Trace Elements Table
advertisement
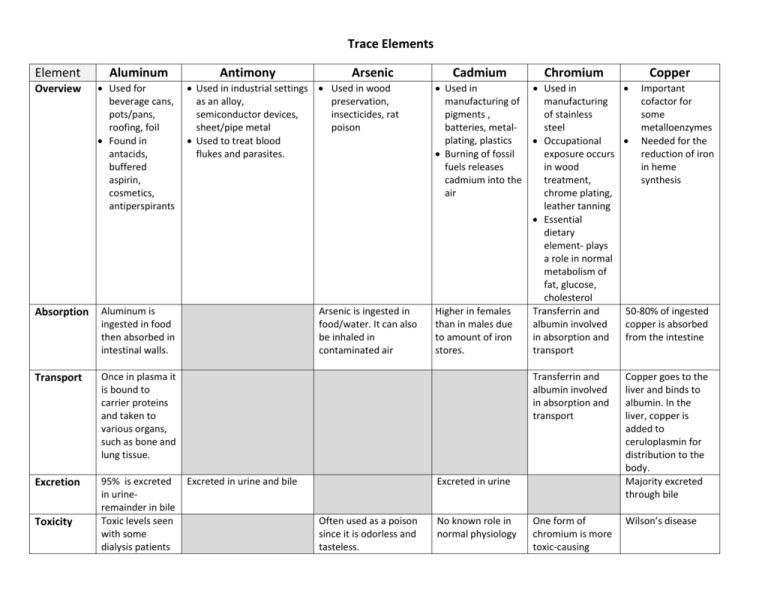
Trace Elements Element Aluminum Overview Used for beverage cans, pots/pans, roofing, foil Found in antacids, buffered aspirin, cosmetics, antiperspirants Absorption Aluminum is ingested in food then absorbed in intestinal walls. Transport Once in plasma it is bound to carrier proteins and taken to various organs, such as bone and lung tissue. Excretion 95% is excreted in urineremainder in bile Toxic levels seen with some dialysis patients Toxicity Antimony Arsenic Used in industrial settings Used in wood as an alloy, preservation, semiconductor devices, insecticides, rat sheet/pipe metal poison Used to treat blood flukes and parasites. Arsenic is ingested in food/water. It can also be inhaled in contaminated air Excreted in urine and bile Cadmium Used in manufacturing of pigments , batteries, metalplating, plastics Burning of fossil fuels releases cadmium into the air Higher in females than in males due to amount of iron stores. Chromium Used in Important manufacturing cofactor for of stainless some steel metalloenzymes Occupational Needed for the exposure occurs reduction of iron in wood in heme treatment, synthesis chrome plating, leather tanning Essential dietary element- plays a role in normal metabolism of fat, glucose, cholesterol Transferrin and 50-80% of ingested albumin involved copper is absorbed in absorption and from the intestine transport Transferrin and albumin involved in absorption and transport Copper goes to the liver and binds to albumin. In the liver, copper is added to ceruloplasmin for distribution to the body. Majority excreted through bile One form of chromium is more toxic-causing Wilson’s disease Excreted in urine Often used as a poison since it is odorless and tasteless. No known role in normal physiology Copper Element Aluminum Antimony Arsenic Cadmium Chromium Copper dermatitis and skin ulcers. When this form is inhaled, can result in airway irritation and lung cancer Effects Anemia Bone disease Progressive demetia Lab Evaluation Mass Spec AAS Mass Spec AAS Eye irritation Gastrointestinal issues Stomach ulcers Antimony spots on skin Gastrointestinal issues Pancytopenia Anemia Basophilic stipping Renal insufficiency/failure Nausea/vomitin g Abdominal pain Renal dysfunction Mass Spec AAS Mass Spec AAS Mass Spec AAS Mass Spec AAS Element Overview Absorption Transport Excretion Toxicity Mercury Manganese Molybdenum Nickel Used in steel production Used in misc. products: dyes, fertilizer, animal feed, wood preservative Helps in formation of connective and bony tissue Involved in blood clotting, fat/carbohydrate metabolism Involved in reproductive functions Used in the production of alloys, flame retardants Vital to human health because it binds to certain enzymes Via inhalation, ingestion, cutaneous , injection 2-15% absorbed in small intestine Absorption is age dependent- infants have higher levels 25-80% absorbed in the stomach and small intestine 50% absorbed from GI tract Fecal/urinary main routes No known normal human physiology. Bile Urine and bile Majority via urine/feces Exposure occurs from food Used in thermometers, dry cell batteries, dental amalgams, germicides, fluorescent light bulbs, diaper ointment, laxatives Rare Used in coins, jewelry, stainless steel Selenium Zinc Used in the electronics industry, pesticides, fungicides, anti-dandruff shampoo Anticarcinogen Involved with thyroid hormone synthesis Antioxidant Used in production of alloys (especially brass) Used in paints, skin lotions, die casting Used to treat Wilson’s disease Influences enzymes used in growth, wound healing, skeletal and sexual maturation Mainly occurs in small intestine – jejunum. 60% found in muscle, with the remaining in the skeleton Relatively nontoxic Element Effects Lab Evaluation Mercury Toxic to CNS/PNS Blurry vision Problems with hearing, taste, and smell Tingling in arms/legs Irritability Cough/ breathing difficulty Mass Spec AAS Manganese Molybdenum Nausea/vomiting Headache Disorientation Memory loss Anxiety Compulsive laughing/crying Mass Spec AAS Mass Spec AAS Nickel Selenium Zinc Dermatitis GI issues Cardiovascular symptoms GI issues Decrease in heme synthesis hyperglyce mia Mass Spec AAS Mass Spec AAS Mass Spec AAS