Best Value Source Selection
advertisement
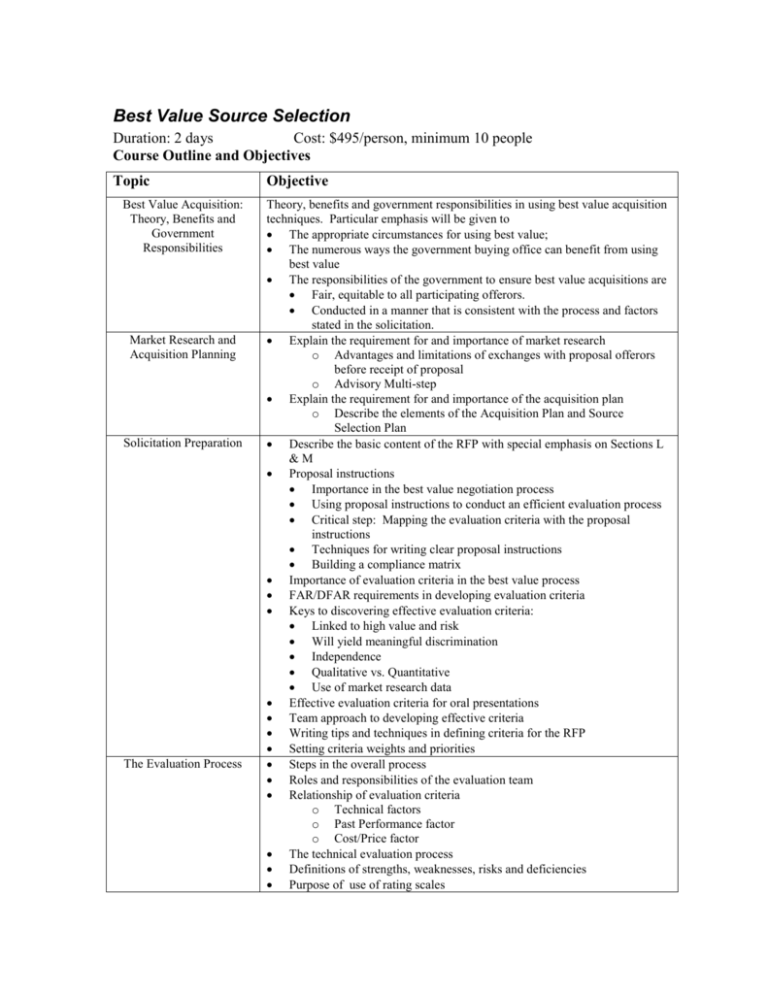
Best Value Source Selection Duration: 2 days Cost: $495/person, minimum 10 people Course Outline and Objectives Topic Best Value Acquisition: Theory, Benefits and Government Responsibilities Market Research and Acquisition Planning Solicitation Preparation The Evaluation Process Objective Theory, benefits and government responsibilities in using best value acquisition techniques. Particular emphasis will be given to The appropriate circumstances for using best value; The numerous ways the government buying office can benefit from using best value The responsibilities of the government to ensure best value acquisitions are Fair, equitable to all participating offerors. Conducted in a manner that is consistent with the process and factors stated in the solicitation. Explain the requirement for and importance of market research o Advantages and limitations of exchanges with proposal offerors before receipt of proposal o Advisory Multi-step Explain the requirement for and importance of the acquisition plan o Describe the elements of the Acquisition Plan and Source Selection Plan Describe the basic content of the RFP with special emphasis on Sections L &M Proposal instructions Importance in the best value negotiation process Using proposal instructions to conduct an efficient evaluation process Critical step: Mapping the evaluation criteria with the proposal instructions Techniques for writing clear proposal instructions Building a compliance matrix Importance of evaluation criteria in the best value process FAR/DFAR requirements in developing evaluation criteria Keys to discovering effective evaluation criteria: Linked to high value and risk Will yield meaningful discrimination Independence Qualitative vs. Quantitative Use of market research data Effective evaluation criteria for oral presentations Team approach to developing effective criteria Writing tips and techniques in defining criteria for the RFP Setting criteria weights and priorities Steps in the overall process Roles and responsibilities of the evaluation team Relationship of evaluation criteria o Technical factors o Past Performance factor o Cost/Price factor The technical evaluation process Definitions of strengths, weaknesses, risks and deficiencies Purpose of use of rating scales Evaluation of Oral Presentations Evaluating Past Performance Exchanges/ Negotiations With Offerors Making the Best Value Award Decision Full and Open Debriefings Compare and contrast evaluating oral presentations and written proposals Preparing to evaluate oral presentations Tips and techniques for optimizing the oral presentation evaluation process Critical requirements in conducting a past performance evaluation Review and application of case law to recent past performance evaluation Definitions of clarifications, communications and discussions. Information government should consider before awarding without discussions Establishing the competitive range The definitions of “meaningful” discussions Meaningful exchanges during oral presentations Proposal revisions and the Final Proposal Revision Limits on exchanges Integrating the final evaluation results Comparative assessment of offerors Considerations in the tradeoff process Documentation requirements for the source selection decision document FAR requirements for debriefings Quality debriefings: example process Techniques for delivering a first-class debriefing