Ch.6 Notes Climate
advertisement

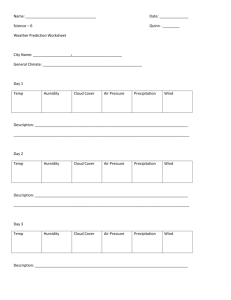
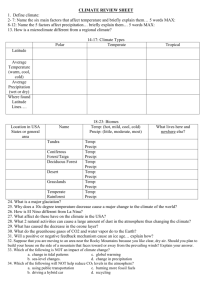
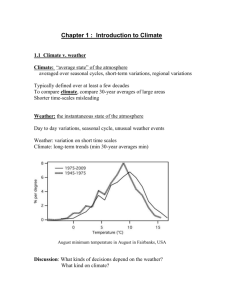
Ch.6 Climate Sect. 1 “What is Climate?” Climate – the pattern of weather that occurs in an area over many years. Determines types of plants or animals that can survive, and influences how people live. 5 elements averaged to determine climate: 1. temperature 2. precipitation 3. days of sunshine 4. humidity 5. air pressure Factors that affect Climate: 1. Latitude – distance N or S of the equator (lay down) a. Tropics – (23˚N & 23˚S) – sun shines almost directly overhead, keeping temperatures high – hot. b. Polar zones – (66.5˚N & 66.5˚S latitude to the poles) – sun shines at a low angle keeping temperature low – cold. c. Temperate zones – (between the tropics & the polar zones – moderate, mild temperatures. 2. Large bodies of water 3. Ocean currents can bring cool or warm temp. and moisture to coastal areas. 4. Mountains At the same latitude, the climate on a mountain is colder than the climate at sea level. Mountains cause air to rise, cool, & condense, creating a wetter climate on the windward side of the mountain & a much drier climate on the leeward side. 5. Cities – have higher temperatures than surrounding areas because of the asphalt & concrete absorbing radiation. Sect. 2: Climate Types Climatologist – studies climate types. W. Koppen developed a system of classification for climate types based on: Temperature Precipitation Plant types 6 types of climate: 1. tropical 2. mild 3. dry 4. continental 5. polar 6. high elevation Adaptation – any structure or behavior that helps an organism survive in its environment. 1. Structural adaptation – body structures that help organisms survive in certain climates. Ex: fur of mammals, needles of a cactus, blubber of a whale, cactus’s thick, fleshy stem helps it hold water. 2. Behavioral adaptation Ex: hibernation, migration Ex: estivation – period of inactivity through warm periods. Sect. 3: Climatic Changes Seasons – short periods of climatic change caused by changes in the amount of solar radiation an area receives. 1. As Earth revolves around the Sun, different areas of Earth are tilted toward the Sun. 2. The tropics don’t experience much seasonal temp. change. 3. High latitudes near the poles experience great seasonal temp. change. El Niño – an occasional climatic event in which strong Pacific winds weaken and sometimes reverse. Effects of El Niño: 1. Ocean temp. near Peru heat up. 2. The position & strength of 1 of the jet streams may be altered, changing wind and precipitation patterns around the world. 3. Africa & Australia may experience drought. La Niña – The winds blowing across the Pacific are stronger than normal. Causes of Climatic Changes can occur over short or long periods of time. 1. volcanic eruptions 2. meteorite collisions 3. pollution 4. variations in solar radiation, possibly related to the presence of sunspots 5. Earth’s movements in space can change the amount of solar energy reaching it. a. Earth’s tilt changes about every 41,000 yrs. b. Earth’s axis wobbles in space. c. The shape of Earth’s orbit changes over a 100,000yr. cycle. 6. The movement of Earth’s crustal plates affects the transfer of heat on Earth. Climatic Changes Today 1. Global Warming – Earth’s average global surface temp. is rising, possibly due to the increase in greenhouse gases in our atmosphere. 2. Greenhouse effect – a natural heating process that occurs when certain gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, & water vapor in Earth’s atmosphere trap heat. 3. Human activities affect the air. a. burning fossil fuels – increases the amount of carbon dioxide. b. Deforestation – results in fewer trees to absorb carbon dioxide. c. Individuals can help reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere by: Plant more trees Electric cars Reduce use of fossil fuels Recycle Reduce use of water and electricity Walk, ride bikes, carpool Burn in a fireplace rather than turning on heater.