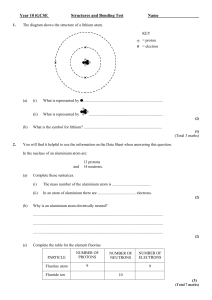
Created by the HTML-to-RTF Pro DLL .Net 4.6.10.19 Q1. The chart
advertisement

Q1. The chart shows the processes involved in the manufacture of nitric acid from ammonia. (a) Complete the word equation for the reaction that takes place in the first reaction vessel. ammonia + .............................. nitrogen monoxide + water (1) (b) (i) What is the use of the platinum gauze in the reaction vessel? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) At first, the platinum gauze is electrically heated. However, as the reaction continues, no further heating is necessary. Explain why. ........................................................................................................................... (1) Page 1 (c) Explain why the heat exchanger is used. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) To convert nitrogen monoxide into nitric acid, two further reactants are needed. What are they? ............................................................ and ............................................................... (1) (e) In an old method, nitrogen monoxide was produced from nitrogen instead of ammonia. The reaction was carried out at a high temperature (3000°C). Suggest two reasons for this. 1 ................................................................................................................................. 2 ................................................................................................................................. (2) (f) Complete the word equation below, to show how to make the fertiliser, ammonium nitrate. ................................... + .............................. ammonium nitrate + water (2) (Total 10 marks) Q2. (a) Copper is a metal. Explain how it conducts electricity. Page 2 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Graphite is a non-metal. Use the information to explain why graphite conducts electricity. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 5 marks) Q3. (a) The diagrams represent the atomic structures of two gases, hydrogen and helium. Page 3 Hydrogen gas is made up of diatomic molecules (molecules with two atoms). Helium gas exists as single atoms. (i) How is a molecule of hydrogen formed from two hydrogen atoms? (You may use a diagram as part of your answer) ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Why does helium exist only as single atoms? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Hydrogen combines with carbon to form methane. Each molecule contains four hydrogen atoms strongly bonded to a carbon atom. Explain why methane has a low boiling point. ..................................................................................................................................... Page 4 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Q4. The diagram shows electrolysis of sodium chloride solution. (a) Complete and balance these equations to show the reactions during electrolysis. At the positive electrode Cl– – e– → Cl2 At the negative electrode Na → Na (2) (b) Silver halides such as silver chloride and silver bromide are used in photography. The equation shows a reaction to prepare a silver halide. Page 5 Name and describe the products of this reaction, in words, as fully as you can. product 1 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... product 2 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 6 marks) Q5. The chart shows the processes involved in the manufacture of nitric acid from ammonia. (a) Complete the word equation for the reaction that takes place in the first reaction vessel. ammonia + ...................................... Page 6 nitrogen monoxide + water (1) (b) What is the use of the platinum gauze in the reaction vessel? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) To convert nitrogen monoxide into nitric acid, two further reactants are needed. What are they? ................................................................ and ............................................................ (1) (d) Complete the word equation below, to show how to make the fertiliser, ammonium nitrate. ................................ + ......................... ammonium nitrate + water (2) (e) Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in the fertiliser, ammonium nitrate NH4NO3. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) Q6. A student does an experiment to examine the rate of reaction between magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid. She adds 25 cm³ of the acid to a weighed amount of the metal. The reaction produces hydrogen gas. Magnesium + hydrochloric acid magnesium + hydrogen chloride Page 7 She collects the gas and measures the volume collected at one minute intervals. All the metal reacted but there was some acid left unreacted. Her results are shown on the graph. (a) The diagram shows part of the apparatus she used for the experiment. Complete the diagram to show how the student could collect the hydrogen produced and measure the volume after each minute. (2) (b) (i) When is the rate of reaction at its fastest? Page 8 .......................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) State one way in which she could increase the rate of reaction. .......................................................................................................................... (1) (c) (i) What is the total volume of hydrogen collected in the experiment? ................................................................................................................... cm³ (1) (ii) State one way in which she could increase the final volume of hydrogen collected. .......................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Q7. The diagram shows some magnesium ribbon burning. Page 9 (a) Choose words from the list to complete the sentences below. electrical an endothermic heat an exothermic light a neutralisation kinetic a reduction When magnesium burns, it transfers ......................................................................... and ............................................................................ energy to the surroundings. We say that it is .................................................................................. reaction. (3) (b) Complete the word equation for the reaction. magnesium + __________________________ magnesium oxide (1) (Total 4 marks) Q8. (a) Write down the symbols for lithium ................................................................................ fluorine ............................................................................... (2) (b) The electronic structure of a lithium atom can be shown like this: In a similar way, complete this diagram to show the electronic structure of a fluorine atom. Page 10 (1) (c) A lithium atom can lose one electron to form a lithium ion which can be written (2)+ A fluorine atom can gain one electron to form a fluoride ion. Choose from the list the correct way to write the fluoride ion. (2,6)+ (2,7)+ (2,7)- (2,8)+ (2,8)– Answer .......................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Q9. This question is about the structure of atoms. (a) Choose words from the list to complete the sentences below. electrons ions neutrons protons In an atom, the particles with a negative charge are called ..................................... Particles in the nucleus with no charge are called ..................................................... An atom has no overall charge because is has the same number of electrons and .................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Two isotopes of the element carbon are: 12 C 6 14 and C 6 Complete the table of information for these two isotopes. ATOMIC NUMBER MASS NUMBER NUMBER OF PROTONS Page 11 NUMBER OF NEUTRONS 12 Isotope C 6 6 12 Isotope C 6 6 6 12 6 6 (2) (Total 5 marks) Q10. (a) The formula for the chemical compound magnesium sulphate is MgSO4. Calculate the relative formula mass (Mr)of this compound. (Show your working.) ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Magnesium sulphate can be made from magnesium and dilute sulphuric acid. This is the equation for the reaction. Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2 Calculate the mass of magnesium sulphate that would be obtained from 4g of magnesium. (Show your working.) ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 12 Answer..................................... g (2) (Total 4 marks) Q11. The diagrams show the giant structures of sodium chloride and diamond. sodium chloride (melting point 801°C) (a) diamond (melting point 4800°C) The equation shows how sodium choride could be formed. Balance the equation. Na + Cl2 → Na Cl (1) (b) By reference to the detailed structure of sodium chloride explain fully why: (i) sodium chloride has a quite high melting point, ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) solid sodium chloride melts when it is heated strongly, Page 13 ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (iii) molten sodium chloride will conduct electricity. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (c) By reference to the detailed structure of diamond, explain why the melting point of diamond, is higher than that of sodium chloride. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) Q12. Marble chips (calcium carbonate) react with dilute hydrochloric acid. calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + carbon dioxide + water A student wanted to find out if the size of the marble chips made a difference to how fast the reaction took place. Page 14 (a) What readings should she take? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) She repeated the experiment but this time used the same mass (10g) of large marble chips. In both experiments there was some marble left in the flask when the reaction stopped. These are the results of the two experiments. TIME (minutes) 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Loss in mass (g), using small chips 0.00 0.40 0.72 0.91 1.04 1.04 1.04 Loss in mass (g), using large chips 0.00 0.28 0.52 0.70 0.84 0.94 1.04 (i) Explain the loss in mass in the two experiments. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) Page 15 (ii) What difference does the size of the chips make? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (c) A chemical reaction occurs when reacting particles collide with sufficient energy. The reaction between marble and hydrochloric acid is faster if the acid is at a higher temperature. Explain why. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) Q13. The formula for the chemical compound magnesium sulphate is MgSO4. Calculate the relative formula mass (Mr) of this compound. (Show your working.) ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (Total 2 marks) Q14. (a) The diagrams below show the electronic structure of a magnesium atom and a magnesium ion. Page 16 What is the charge on the magnesium ion? ............................................................... (2) (b) Calcium bromide has the formula CaBr2. What does this tell you about the ions in this compound? .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 4 marks) Q15. Calculate the formula mass (Mr), of the compound calcium hydroxide, Ca (OH)2. (Show your working) ............................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................ (Total 3 marks) Page 17 ## Here is a symbol equation, with state symbols, for a chemical reaction between solutions of lead nitrate and potassium chloride. Pb (NO3)2 (aq) + 2 KCl (aq) 2KNO3 (aq) + PbCl2 (s) The equation tells you the formulae of the two products of the reaction. (a) What are the names of the two products? 1 ................................................................................................................................. 2 ................................................................................................................................. (2) (b) What else does the equation tell you about these products? .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 4 marks) Q17. The diagram shows one molecule of the compound ammonia. Write down everything that the diagram tells you about each molecule of ammonia. ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... Page 18 ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (Total 4 marks) ## Atoms of calcium, phosphorus and fluorine are represented below, each with its mass number and proton number. (a) Use this information to complete the table. CALCIUM Number of protons in the nucleus 20 Number of neutrons in the nucleus 20 PHOSPHOROUS Number of electrons FLUORINE 9 16 15 9 (3) (b) Calcium and fluorine atoms can combine to form the compound calcium fluoride, CaF2. The fluoride ion is represented by F–. (i) Explain how the fluorine atom forms a fluoride ion. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) How is the calcium ion represented? Page 19 .......................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Phosphorus and fluorine form a covalent compound, phosphorus trifluoride. Complete the sentences below which are about this compound. Phosphorus trifluoride is made up of phosphorus and fluorine ................................ These are joined together by sharing pairs of ............................................... to form phosphorus trifluoride ........................................................ . (3) (d) (i) Sodium chloride, an ionic compound, has a high melting point whereas paraffin wax, a molecular compound, melts easily. Explain why. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Molten ionic compounds conduct electricity but molecular compounds are non-conductors, even when liquid. Explain why. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 14 marks) Q19. Here is a word equation for a chemical reaction. Page 20 copper oxide + sulphuric acid copper sulphate + water Write down everything that the word equation tells you about the reaction. ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (Total 4 marks) Q20. The information on the Data Sheet will be helpful in answering this question. (a) Calculate the formula mass (Mr) of the compound iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3. (Show your working.) ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Calculate the mass of iron produced when 32g of iron (III) oxide is completely reduced by aluminium. The reaction is shown in the symbol equation: Fe2O3 + 2Al → 2Fe + Al2O3 (Show your working.) ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Answer = ..................................... grams (3) (Total 6 marks) Page 21 Q21. The diagram shows the elements in Group 4 of the periodic table. Carbon is a non‑metal and silicon is usually considered to be a non‑metal. Tin and lead have all the usual properties of metals. Germanium has these properties: (a) • grey-white shiny solid • melting point 937°C • semi-conductor • reacts with chlorine to form the chloride (GeCl4) which is a liquid molecular compound • germanium oxide reacts with acids to form a salt solution and water. It also reacts with alkalis. With reference to their structure, explain why tin and lead are good conductors of electricity. ..................................................................................................................................... Page 22 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Would you classify germanium as a metal or as a non-metal? Give your reasons. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) Q22. You will find it helpful to use the information on the Data Sheet when answering this question. In the nucleus of an aluminium atom are: and (a) 13 protons 14 neutrons. Complete these sentences. (i) The mass number of the aluminium atom is ...................................... . (ii) In an atom of aluminium there are ....................................... electrons. (2) Page 23 (b) Why is an aluminium atom electrically neutral? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Complete the table for the element fluorine. PARTICLE NUMBER OF PROTONS Fluorine atom 9 Fluoride atom NUMBER OF NEUTRONS NUMBER OF ELECTRONS 9 10 (3) (Total 7 marks) Q23. (a) Balance these chemical equations. (i) H2 + O2 → H2O (1) (ii) Al + O2 → Al2O3 (1) (b) Briefly explain why an unbalanced chemical equation cannot fully describe a reaction. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) Page 24 (c) Explain, as fully as you can, why a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms but a hydrogen chloride molecule contains only one. (You may use a diagram in your answer if you wish). ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) Q24. (a) The formula for ammonia is NH3. What does the formula tell you about each molecule of ammonia? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Ammonia is used to make nitric acid (HNO3). Calculate the formula mass (Mr) for nitric acid. (Show your working). ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 25 ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) Q25. When a solution of lead nitrate is added to a solution of sodium chloride, a white precipitate of lead chloride is produced. (a) (i) Why is a precipitate formed? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Complete and balance the equation for this precipitation reaction. Pb+2(aq) + Cl–(aq) → (3) (b) Complete the table below by writing in the name and formula of the precipitate formed for each reaction. If there is no precipitate, write “no precipitate”. Page 26 (5) (Total 9 marks) Q26. The questions which follow refer to the element hydrogen. (a) Draw a diagram to show the bonding in one molecule of hydrogen. (2) (b) The table gives information about two compounds which contain hydrogen. Page 27 Use the information in the table to explain why it is difficult to classify hydrogen as a metal or a non metal. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 6 marks) Q27. Sodium carbonate reacts with acids. (i) Complete the word equation. sodium carbonate + hydrochloric acid → sodium chloride + ...................... + water (1) (ii) Name the salt produced if sodium carbonate reacts with dilute nitric acid. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 2 marks) Page 28 Q28. (a) The chart shows the reactions of the metal calcium with water, oxygen and dilute hydrochloric acid. Name (i) solution A ................................................................................................. (ii) solid B ..................................................................................................... (iii) gas C ........................................................................................................ (3) (b) The diagrams below show the electronic structure of an atom of calcium and an atom of oxygen. Describe fully what happens to its electrons when: (i) a calcium atom forms a calcium ion. State the charge on the calcium ion formed. ........................................................................................................................... Page 29 ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) an oxygen atom forms an oxygen ion. State the charge on the oxygen ion formed. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (c) Calcium oxide is an ionic compound. Why do ionic compounds have high melting points? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 11 marks) Q29. (a) By reference to their structure, explain how the particles in a piece of metal are held together and how the shape of the metal can be changed without it breaking. (You may use a diagram in your answer.) ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 30 (5) (b) Explain why metals are good conductors of electricity and suggest why this conductivity increases across the periodic table from sodium to magnesium to aluminium. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 9 marks) Q30. The diagrams show what happens when an acid is added to an alkali. Page 31 (a) What is present in the solution at stages 2 and 3 apart from universal indicator and water? (i) At stage 2 ......................................................................................................... (ii) At stage 3.......................................................................................................... (3) (b) Write an ionic equation to show how water is formed in this reaction and state the sources of the ions. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) Q31. Some students were investigating how fast hydrogen gas is released in the reaction between magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid. To begin with they used 0.1 g of magnesium ribbon. Next, they repeated the experiment using 0.1 g of magnesium powder. In each case, they used enough acid to react with all the metal. Page 32 (a) Their results are shown on the graph below. Hydrogen is produced in both the reactions. Use the information on the graph to describe two other ways in which the two reactions are similar. 1. ................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... 2. ................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Describe one way in which the reactions are different. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 3 marks) Page 33 Q32. The diagram below shows the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution, in the laboratory. (a) Which gas forms at the negative electrode? .............................................................. (1) (b) Explain why chlorine gas forms at the positive electrode. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) State one use of chlorine gas. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 4 marks) Page 34 Q33. The diagrams show what happens when an acid is added to an alkali. (a) What is present in the flask at stage 2, besides universal indicator and water? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Write an ionic equation to show how water is formed in this reaction and state the sources of the ions. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 4 marks) Q34. The two carbon atoms represented below are isotopes. ISOTOPE 1 14 ISOTOPE 2 mass number C 6 (a) proton number 12 C 6 Describe two ways in which the isotopes are similar. Page 35 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Describe as fully as you can one way in which they are different. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 4 marks) Q35. Chlorine will combine with the non-metal element, carbon, to form this molecular compound. (a) What is the type of bond in this molecule? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Explain how these bonds are formed. (You may use a diagram). ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 36 ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 3 marks) Q36. Magnesium oxide is a compound, made up of magnesium ions and oxide ions. (a) What is the charge on each magnesium ion? ............................................................. (1) (b) Explain how the magnesium ions get this charge. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 3 marks) Q37. (a) Iron powder is used in the manufacture of ammonia. Why is it used? ..................................................................................................................................... Page 37 ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Ammonia is manufactured from nitrogen and hydrogen. The equation for the reaction between them is: N2(g) + 3H2(g) (i) 2NH3(g) Which two raw materials are used to make the hydrogen? .......................................................... and ........................................................ (1) (ii) Why does increasing the pressure increase the chance of molecules of nitrogen reacting with molecules of hydrogen? .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Calculate the mass, in tonnes, of ammonia which could be produced from 560 tonnes of nitrogen. The relative atomic masses are: H 1; N 14. Show clearly how you get to your answer. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... Mass of ammonia = ............................................ tonnes (3) (Total 6 marks) Q38. Part of a reactivity series is: Page 38 (a) Carbon is used in blast furnaces to obtain iron and zinc from their oxides, but electrolysis has to be used to obtain aluminium from its oxide. Draw an arrow on the reactivity series above to show where carbon fits into the series. (1) (b) Predict the method of extraction used to obtain calcium from its ore and explain your answer. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) The formula for zinc oxide is ZnO. Write a balanced equation for the extraction of zinc in the blast furnace. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Q39. (a) The equation for the reaction that takes place when ammonium chloride is heated is: NH4Cl(s) ammonium chloride NH3(g) + ammonia HCl (g) hydrogen chloride The diagram shows how a teacher demonstrated this reaction. The demonstration was carried out in a fume cupboard. Page 39 (i) Apart from the gases normally in the atmosphere, which two gases would be at X? ..................................................... and ........................................................... (1) (ii) Name the white solid that has formed at Y. .......................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Why was the demonstration carried out in a fume cupboard? .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (1) (iv) Complete the four spaces in the passage. The chemical formula of ammonia is NH3. This shows that there is one atom of .......................................... and three atoms of .................................. in each ......................................... of ammonia. These atoms are joined by bonds that are formed by sharing pairs of electrons. This type of bond is called Page 40 a ............................... bond. (4) (b) Electrons, neutrons and protons are sub-atomic particles. (i) Complete the three spaces in the table. Name of sub-atomic particle Relative mass Relative charge ............................... 1 +1 ............................... 1 0 –1 ............................... (2) (ii) Which two sub-atomic particles are in the nucleus of an atom? ........................................................... and ............................................... (1) (Total 10 marks) Q40. The diagram represents the particles in a piece of reactive metal. Page 41 The piece of reactive metal is added to dilute hydrochloric acid. (a) (i) Which particle will probably react first? Choose from: • • • a particle inside the piece; a particle at the centre of a face; a particle on one of the corners. .......................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain the reason for your choice. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (1) (b) The reaction can be speeded up by making changes to the hydrochloric acid or the solid. (i) State two ways to speed up the reaction by changing the hydrochloric acid. In each case explain in terms of particles why the reaction is faster. 1. ...................................................................................................................... Page 42 .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (2) 2. ...................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) What change can you make to the piece of solid to speed up the reaction? Explain in terms of the particles why the reaction is able to speed up. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) Q41. Read the passage carefully and then answer the questions. The electrolysis of acidified water After a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid have been added to some distilled water, there will be three types of ion in solution: from the water, H2O(l) → H+(aq) + OH–(aq) from the acid, H2SO4(aq) → 2H+(aq) + SO42– (aq) When the electrodes (anode and cathode) in a circuit are put into the acidified water, the hydroxide ions and the sulphate ions are both attracted to the electrode called the anode. However, it is harder for the sulphate ions to give up their electrons than for the hydroxide ions to do this. So the hydroxide ions are the ones which react and bubbles of oxygen are formed at the anode. There are only hydrogen ions to be attracted towards the cathode and, when they get there, they take up electrons to form hydrogen molecules. From Chemistry Matters by Richard Hart, reproduced by permission of Oxford University Press Even in a small volume of water acidified with dilute sulphuric acid there will be billions of Page 43 ions. Some will be anions and some will be cations. (i) Name the ions in water acidified with dilute sulphuric acid. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain why only some of the ions are attracted to the anode. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (iii) Balance the equation for the reaction of hydroxide ions at the anode. 4OH– → H2O + O2 + e– (1) (Total 4 marks) Q42. (a) The diagram shows part of the ionic lattice of a sodium chloride crystal. (i) Complete the spaces in the table to give information about both of the ions in this lattice. Page 44 Name of ion Charge ..................................................... ..................................................... ..................................................... ..................................................... (2) (ii) When it is solid, sodium chloride will not conduct electricity. However, molten sodium chloride will conduct electricity. Explain this difference. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (2) (iii) Complete the sentence. Sodium chloride conducts electricity when it is molten and when it is .......................................................................................................................... (1) (b) The symbol for a calcium atom can be shown like this: (i) What is the mass number of this atom? .......................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) What information is given by the mass number? .......................................................................................................................... Page 45 .......................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Calcium burns in oxygen with a brick-red flame. The product is a white solid. It is calcium oxide and its formula is CaO. (i) Balance the chemical equation for the reaction. Ca(s) + O2(g) → CaO(s) (1) (ii) Describe, in terms of electrons, what happens to a calcium atom when it becomes a calcium ion. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 10 marks) Q43. Part of the Periodic Table showing the symbols for the first twenty elements is given below. (a) Draw diagrams showing the arrangement of electrons (electronic structures) in: (i) an aluminium atom; Page 46 (ii) a chlorine atom. (2) (b) (i) Use electronic structures to help you show why the formula of sodium oxide is Na2O. (3) (ii) State why the formation of sodium ions is classified as an oxidation. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Q44. (a) Ammonium sulphate is made by the reaction: 2NH3(aq) + H2SO4(aq) →(NH4)2SO4(aq) Page 47 (i) Complete the three answers in the table. Question Answer How many hydrogens are there in the formula of ammonium sulphate? .............................................................. What is the name of the substance with the formula NH3? .............................................................. What is the name of the substance with the formula H2SO4? .............................................................. (3) (ii) What is the main use for ammonium sulphate? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) A similar reaction is used to make ammonium nitrate. What is the name of the acid which must be used? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) NH3 is made by the reversible reaction: N2(g) + 3H2(g) (i) 2NH3(g) Explain what the term reversible reaction means. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) Page 48 (ii) What is the name of the raw material which is the source of nitrogen (N2)? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Nitrogen is an element. Explain what the term element means. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 10 marks) Q45. The apparatus shown in the diagram was used to investigate the rate of reaction of excess marble chips with dilute hydrochloric acid, HCl. Marble is calcium carbonate, formula CaCO3. The salt formed is calcium chloride, CaCl2. (a) Write a balanced equation for the reaction. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) Page 49 The following results were obtained from the experiment. (b) (i) Time in minutes Reading on balance in g 0.5 269.6 1.0 269.3 2.0 269.0 3.0 268.8 5.0 268.7 9.0 268.6 Plot the results and draw a graph on the axes below. (3) (ii) Continue the graph you have drawn to show the expected reading after11 minutes. (1) Page 50 (iii) On the axes above, sketch a graph of the result which would be obtained if in a similar experiment the same mass of powdered marble was used instead of marble chips. (2) (Total 8 marks) Q46. Ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulphate are used as fertilisers. (i) Which acid reacts with ammonia to form ammonium nitrate? .................................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Which acid reacts with ammonia to form ammonium sulphate? Page 51 .................................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) The reactions in (i) and (ii) are both exothermic. How can you tell that a reaction is exothermic? .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (1) (iv) The reactions in (i) and (ii) are both examples of acid + base reactions. What is the name of the chemical change which takes place in every acid + base reaction? .................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 4 marks) Q47. The drawing shows a container of a compound called magnesium chloride. (i) How many elements are joined together to form magnesium chloride? .................................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Magnesium chloride is an ionic compound. What are the names of its ions? Page 52 ................................................. ions and ................................................. ions (1) (iii) How many negative ions are there in the formula for magnesium chloride? .................................................................................................................................... (1) (iv) Complete the sentence. Ions are atoms, or groups of atoms, which have lost or gained ......................................... . (1) (v) Suggest three properties which magnesium chloride has because it is an ionic compound. Property 1 ................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... Property 2 .................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................... Property 3 .................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) Q48. (a) Atoms are made of sub-atomic particles. Complete the six spaces in the table. Name of sub-atomic particle Relative mass ................................. Neutron Relative charge ...................... ..................... Page 53 ....................... ................................. 1 ....................... (3) (b) Complete the spaces in the sentences. (i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of ..................................... in its nucleus and is equal to the number of ..................................................... if the atom is not charged. (1) (ii) The mass number of an atom is the total number of ................................. and ...................................... in its nucleus. (1) (c) The table gives information about the atoms of three elements. Number of electrons in: Name of element Chemical symbol 1st shell 2nd shell 3rd shell Fluorine F 2 7 0 Neon Ne 2 8 0 Sodium Na 2 8 1 Two of these elements can react together to form a chemical compound. (i) What is the name and the formula of this compound? Name ................................................... Formula .......................................... (2) (ii) What type of bonding holds this compound together? ........................................................................................................................... Page 54 (1) (iii) Explain, in terms of electron transfer, how the bonding occurs in this compound. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 10 marks) Q49. The diagram shows the apparatus for an experiment. Hydrated copper sulphate crystals were heated. They became anhydrous copper sulphate. (a) Name a suitable piece of equipment to heat tube A. Page 55 ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Use words from the box to complete the two spaces in the table. You may use each word once or not at all. black blue orange red purple white Name Colour Hydrated copper sulphate crystals ................................................... Anhydrous copper sulphate .................................................... (2) (c) What is the purpose of the ice and water in the beaker? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Drops of a clear, colourless liquid formed on the inside of tube B. (i) Name the liquid. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain how the liquid came to be inside tube B. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (e) Anhydrous copper sulphate can be turned into hydrated copper sulphate. What would you need to add? Apart from the change in colour, what could you observe? Page 56 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (f) Copper sulphate can be made from black copper oxide by reacting it with an acid. Name the acid. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 10 marks) Q50. The graph shows the volume of gas given off during an experiment using hydrogen peroxide solution and manganese oxide. Draw, on the axes above, a graph to show the result you would expect if the volume of hydrogen peroxide solution had been the same, but it was twice as concentrated. (Total 3 marks) Page 57 ## In this question you will need to use the following information: Relative atomic masses: H 1; O 16; Mg 24. The volume of one mole of any gas is 24 dm3 at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The diagram shows a chemical reaction taking place in a conical flask. The balanced equation for this reaction is: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) (a) Write a balanced ionic equation for this reaction. .................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Calculate the mass of magnesium required to produce 0.50 g of hydrogen. Show clearly how you work out your final answer and give the unit. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Mass = ............................... (2) Page 58 (c) (i) Draw a diagram to show how the electrons are arranged in a hydrogen molecule. (1) (ii) What is the name of the type of chemical bond between the hydrogen atoms in a hydrogen molecule? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (d) The chemical formula for hydrogen peroxide is H2O2. Calculate, to the nearest whole number, the percentage, by mass, of hydrogen in hydrogen peroxide. Show clearly how you work out your answer. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... Percentage = ................................. % (2) (Total 8 marks) Q52. Electrons, neutrons and protons are sub-atomic particles. (a) Complete the six spaces in the following table. Name of sub-atomic particle Relative mass Relative charge ....................................... 1 ........................................ Page 59 ....................................... ........................................ ....................................... 0 ......................................... (3) (b) An aluminium atom has 13 electrons. How are these arranged in shells around the nucleus? .................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Chromium atoms have 24 protons and 28 neutrons. (i) How many electrons does each neutral chromium atom have? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) What is the mass number of chromium? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (d) What change occurs to an atom which undergoes the process of reduction in a chemical reaction? .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (1) (e) The diagram shows part of the ionic lattice of a sodium chloride crystal. Page 60 Explain why the ions in this lattice stay in place. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 10 marks) Q53. Sea water is a good source of bromine. To obtain the bromine from the bromide ions dissolved in sea water, it is displaced by reacting with chlorine. The bromine is removed by blowing air through the mixture to carry away the bromine. Bromine and chlorine are both in Group 7 of the Periodic Table. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction between chlorine molecules and bromide ions. .............................................................................................................................................. . (Total 3 marks) Q54. (a) Every chemical element has a chemical symbol. Choose the correct chemical symbols from the box and complete the three spaces in the table. Page 61 C Co Cu Fe I Ir Zn Zr Name of element Chemical symbol Copper .................................... Iron .................................... Zinc .................................... (3) (b) Give one use for each of the following metals. You should give a different use for each metal. Copper ...................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... Iron ........................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... Zinc ........................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (c) Give four physical properties which metals usually have. 1. ................................................................................................................................ .................................................................................................................................... 2. ................................................................................................................................ .................................................................................................................................... 3. ................................................................................................................................ .................................................................................................................................... 4. ................................................................................................................................ .................................................................................................................................... (4) Page 62 (d) Metals usually form ionic compounds. Give one property of an ionic compound. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (1) (e) The diagrams show two different atoms, atom A and atom B. Atom A (i) Atom B Complete the following sentence. For these two atoms to become ions one ............................................ would be transferred from atom ........... to atom ........... . (1) (ii) Atom A and atom B are from different elements. How can you tell this from their nuclei? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 13 marks) Page 63 Q55. Zinc powder normally reacts slowly with hydrochloric acid. (a) Balance the symbol equation for the reaction. Zn + HCl → ZnC12 + H2 (1) The graph shows the results from a reaction of 1.0 g of zinc powder with 20 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid. It gives off a gas and forms zinc chloride, ZnCl2. Some unreacted zinc is left at the end. (b) Copper powder is a good catalyst for the reaction of zinc with hydrochloric acid. (i) A mixture of 10 cm3 of the same dilute hydrochloric acid and 1.0 g of copper powder was added to 1.0 g of zinc powder. What is the maximum volume of gas which could be given off? .................................................................................................................... cm3 (1) (ii) Draw a graph, on the axes above, for an experiment where 20 cm3 of the same dilute hydrochloric acid was added to 1.0 g of copper powder mixed with 1.0 g of zinc powder. (2) Page 64 (iii) Give two other ways the reaction described in part (i) could be made to go faster. 1. ....................................................................................................................... 2. ....................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Copper powder can be formed by adding copper sulphate solution to the mixture of zinc powder and acid. (i) Why does zinc react with copper sulphate solution to produce copper? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Write the word equation for the reaction. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 8 marks) Q56. Many indigestion tablets contain calcium carbonate as their only active ingredient. Calcium carbonate neutralises some of the hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Two different indigestion tablets, X and Y, were separately reacted with excess hydrochloric acid. The volume of gas given off in each reaction was measured every minute. The results are shown in the graph. Page 65 (i) Which tablet, X or Y, contained most calcium carbonate? .............................. Explain the reason for your answer. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Which tablet, X or Y, reacted faster with hydrochloric acid?........................... Explain the reason for your answer. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Explain the shape of the graph for tablet X between 3 and 5 minutes. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 3 marks) Page 66 Q57. The balanced symbol equation for the reaction is H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl (g) Starting with 2 g of hydrogen, what mass of hydrogen chloride would be produced? (Relative atomic masses: H = 1; Cl = 35.5) ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... Mass of hydrogen chloride = ...................................... g (Total 3 marks) Q58. (i) Complete the drawing to show the electron structure of a hydrogen fluoride molecule. Draw electrons as dots or crosses. (1) (ii) Explain why hydrogen fluoride is a gas at room temperature. ..................................................................................................................................... Page 67 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 3 marks) Q59. The flow diagram shows how to make ammonia and nitric acid from the nitrogen in the air. (a) A fertiliser is made by neutralising ammonia with nitric acid. What is the name of this fertiliser? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) In the flow diagram, why are two different catalysts used? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 68 (1) (c) What happens to catalysts at the end of a reaction? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Explain why catalysts are used in many industrial chemical reactions. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (e) Explain, in terms of collisions between molecules, why a high pressure is used in the reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) Q60. Ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, is made up of nitrogen, hydrogen and chlorine atoms. (i) Complete the table to show the number of atoms of each element present in NH4Cl. Element Number of atoms in NH4Cl nitrogen 1 hydrogen chlorine Page 69 (1) (ii) Calculate the relative formula mass of ammonium chloride, NH4Cl. (Relative atomic masses: H = 1, N = 14, Cl = 35.5) ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Relative formula mass = ................................................. (2) (Total 3 marks) Q61. (a) A piece of lithium is placed on the surface of some water in a beaker. Hydrogen is given off. Lithium hydroxide is also formed. Write a word equation for this reaction. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) The diagram shows the structure of a molecule of methane. Write down everything that this diagram tells you about a methane molecule. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 70 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 6 marks) Q62. Magnesium reacts with dilute sulphuric acid. magnesium + sulphuric acid → magnesium sulphate + hydrogen A student measured the volume of hydrogen given off every 10 seconds. The results are shown on the graph. (a) The average rate of hydrogen production in the first 10 seconds is Page 71 (60 cm3 ÷ 10 s) = 6 cm3/s. (i) Calculate the average rate of production of hydrogen between 30 seconds and 50 seconds. Show clearly how you work out your answer. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Rate ............................... cm3/s (3) (ii) Explain, as fully as you can, why the average rate between 30 and 50 seconds is different from the rate between 0 and 10 seconds. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) In industry, enzymes are used in both batch processes and continuous processes. Give one reason why continuous processes are usually more profitable than batch processes. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Q63. Hydrogen peroxide slowly decomposes into water and oxygen. hydrogen peroxide → water + oxygen The reaction can be speeded up by adding manganese dioxide. (a) (i) What do we call a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being changed itself? Page 72 ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Give two other ways of increasing the rate of this reaction. 1 ........................................................................................................................ 2 ........................................................................................................................ (2) (b) The diagram shows how the rate of this reaction can be measured. As the hydrogen peroxide decomposes, the mass of the flask and its contents decreases. Why does this decrease in mass take place? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 4 marks) ‘Iron tablets’ usually contain iron sulphate (FeSO4). Q64. (a) This salt can be made by reacting iron with sulphuric acid. Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2 Calculate the mass of iron sulphate that could be obtained from 4 g of iron. (Relative atomic masses: Fe = 56, H = 1, O = 16, S = 32) ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 73 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Mass of iron sulphate = ........................... g (3) (b) Under different conditions, another type of iron sulphate may form. Balance the symbol equation for this reaction. Fe + H2SO4 → Fe2(SO4)3 + H2 (1) (Total 4 marks) Q65. The diagram shows the structure of diamond. (a) To gain full marks for this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. Explain, as fully as you can, why diamond has a high melting point. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 74 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) The diagram below shows the outer electron shells of five carbon atoms in the giant lattice of diamond. Carbon atom C forms bonds with each of the carbon atoms W, X, Y and Z. Draw the positions of all the electrons in the outer shells of each of carbon atoms C, W, X, Y and Z. (3) (Total 6 marks) Q66. The flow diagram shows some stages in the manufacture of the fertiliser ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3). Page 75 (a) The elements needed to make ammonia (NH3) are obtained from natural gas and air. Which element is obtained from the air? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) The word equation for the formation of nitrogen monoxide is: ammonia + oxygen → nitrogen monoxide + water The platinum catalyst needs to be heated only at the start of the reaction. Suggest why. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Name the liquid A that reacts with nitrogen dioxide (NO2) to produce nitric acid (HNO3). ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Describe how ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) can be made from two of the products shown in the flow diagram. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 76 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Q67. Marble is a rock that contains mainly calcium carbonate. This reacts with hydrochloric acid. calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + water + carbon dioxide The rate of this reaction was followed by measuring the mass of carbon dioxide formed. Two 10 g samples of marble, A and B, were each reacted with 50 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid, at different temperatures. The mass of carbon dioxide formed in each reaction was recorded and plotted to produce the graph below. Page 77 Each reaction stopped when no more carbon dioxide was formed. In both experiments some marble was left unreacted when the reaction stopped. (a) Explain how you can tell which sample, A or B, reacted faster with the dilute hydrochloric acid. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) The faster rate of reaction was caused by using a higher temperature. Explain, in terms of particles, why a higher temperature causes a faster rate of reaction. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 5 marks) Page 78 Q68. Calculate the percentage of iron in iron sulphate (FeSO4). (Relative atomic masses: Fe = 56, O = 16, S = 32) ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... Percentage of iron in iron sulphate = ..........................% (Total 3 marks) Q69.Hydrated copper sulphate is a blue solid. When it is heated, white solid anhydrous copper sulphate is made. This is a reversible reaction. hydrated copper sulphate sulphate + water (blue) (a) [+ heat energy] anhydrous copper (white) To make the forward reaction work, the hydrated copper sulphate must be heated all the time. What type of reaction is this? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Anhydrous copper sulphate can be used in a test for water. What two things will happen when water is added to anhydrous copper sulphate? 1 .................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... 2 .................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 3 marks) Page 79 Q70. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) contains the same elements as water (H2O). (a) Name the hazard symbol shown by using the correct word from the box. corrosive flammable oxidising toxic (1) (b) Hydrogen peroxide decomposes in the presence of a catalyst. 2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g) (i) Complete the word equation for this chemical reaction. hydrogen peroxide → water + ................................ (1) (ii) What does a catalyst do to a chemical reaction? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 3 marks) Page 80 Q71. (a) Magnesium burns in oxygen, forming magnesium oxide. This equation represents the reaction. Mg (s) + O2 (g) → MgO (s) (i) Balance the equation. (1) (ii) Give the meaning of the state symbols (s) and (g). (s) .............................................. (g) .............................................. (2) (b) Use the Formulae of Some Common Ions table on the Data Sheet to help you to answer this question. Magnesium also reacts with chlorine to form magnesium chloride. Give the formula of magnesium chloride .................................................................. (1) (Total 4 marks) Q72. Iron is the most commonly used metal. Iron is extracted in a blast furnace from iron oxide using carbon monoxide. Fe2O3 (a) + 3CO → Fe + 3CO2 A sample of the ore haematite contains 70% iron oxide. Calculate the amount of iron oxide in 2000 tonnes of haematite. ............................................................................................................................... ...... ............................................................................................................................... ...... Amount of iron oxide = ......................................... tonnes Page 81 (1) (b) Calculate the amount of iron that can be extracted from 2000 tonnes of haematite. (Relative atomic masses: O = 16; Fe = 56) ............................................................................................................................... ..... ............................................................................................................................... ..... ............................................................................................................................... ..... ............................................................................................................................... ..... ............................................................................................................................... ..... ............................................................................................................................... ..... Amount of iron = .................................................... tonnes (4) (Total 5 marks) Q73. The diagram shows a model of part of the giant lattice of a metal. Page 82 (a) Name particles X and Y. X ..................................................... Y ..................................................... (2) (b) Explain, in terms of the giant structure above, why is it possible to bend a piece of metal. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 4 marks) Page 83 Q74. Calcium carbonate reacts with nitric acid to produce carbon dioxide. CaCO3 + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2 A 10 g lump of calcium carbonate was reacted with 20 cm3 of dilute nitric acid. When the reaction was finished, some of the calcium carbonate was left unreacted. The graph shows the volume of carbon dioxide made in each minute for sixteen minutes. (a) The volume of carbon dioxide made in each minute decreases until it remains steady at 83 cm3. Explain why. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Draw a graph line, on the axes above, for an experiment where 20 cm3 of the same Page 84 dilute nitric acid was reacted with 10 g of powdered calcium carbonate. (2) (c) Give one way of changing the rate of this reaction (other than using powdered calcium carbonate). .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Q75. Calcium carbonate reacts with nitric acid to produce carbon dioxide. CaCO3 + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2 A 10 g lump of calcium carbonate was reacted with 20 cm3 of dilute nitric acid. When the reaction was finished, some of the calcium carbonate was left unreacted. The graph shows the volume of carbon dioxide made in each minute for sixteen minutes. Page 85 (a) The volume of carbon dioxide made in each minute decreases until it remains steady at 83 cm3. Explain why. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Draw a graph line, on the axes above, for an experiment where 20 cm3 of the same dilute nitric acid was reacted with 10 g of powdered calcium carbonate. (2) (c) Give one way of changing the rate of this reaction (other than using powdered calcium carbonate). .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Page 86 M1. (a) oxygen / O2 (do not allow air) for 1 mark 1 (b) (i) idea that it is a catalyst / it increases the rate of reaction / lowers activation energy for 1 mark 1 (ii) the reaction is exothermic or releases energy / heat for 1 mark 1 (c) idea that • hot gases from the first reaction vessel need to be cooled • incoming gases / ammonia / oxygen need to be heated • there is an energy saving / cost saving any two for 1 mark each 2 (d) water and oxygen (need both) (accept H2O and O2) for 1 mark 1 (e) idea that • breaking bonds / breaking up molecules requires a lot of energy / reaction has a high activation energy • gives a better / faster rate of reaction • the reaction is endothermic / more energy needed to break existing bonds than to form new ones allow a higher temperature gives a greater yield / pushes the equilibrium position to the right any two for 1 mark each 2 Page 87 (f) ammonia (solution) / ammonium hydroxide (credit NH3 NH4OH) nitric acid / HNO3 in any order for 1 mark each 2 [10] M2. (a) • idea that copper has free electrons / electrons that move throughout the structure gains 1 mark but • in copper, electrons from the highest (occupied) energy level /outer shell, are free / can move throughout the structure gains 2 marks 2 (b) idea that • in graphite, only three bonds are formed by each carbon atom for 1 mark • one outer electron (per atom), free to move for 1 mark • an electric current is a flow of (free) electrons* for 1 mark (* this mark to be given in either (a) or (b) but not in both) 3 [5] M3. (a) (i) idea that • two hydrogen atoms share one pair of electrons • linked by a covalent bond Page 88 • each then has two outer electrons / a full outer shell / two • electrons in the highest (occupied) energy level (2 marks may be awarded for a correct electron diagram i.e. with electrons on boundary of or within marked area). any two for 1 mark each 2 (ii) idea that • helium atoms do not give / take / share electrons / react • because the (outer) shell / orbit is full or • highest (occupied) energy level is full (but not just “contains two electrons”) for 1 mark each 2 (b) idea that • the (attractive) forces between molecules are weak (not bonds between atoms) • so little energy is required / it is easy for molecules to escape from the liquid* / escape from other molecules* (allow evaporate / change into a gas) for 1 mark each 2 [6] M4. (a) 2Cl– – 2e– → Cl2 (allow unaltered LHS to produce ½ Cl2) + Na + e– → Na (allow × 2 for all terms) (credit candidates who point out that hydrogen / H2 is in fact produced) for 1 mark each 2 Page 89 (b) for product 1*, idea of a solid / precipitate or silver bromide gains 1 mark but solid / a precipitate of silver bromide gains 2 marks for product 2*, idea of aqueous / a solution / dissolved (in water) / or sodium nitrate gains 1 mark (do not allow liquid) but aqueous / a solution / dissolved (in water) of sodium nitrate (*do not credit formulae) gains 2 marks 4 [6] M5. (a) oxygen / O2 (do not allow air) for 1 mark 1 (b) idea that (it is a) catalyst / it increases the rate of reaction for 1 mark 1 (c) water H2O and oxygen / O2 (need both) (in either order) for 1 mark 1 (d) ammonia / NH3 (do not allow ammonium) (allow ammonium hydroxide / NH4OH or ammonia solution) nitric acid / NHO3 in any order for 1 mark each 2 (e) 14 + 4 + 14 + 48 or Mr = 80 gains 1 mark but or 35% gains 2 marks 2 [7] Page 90 M6. (a) (must be possible for the gas to enter and displace the water) or other suitable apparatus • apparatus to collect the gas correctly assembled for 1 mark • calibrated collection vessel (award even if diagram is wrong) for 1 mark 2 (b) (i) at the start / in the first 1/2 minutes (or any time within this range) for 1 mark 1 (ii) increase the temperature / use smaller pieces of metal / use more metal / increase the surface area of the metal / add a catalyst / shake the flask / increase the concentration / strength of the acid for 1 mark 1 (c) (i) 48 for 1 mark 1 (ii) increase the amount of magnesium used for 1 mark (do not allow increase the amount of acid used) 1 [6] M7. (a) heat light an exothermic in any order for 1 mark each 3 Page 91 (b) oxygen / O2 for 1 mark 1 [4] M8. (a) lithium = Li (ignore mass / atomic numbers) fluorine = F (do not allow if case is incorrect) for 1 mark each 2 (b) (allow ● or o for electrons) (allow any positions for the seven electrons added provided they are on the outer ring) for 1 mark 1 (c) (2,8)+ or (2,7)– (brackets not required) gains 1 mark but (2,8)– gains 2 marks 2 [5] M9. (a) electrons neutrons protons for 1 mark each 3 (b) mass number no. of neutrons 14 8 for 1 mark each 2 [5] Page 92 M10. (a) Mg S O4 24 + 32 + 16 (×4) or 64 / evidence of all Ar’s gains 1 mark but (Mr) = 120 gains 2 marks 2 (b) evidence that 24(g) magnesium would produce 120(g) mapesiurn sulphate gains 1 mark or correct scaling by 1/6 but 20(g) magnesium sulphate gains 2 marks [credit error carried forward from (a) with full marks in (b)] 2 [4] M11. (a) 2 Na + Cl2 → 2 NaCl allow 2 Na+ Cl– for 1 mark (allow Na + ½Cl2 → Na Cl) 1 (b) (i) idea that • it has strong (attractive) forces/bonds between ions / charged particles for 1 mark (not ‘..it has a rigid structure’- this defines a solid or ‘...particles close together’ – they are in a liquid) 1 (ii) ideas that • there is increased vibration of ions / particles on heating Page 93 • ions have sufficient energy to overcome attractive forces / to break out of the • rigid structure / to move about (must be in terms of increased energy of particles lions) each for 1 mark 2 (iii) • ions can go to electrodes / ions are free to move for 1 mark [do not credit ‘ions carry charges’] 1 (c) ideas that • it has stronger attractive forces between atoms/particles (not ‘ions’) • each carbon atom forms covalent bonds with neighbouring atoms each for 1 mark 2 [7] M12. (a) ideas that • ref to read the balance / read the mass / weight • ref to read the stop clock / read the time • ‘readings’ taken at the beginning and end / at regular intervals for 1 mark each 2 (b) (i) • (ii) • • loss of carbon dioxide (from the flask) } smaller chips give faster reaction / reaction } mark as a whole finishes quicker /dissolved faster [or reverse] } smaller chips have a larger surface area } any 2 for 1 mark each [Allow converse answers] 2 Page 94 (c) ideas that • heating increases the speed / energy / vibration of the (acid) particles / marble particles • (acid) particles collide (with marble chips / (particles)) more frequently / more likely to collide • reacting particles collide with greater energy / collide faster • so particles more likely to react [do not accept ‘react faster’] [Accept ‘atoms’, ‘molecules’ or ‘ions’ instead of ‘particles’ in this question] any three for 1 mark each 3 [7] M13. Mg S O4 24 + 32 + 16 (×4) or 64 / evidence of all Ar’s correct [so 24 + 32 + 16 1 mark] gains 1 mark but (Mr) = 120 No ECF gains 2 marks [2] M14. (a) positive / + / 2 gains 1 mark but 2+ / ++ / +2 gains 2 marks 2 (b) Ideas that: 2 Ca2+ Br- [Do not disqualify for "bromine" ions] Ions / They are in the ratio 1:2 any two for 1 mark each 2 Page 95 [4] M15. Ca = 40 (OH)2 = (16 + 1)2 or 34 gain 1 mark each but Mr = 74 gains 3 marks [3] M16. (a) lead chloride } in any order potassium nitrate } for 1 mark each 2 (b) lead chloride is solid / a precipitate potassium nitrate is aqueous / in solution / dissolves in water NOT liquid for 1 mark each 2 (Accept ratio of molecular KNO3 : PbC12 is 2:1 for 2 marks) (do not accept relative number of atoms in each compound) One is a solid, one is a solution – worth 1 mark [4] M17. idea that Page 96 • contains nitrogen atoms • contains hydrogen atoms • atoms are chemically bonded • ratio of one nitrogen to three hydrogen (atoms) formula of ammonia is NH3 for 1 mark each NOT linked/joined [4] M18. (a) Calcium No of protons Phosphorus Fluorine 15 No of neutrons 10 No of electrons 20 for 1 mark each 3 (b) (i) gain of electron(s) from (atoms) (of) calcium for 1 mark 2 (ii) Ca+ gains 1 mark but superscript only Ca2+ / Ca ++ gains 2 marks 2 (c) atoms electrons molecule(s) not compound Page 97 each for 1 mark 3 (d) (i) ideas that • ionic – strong forces between ions • molecular – weak forces between molecules each for 1 mark 2 (ii) ideas that • ionic – ions/charged particles are free to move • molecular -molecules do not carry a charge each for 1 mark 2 [14] • correct use of react/reaction/reactants NOT mixed added to join/combine/displace NOT equals M19. • correct use of produce/products/gives/forms/makes/creates • reactants correctly identified • products correctly identified (copper oxide reacts with sulphuric acid to produce copper sulphate and water, will be awarded all 4 marks) for 1 mark each Reactants must be correctly identified for ‘react’ mark to be given. Similarly for products [4] ## (a) Fe2 [56 × 2] or 112 O3 [16 × 3] or 48 each gain 1 mark Page 98 but Mr = 160 gains 3 marks 3 (b) [Fe2 O3 + 2A1 → 2Fe + A12 O3] 160 → 112 (NB Credit if unworked (or value (or value but should be totalled) from (a)) from (a)) gains 1 mark but 32 g. of Fe2 O3 → 32/160 × 112 gains 2 marks but = 22.4 gains 3 marks 3 [6] ## (a) idea that some of the outer electrons of the atoms are free to move can move anywhere across the (giant) structure the flow of electricity is a stream of electrons each for 1 mark or electrons carry a (negative electrical) charge 3 (b) metal element [shiny] appearance [high] melting point forms an oxide that reacts with acids to make a salt 1 of these for 1 mark non metal element forms an oxide that reacts with alkalis with chlorine forms a molecular chloride 1 of these for 1 mark semi-conductor suggests in between this, or any other for 1further mark [NB Maximum of 2 for arguing metal/non-metal only] Page 99 Under each head 1 wrong reason → maximum of 1 available 2 wrong reasons → no mark available] 3 [6] M22. (a) (i) (ii) 13 27 each for 1 mark 2 (b) each proton has a/1 positive charge and each electron has a/1 negative charge OR electrons and protons have (equal but) opposite charges there are equal numbers of protons and electrons in the atom/ so charges cancel or balance (each other) each for 1 mark 2 (c) PARTICLE NUMBER OF PROTONS NUMBER OF NEUTRONS Fluorine atom Fluoride atom NUMBER OF ELECTRONS 10 9 10 each for 1 mark 3 [7] M23. (a) (i) 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O (allow H2 + ½O2 → H2O) both circled for 1 mark 1 Page 100 (ii) 4 A1 + 3 O2 → 2 A12O3 all circled for 1 mark 1 (b) idea that: must end up with the same number of atoms otherwise matter is shown to be lost/gained doesn’t show correct amount of each element/compared each for 1 mark 2 (c) idea that: oxygen has 2 electrons short in outer shell ) in words or chlorine has 1 electron short in outer shell ) indicated on diagram (shared pair/covalent bond with) hydrogen atom supplies one further electron* *(but do not allow hydrogen gives away electron or ionic bond) for 1 mark each 3 [7] M24. (a) reference to hydrogen (atoms) ) nitrogen (atoms) ) each for 1 mark but not molecules ratio of 1N to 3H atoms for 1 further mark or 1 nitrogen atom and 3 hydrogen atoms (ignore any incorrect statements about nature of bonding) 3 (b) evidence of H=1 N = 14 O = 16 gains 1 mark but H=1 N = 14 O = 16 × 3 or 48 Page 101 gains 2 marks but 63 gains 3 marks 3 [6] M25. (a) (i) lead chloride/product of lead + chloride ions is insoluble (in water) for 1 mark 1 (ii) Pb2+ + 2C1¯ → PbC12 *(s) (allow (Pb)2+ 2 (C1–) ) formula solid state symbol balancing for 1 mark each 3 (b) copper hydroxide Cu(OH)2 each for 1 mark lead sulphate PbSO4 each for 1 mark no precipitate for 1 mark Allow 1 mark for correct formula Na2SO4 in (i) Allow 1 mark for correct formula Mg (NO3)2 in (ii) 0 marks for any formula in (iii) 5 [9] M26. (a) correct representation of 1 atom of hydrogen e.g. Page 102 gains 1 mark but correct representation of 1 molecule of hydrogen e.g. or H-H gains 2 marks 2 (b) idea that: hydrogen/metals form positive ions/lose electrons gains 1 mark but hydrogen and the metals form positive ions/lose electrons gains 2 marks hydrogen/non-metals form covalent bonds/share electrons gains 1 mark but hydrogen and the non-metals form covalent bonds/share electrons gains 2 marks 4 [6] M27. (i) carbon dioxide (allow CO2) for 1 mark 1 (ii) sodium nitrate (accept correct formula) for 1 mark 1 [2] Page 103 M28. (a) (i) A calcium hydroxide/limewater/Ca(OH)2 not CaOH (ii) B calcium oxide/Quicklime/CaO (iii) C hydrogen/H2 (accept correct formulae)/ not H2/H each for 1 mark 3 (b) (i) idea that electrons are lost (by the calcium atom) gains1 mark but two electrons are lost (by the calcium atom)/lose outer electrons to get full shell gains 2 marks calcium ions are 2+ for 1 mark (ii) electrons are gained (by the oxygen atom) gains 1 mark but two electrons are gained (by the oxygen atom)/gain electrons to get full outer shell gains 2 marks oxygen ions are 2– for 1 mark 6 (b) (c) (i)(ii) needs: electron loss/gain number (2) charge (+/–) idea that they are held together by many/strong forces/bonds a lot of energy/high temperature is required to break these forces/bonds each for 1 mark 2 [11] Page 104 ## (a) Idea that the electrons do not belong to specific atoms/delocalised electrons [credit if done on appropriate diagram] metal atoms form positive ions the attraction which exists between particles with opposite charges, holds the metal together no specific bonds exist between adjacent atoms/ions atoms/ions can slide over each other so allowing metals to bend each for 1 mark 5 (b) some electrons in the structure are delocalised/free to move for 1 mark these free electrons carry the electric current for 1 mark from left to right across the period, atoms of elements have more free electrons gains 1 mark but from left to right across the period, atoms of elements have more free electrons because they have more electrons in the outer shells gains 2 marks 4 [9] M30. (a) (i) sodium ions and chloride ions (allow sodium chloride/salt) [not “chlorine”] for 1 mark 1 (ii) sodium ions and chloride ions (allow sodium chloride/salt) for 1 mark H + ions (allow hydrochloric acid) for 1 mark 2 Page 105 (b) H+ + OH– → H2O [N.B Na+ and Cl– may also be present] + H ions from acid OH– ions from alkali each for 1 mark [N.B First mark lost if changes on ions not shown] 3 [6] ## (a) both reactions slow down with time; both reactions produce same volume of hydrogen each for 1 mark 2 (b) idea rate is faster with powder or idea rate is slower with ribbon (allow powder completed before ribbon) for 1 mark 1 [3] - ## (a) hydrogen for 1 mark 1 (b) chloride ions are negative; negative ions move to positive electrode each for 1 mark 2 (c) any one use of chlorine e.g. sterilisation; bleaching; making plastics any one for 1 mark 1 Page 106 [4] ## (a) sodium ions and chloride ions (not chlorine) allow sodium chloride/salt/common salt for 1 mark 1 (b) H+ + OH– →H2O H+ from (hydrochloric) acid OH- from alkali/sodium hydroxide lose 1 mark if no charge shown disregard other ions each for 1 mark 3 [4] - M34. (a) same number/six electrons; same number/six protons; react in same way not same element or both carbon any two for 1 mark each 2 (b) different number of neutrons gains 1 mark but C or has two more neutrons gains 1 mark different mass number or but two mass units bigger gains 2 marks C has 8 neutrons while C Page 107 has 6 neutrons gains 2 marks 2 [4] ## (a) covalent bonds for 1 mark 1 (b) any reference to shared electrons gains 1 mark but idea that bond is shared pair of electrons gains 2 marks 2 [3] ## (a) positive for 1 mark 1 (b) any reference to loss of electrons for 1 mark reference to charge being +2 (in (a)) or to loss of 2 electrons (in (b)) for 1 mark 2 [3] M37. (a) any one from (as a) catalyst or to mix with promoters Page 108 to speed up the reaction (process) or process is quicker do not credit just it is quicker to save energy to reduce costs or process is cheaper do not credit just it is cheaper larger surface area (than lumps of iron) or larger surface area for the (catalysed) reaction (to take place) 1 (b) (i) water or steam and methane or natural gas or North Sea gas both required either order 1 (ii) EITHER more (chance) of them colliding / coming into contact do not credit just faster OR volume of the product / ammonia less than / only half the volume of the reactants / the nitrogen and hydrogen 1 (iii) EITHER 680 (tonnes) OR 28 (of nitrogen) → 34 (of ammonia) accept any correct 14 : 17 ratio 1 560 (of nitrogen) → 34 × 20 (of ammonia) 3 [6] M38. (a) This part was not marked 1 Page 109 (b) electrolysis 1 because calcium is more reactive (than aluminium or carbon) accept it is more reactive or very reactive 1 OR in a blast furnace 1 because calcium is less reactive (than carbon or lower) 1 (c) any equation from 1 mark for correct formulae 1 mark for balancing 2ZnO + C → 2Zn + CO2 ZnO + CO → Zn + CO2 ZnO + C → Zn + CO 1 [5] M39. (a) (i) ammonia and hydrogen chloride both required either order accept formulae if correct in every detail 1 (ii) ammonium chloride / NH4Cl do not credit ammonia chloride 1 (iii) the fumes / gases / are poisonous / toxic or ammonia and hydrogen chloride are poisonous / toxic / lethal accept just ammonia is poisonous / toxic accept just hydrogen chloride is poisonous / toxic accept vapour is poisonous / toxic do not credit just fumes are dangerous or harmful Page 110 1 (iv) nitrogen do not credit N/N2 1 hydrogen do not credit H/H2 1 molecule do not credit compound or mole 1 covalent accept single / molecular 1 (b) (i) proton neutron electron either all three correct or one or two correct however do not credit a response which is repeated 2 (ii) protons and neutrons both required in either order 1 [10] M40. (a) (i) corners accept an arrow to any corner 1 (ii) more (surface) exposed accept can be attacked from more directions or more space around it 1 Page 111 (b) (i) 1 any two pairs from more concentrated answers may be in either order do not accept more acid do not accept more powerful or stronger (but stronger is neutral) a reference to sulphuric acid is neutral 1 more particles to hit the solid accept more collisions per second do not accept more collisions 1 2 hotter solution or increasing temperature (faster) particles hit more often or harder accept particles have more energy or are more powerful or more successful collisions 1 3 stirring more surface area exposed or particles available accept more collisions per second do not accept more collisions 1 (ii) cut it up or increase the surface area accept grind it up or powder it or flatten it do not accept make it smaller or use a smaller piece 1 more particles are exposed or available or can react accept heat it and there are more successful collisions for both marks 1 [8] Page 112 M41. (i) hydrogen, hydroxide and sulphate all three and no others any order do not credit any formula(e) 1 (ii) the anode is positive 1 (so) only the negative ions are attracted to it or (so) only the hydroxide ions and the sulphate ions are attracted (to it) or (so) only the anions are attracted (to it) 1 (iii) 2H2O + O2 + 4e– 1 [4] M42. (a) (i) sodium........ positive or + both required 1 chloride... negative or – both required do not credit chlorine 1 (ii) ions not free (to move) in solid crystal / lattice ions are free to move when sodium chloride is molten 1 or ions are mobile do not credit when ions are molten allow 'particles' for ions (1) mark do not credit electrons etc 1 (iii) dissolved in water or in aqueous solution accept in solution Page 113 accept in water or when a gas/ vapour or solid it will not 1 (b) (i) 40 1 (ii) (total) number of protons and neutrons (in the nucleus) 1 (c) (i) 2Ca + O2 -+ 2CaO accept any 2n : n : 2n ratio do not credit if any other change has been made 1 (ii) any two from electron(s) is / are lost from the outer shell / orbit / ring or from the shell furthest the nucleus or from the 4th shell two / both (electrons are lost) accept two electrons are lost for (2)marks accept both electrons are lost from the atom for (1) mark 2 [10] M43. (a) (i) rings of 2, 8 and 3 electrons credit 2, 8, 3 pay particular attention to the outer shell in diagrams 1 (ii) rings of 2, 8 and 7 electrons credit 2, 8, 7 pay particular attention to the outer shell in diagrams 1 (b) (i) labels not required on atoms charges need to be shown on ions reference to outer shell is required otherwise a maximum of two marks Page 114 structure of atoms/ions marks (ring of 2, 8, 1 for sodium) or the outer shell of sodium only contains 1 electron credit 2, 8, 1 or an ion 2, 8 or two circles and 1 electron in outer shell 1 (ring of 2, 6 for oxygen) or outer shell only contains 6 electrons credit 2, 6 or an ion 2, 8 or two circles 1 transfer of electrons mark two sodiums needed to supply two outer electrons to oxygen to complete the (one oxygen's) outer shell award maximum of two marks if a covalent structure is given credit two rings of electrons for sodium showing outer electrons transferring to outer shell of one oxygen for three marks do not accept diagrams showing overlapping rings for third mark 1 (ii) loses an electron credit atoms lose electrons or oxygen takes the electron ignore oil rig 1 [6] M44. (a) (i) 8 ammonia do not credit ammonium sulphuric acid do not credit just sulphuric; credit sulfuric acid do not credit hydrogen sulphate 3 (ii) (as a) fertiliser 1 Page 115 (iii) nitric (acid) accept HNO3 if correct in every detail 1 (b) (i) chemical change (in which) or under suitable conditions 1 product(s) can be converted to reactant(s) or direction of reaction can be reversed or equilibrium can be achieved do not credit reaction can be reversed 1 (ii) air or (the) atmosphere 1 (iii) made of atoms 1 which are all the same credit the idea that the particles (in an element) are all the same even if the name of the particles (the first mark) is incorrect or which have the same number of protons or which have the same atomic number / proton number it cannot be broken down into anything simpler (2) marks 1 [10] M45. (a) CaCO3 + 2HC1 → CaC12 + CO2 + H2O one mark for CO2 and H2O or H2CO3 one mark for balancing the equation 2 (b) (i) linear suitable scale for y axis ± one small square 1 accurate plots Page 116 deduct one mark for each error plot 1 smooth curve through the points or a line of best fit this mark requires a neat smooth curve 1 (ii) curve becomes almost horizontal at or above 268.5 do not credit a straight line reaching 268.5 at 11 mins accept a plot at 268.6 1 (iii) steeper initial part to curve 1 becoming nearly horizontal between 268.6 and 268.4 g 1 [8] M46. NOTE In this question and throughout the Paper, if the name of a chemical is asked for, then the formula is acceptable only if it is correct in every detail. If the name is correct and the candidate has tried to be ‘helpful’ by giving, in addition, an incorrect version of the formula, then this is acceptable provided it does not lead to ambiguity. (i) nitric (acid) accept HN03 1 (ii) sulphuric (acid) accept H2SO4 1 (iii) heat given out or temperature rise or energy given out Page 117 or steam do not credit just ‘use a thermometer’ do not credit just 'change in temperature' 1 (iv) neutralisation accept neutralise accept neutral accept formation of salt or water do not credit exothermic 1 [4] M47. (i) two or 2 1 (ii) magnesium and chloride either order not positive / negative do not credit’chlorine’ accept Mg++ and Cldo not credit just Mg and Cl– accept cation(s) and anion(s) 1 (iii) 2 1 (iv) electrons accept charges 1 (v) any three from • (is a) giant structure/lattice structure • crystalline / hard accept just 'crystals(s)’ • high melting point / solid Page 118 • high boiling point • conductor (of electricity) when dissolved in water or conductor (of electricity) when ions are free to move • conductor (of electricity) when molten • soluble in water 3 [7] M48. (a) both correct in each row electron ...– (1) allow negative 1 1 .......... 0 allow neutral or none 1 proton .....+ (1) allow positive 1 (b) (i) protons...electrons both correct in correct order 1 (ii) protons....neutrons both correct in either order 1 (c) (i) sodium fluoride do not credit sodium fluorine 1 NaF must be correct in every detail do not credit NAF and the like 1 Page 119 (ii) ionic accept ion (bonding) do not credit ironic or iron (bonding) 1 (iii) electron transferred from sodium to fluorine accept electron transferred from metal to non-metal either positive sodium ion and negative fluoride ion or correctly identified by the symbols Na+ and F- accept ‘positive sodium ion and negative fluorine ion’ 1 or attracted because have opposite charge(s) or (atoms/ions) form an (ionic) lattice or (atoms/ions) form a crystal e.g. or both marks may be gained by a suitable dot and cross diagram 1 [10] M49. (a) Bunsen (burner) accept spirit burner do not credit candle 1 (b) blue 1 white credit (1) if both colours correct but answers are reversed 1 to cool the tube (B) accept answers which anticipate part (d) e.g. ‘to condense the water vapour’ or gases or vapours 1 Page 120 (d) (i) water do not credit ‘condensation’ 1 (ii) (Water) vapour from the crystals (from tube A) accept steam or steam from tube A 1 condenses or cools accept turns to (liquid) water 1 (e) add water gets hot or hotter or warm or warmer turns into solution dissolves or the temperature rises or there is an exothermic reaction accept steams or hisses ignore any reference to colour(s) 2 (f) sulphuric acid accept H2S04 only if correct in every detail 1 [10] M50. graph steeper 1 becomes horizontal 1 reaches twice the height_, 40 cm3 1 cm3 Page 121 1 [3] M51. (a) Mg + 2H+ → Mg2+ + H2 * reactants correct in every detail * products correct in every detail if the spectator ions are sown then (1) mark should be credited but only if they are shown correctly on both sides e.g. Mg + 2H+ + 2CI- → Mg2+ + 2CI- + H2 2 (b) 24 (parts) of magnesium → 2 (parts) 1 of hydrogen or equally clear working (so) 6 grams/g (are needed) 1 unit required (c) (i) two (and no more) atoms shown to be sharing their single electrons examples do not credit if anything which contradicts the impression that these are hydrogen atoms 1 (ii) (single) covalent (bond) 1 (d) (×100) = 6 (just 6 is worth (1) mark) 1 × 100 = 6 or similar is (0) do not credit 5.8823529 and the like Page 122 1 [8] M52. (a) proton + (1) both required neutron 1 both required electron – (1) both required 3 (b) 2.8.3 accept words or diagram to this effect 1 (c) (i) 24 1 (ii) 52 1 (d) any one of • gains one or more electrons accept gains an electron • becomes an anion do not credit becomes an ion • becomes a negative ion 1 (e) sodium ions have a (single) positive charge and chloride ions have a (single) negative charge do not credit ‘chlorine ions’ but allow this error to be carried forward 1 Page 123 ions with opposite charge are attracted (to each other) or the positive ions and the negative ions are attracted (to each other) or the sodium ions and the chloride ions are attracted (to each other) 1 (positive and negative) ions are arranged alternatively (in each direction or dimension) or ions with the same charge are repelled (by each other) no mark for just ionic bonds 1 [10] Cl2 + 2Br → 2Cl + Br2 formulae correct for elements M53. 1 correct charge on both ions 1 credit balanced if Cl2 and Br2 included 1 [3] M54. (a) Cu 1 Fe 1 Zn 1 (b) one significant use for each metal do not credit vague answers such as ‘in experiments’ and Page 124 the like do not credit the same use more than once copper examples: do not credit diet supplement 1 • coins or coinage (metal) or make alloys or bronze or brass • conducting electricity or (electrical) wiring or motors or cables • (domestic) (water) pipes • heat exchangers • roofing • steam pipes • stills or cooking utensils accept any specified still e.g. whisky still • bracelets or rings iron or steel answers examples: do not credit diet supplement * access-hole covers (sometimes known as ‘manhole’ covers) * catalyst (in the production of ammonia) * manufacture of steel(s) or in the basic oxygen process * named vehicle or transport or machinery or railings any other uses for iron and steel can be credited provided that the use is clear so, for example, ‘bridges’ and ‘railway lines’ would be creditworthy but do not credit ‘buildings’ and ‘transport’ which are too vague 1 zinc examples: do not credit diet supplement * brass manufacture * die castings * rust prevention * to galvanise (iron or steel) or (as a) protective coating * battery casing Page 125 1 (c) any four general properties of do not credit hard or strong or tough or magnetic • are not brittle accept can be bent (into shape) or flexible • can be hammered (into shape) accept are malleable • can be stretched (into shape) accept are ductile • (good) conductors of heat accept just ‘(good) conductor’ once only • (good) conductors of electricity • high boiling points • high density or heavy or dense • high melting points • ringing sound when struck accept sonorous • solids (at room temperature) accept shiny (when polished) or silvery 4 (d) any one of do not credit electron references * (good) conductor (of electricity) when molten or liquid accept dissolves in water or crystalline * (good) conductor (of electricity) when in aqueous solution accept (good) conductor (of electricity) when dissolved in water * high melting point or high boiling point do not credit just ‘solid’ 1 Page 126 (e) (i) electron from A to B both parts required 1 (ii) different numbers of protons accept different atomic numbers do not credit references to neutrons 1 [13] M55. (a) Zn + 2HC 1 → ZnC12 + H2 1 (b) (i) 12.5 1 (ii) steeper curve same volume of gas evolved do not credit two intersects of straight lines accept a sharp bend 2 (iii) any two from: stir it accept mix it better heat it accept warm it use a more finely divided catalyst accept use a better catalyst or more finely divided zinc do not credit use acid of a higher 2 (c) (i) any one from zinc is more reactive than copper accept zinc is above copper in the reactivity series zinc displaces copper accept it is higher than copper in the reactivity series 1 Page 127 (ii) zinc + copper sulphate → copper + zinc sulphate ignore the presence of acid or water accept a balanced equation 1 [8] M56. (i) (Y) more gas / carbon dioxide given off 1 (ii) (X) curve / slope steeper accept rises more rapidly / only took 30 seconds 1 (iii) (flat) since calcium carbonate / substrate all used up accept the reaction has stopped / no more gas is being produced 1 1 [3] M57. 73 (seventy three) if answer is incorrect allow 1 mark for the correct proportion that H2:HCl is 1:2 and 1 mark for 36.5 [3] Page 128 M58. (i) (ii) 1 weak forces accept weak bonds 1 between molecules / intermolecular reject intramolecular 1 [3] M59. (a) ammonium nitrate accept NH4NO3 do not accept ammonia nitrate 1 (b) different reactions need different catalysts 1 (c) they are used over and over again accept they are reused accept they are not used up accept they are not changed recycling is neutral 1 (d) any two from Page 129 they speed up reactions they reduce energy requirements accept allow reactions to take place at a lower temperature they reduce costs accept make process more economic 2 (e) (high pressure) increases the frequency of collisions accept more collisions move faster is neutral 1 this increases the rate of reaction accept ‘more successful collisions’ for 2 marks 1 [7] M60. (i) 4 and 1 both answers must be correct 1 (ii) 53.5 if incorrect relative formula mass allow 1 mark for correct working accept e.c.f. from c(i) for 2 marks 2 [3] M61. (a) LHS lithium + water accept Li and H2O accept hydrogen oxide for water 1 RHS hydrogen + lithium hydroxide accept H2 and LiOH Page 130 ignore attempts at balancing ignore charges 1 (b) Quality of written communication One mark for the correct use of any three of the terms atom, covalent, bond(ing), saturated, hydrocarbon or alkane 1 any three from: one / the carbon (atom) reject molecules once four hydrogen (atoms) shape / properties neutral CH4 hydrocarbon saturated / single bond covalent bond / shared electrons alkane reject ionic bond 3 [6] M62. (a) (i) 2.25 correct answer gains three marks if incorrect allow 1 mark for 2 correct readings (130 and 175) and further mark for 45 ÷ 20 allow e.c.f. 3 (ii) concentration of reactant(s) lower 1 fewer collisions per second / time unit 1 Page 131 (b) labour costs lower / enzymes costs lower not stop and start 1 [6] M63. (a) (i) catalyst / enzyme 1 (ii) any two from do not accept increase volume of peroxide • heat • stir / shake • increase concentration of peroxide / catalyst 2 (b) oxygen lost do not allow incorrect gas 1 [4] M64. (a) 10.86 accept answers between 10.64 to 10.9 if answer is incorrect allow 1 mark for rfm FeSO4 = 152 2 marks for 152 × 4/56 3 (b) 2 Fe + 3 H2SO4 → Fe2(SO4)3 + 3H2 accept other correct multiples for balancing 1 [4] Page 132 M65. (a) Quality of written communication: All scientific words used correctly (covalent, bonds, atoms) 1 any two from • large numbers of covalent bonds allow giant lattice / structure • between atoms do not accept between molecules • (covalent) bonds strong accept need much energy to break 2 (b) each carbon has 4 electrons 1 one shared pair 1 four shared pairs 1 [6] Page 133 M66. (a) nitrogen accept N or N2 1 (b) the reaction is exothermic accept the reaction releases heat energy 1 (c) water accept H2O or hydrogen oxide 1 (d) with ammonia and nitric acid 1 neutralisation accept a correct description of reacting (ammonia and nitric acid) 1 [5] M67. (a) A faster because: the graph line steeper / the reaction had stopped earlier accept sample B slower because: the graph line was less steep / the reaction stopped later A because CO2 given off faster / fizzes more for 1 mark B because CO2 given off slower / fizzes less for 1 mark 2 (b) increases the speed / energy of the (hydrochloric acid) particles 1 collide more frequently 1 collide more energetically / successfully accept more successful collisions = 2 marks 1 [5] Page 134 M68. 36.8 / 37 correct answer, no workings = 3 if incorrect, allow 1 mark for rfm FeSO4 = 152 or if incorrect rfm, allow 1 mark for 56/Y × 100 where Y is incorrect formula mass allow 2 marks for × 100 [3] M69. (a) endothermic (reaction) accept thermal decomposition 1 (b) gives out heat (energy) accept exothermic (reaction) 1 turns blue accept goes to hydrated copper sulphate 1 [3] M70. (a) oxidising 1 (b) (i) oxygen ignore any numbers 1 Page 135 (ii) (catalyst) speeds up a (chemical reaction) accept changes the rate (of reaction) 1 [3] M71. (a) (i) 2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO both 2s needed allow O2 or any correct multiple 1 (ii) solid 1 gas 1 (b) MgCl2 / C12Mg do not accept MG mg mG CL cl cL ignore charges 1 [4] M72. (a) 1400 1 (b) 980 correct answer gains full credit 160 tonnes Fe2O3 produces 112 tonnes Fe if incorrect allow one mark for relative formula mass iron oxide = 160 allow e.c.f. 1400 tonnes Fe2O3 will produce 1400 / 160 × 112 tonnes Fe use of 2000 tonnes Fe2O3 – deduct one mark only if working out is correct 4 Page 136 [5] M73. (a) X – (metal) atom / ion 1 Y – electron 1 (b) free electrons or electrons move 1 (allow metal) atoms / ions to slide over each other OR bonding non - directional for 2 marks 1 [4] M74. (a) the concentration of the (nitric) acid is decreasing accept the number of acid particles is decreasing or there are fewer collisions 1 (the volume of carbon dioxide remains at 83 cm3) when the concentration of the (nitric) acid is zero accept no acid remains or all the acid is used up or no acid particles 1 (b) line starts at origin is steeper and remains to the left of the original line 1 graph line levels off at 83 cm3 and before 12 minutes tolerance square 1 Page 137 (c) change the temperature accept increase or decrease the temperature accept change (increase or decrease) the concentration (of the nitric acid) ignore amounts of reactants or changes in pressure or stirring or use of catalyst 1 [5] M75. (a) the concentration of the (nitric) acid is decreasing accept the number of acid particles is decreasing or there are fewer collisions 1 (the volume of carbon dioxide remains at 83 cm3) when the concentration of the (nitric) acid is zero accept no acid remains or all the acid is used up or no acid particles 1 (b) line starts at origin is steeper and remains to the left of the original line 1 graph line levels off at 83 cm3 and before 12 minutes tolerance square 1 (c) change the temperature accept increase or decrease the temperature accept change (increase or decrease) the concentration (of the nitric acid) ignore amounts of reactants or changes in pressure or stirring or use of catalyst 1 [5] Page 138