should-a-bundle-of-goal-directed-therapies
advertisement
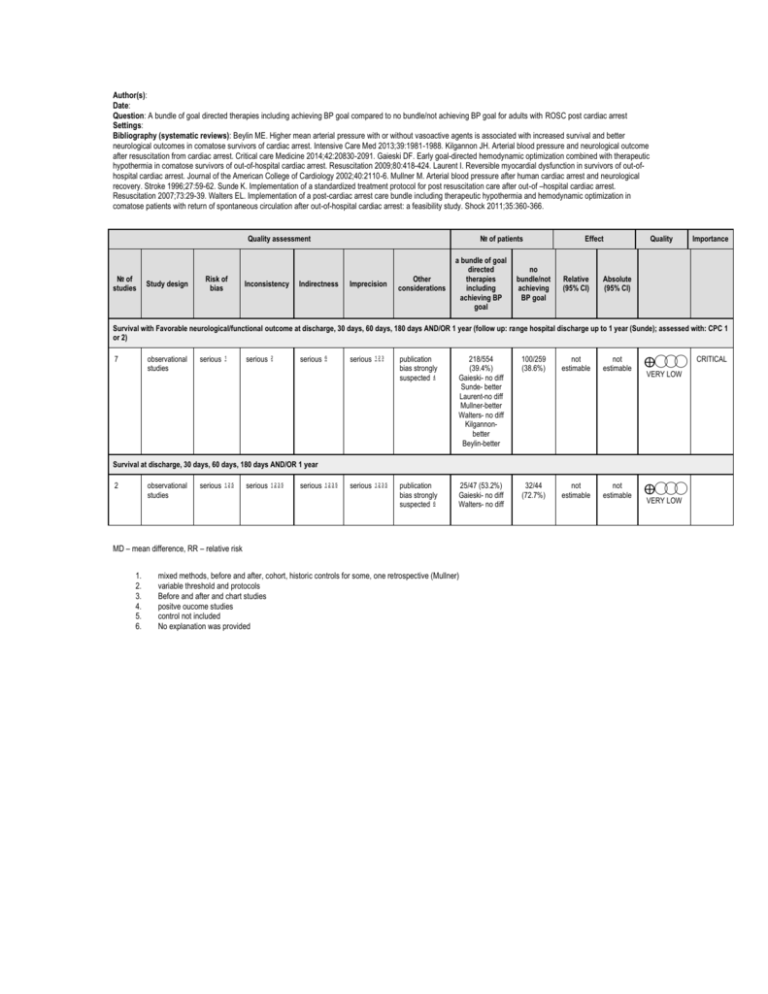
Author(s): Date: Question: A bundle of goal directed therapies including achieving BP goal compared to no bundle/not achieving BP goal for adults with ROSC post cardiac arrest Settings: Bibliography (systematic reviews): Beylin ME. Higher mean arterial pressure with or without vasoactive agents is associated with increased survival and better neurological outcomes in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest. Intensive Care Med 2013;39:1981-1988. Kilgannon JH. Arterial blood pressure and neurological outcome after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Critical care Medicine 2014;42:20830-2091. Gaieski DF. Early goal-directed hemodynamic optimization combined with therapeutic hypothermia in comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2009;80:418-424. Laurent I. Reversible myocardial dysfunction in survivors of out-ofhospital cardiac arrest. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2002;40:2110-6. Mullner M. Arterial blood pressure after human cardiac arrest and neurological recovery. Stroke 1996;27:59-62. Sunde K. Implementation of a standardized treatment protocol for post resuscitation care after out-of –hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2007;73:29-39. Walters EL. Implementation of a post-cardiac arrest care bundle including therapeutic hypothermia and hemodynamic optimization in comatose patients with return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a feasibility study. Shock 2011;35:360-366. Quality assessment № of studies Study design Risk of bias Inconsistency № of patients Indirectness Imprecision Other considerations a bundle of goal directed therapies including achieving BP goal no bundle/not achieving BP goal Effect Relative (95% CI) Quality Importance Absolute (95% CI) Survival with Favorable neurological/functional outcome at discharge, 30 days, 60 days, 180 days AND/OR 1 year (follow up: range hospital discharge up to 1 year (Sunde); assessed with: CPC 1 or 2) 7 observational studies serious 1 serious 2 serious 6 serious 123 publication bias strongly suspected 4 218/554 (39.4%) Gaieski- no diff Sunde- better Laurent-no diff Mullner-better Walters- no diff Kilgannonbetter Beylin-better 100/259 (38.6%) not estimable not estimable ⨁◯◯◯ publication bias strongly suspected 6 25/47 (53.2%) Gaieski- no diff Walters- no diff 32/44 (72.7%) not estimable not estimable ⨁◯◯◯ VERY LOW Survival at discharge, 30 days, 60 days, 180 days AND/OR 1 year 2 observational studies serious 125 serious 1235 serious 1235 serious 1235 MD – mean difference, RR – relative risk 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. mixed methods, before and after, cohort, historic controls for some, one retrospective (Mullner) variable threshold and protocols Before and after and chart studies positve oucome studies control not included No explanation was provided VERY LOW CRITICAL














