Tuberculosis. E-medicine. Retrieved on July 17th, 2008 from http://www.emedicine.com/emerg/topic618.htm. Mayo Clinic Staff. (2007, May 24). Chest X-rays: sorting out problems in your chest. Mayoclinic.com. Retrieved on July 17th, 2008 from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/chest-x-rays/HB00019.