Outline #1 Weather
advertisement

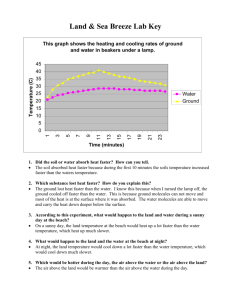
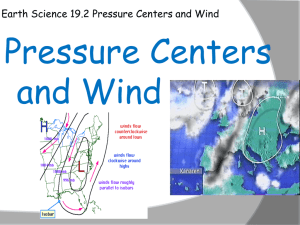
Name__________________________ Unit 4: WEATHER Lesson 1 pages 269-279 Define the Following Terms: atmosphere____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ weather_______________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ air pressure____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ convection current______________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ prevailing wind_________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Directions: Use this outline as you read through this lesson. The outline follows directly along with the book. Please scan through a section of the outline, and then read the section of the book that discusses that material. For example, the first paragraph of this outline deals with the heading labeled “The Atmosphere” in your book. All of this first paragraph should be filled after you have read through this section. If you missed one from this paragraph, go back and find it. IT IS IN THERE. You should be able to fill in all of the blank spaces, in order, as you read through the lesson. Become an investigative reader and find those necessary details. Spelling does count. Have fun! The _________________ is made up of several layers and surrounds Earth. Most of Earth’s weather happens in the layer of the atmosphere called the ___________________. ________ is all around us, and we know this because every time the wind blows we can feel it on our skin. _______ _________________(2 words) refers to the weight of a given area of air in our atmosphere. It is greatest near sea level due to gravity and ___________________. This is the second paragraph, so it correlates with the second heading of this lesson “Air Pressure” By measuring the air pressure around you at a certain place, you can determine how far above sea level you are. The more pressure you measure the ___________ ____ sea level you are. By using a balloon we can see that air doesn’t just push downward due to gravity, but it pushes in all _______________. Cold air affects the amount of pressure as well. Cold air is more _____________, so it sinks toward Earth’s surface. In contrast, warm air is less _________________ and has a tendency to rise. As it rises, it begins to _________ causing it to drop back down toward the surface. The _________ energy is what powers all of the wind and weather we see and feel. Earth absorbs some of this solar energy, but not evenly over its surface. _______, or earth, heats up faster than ___________. This results in air over either of these two areas being warmer and cooler respectively. Since this occurs, we have air that is less dense (warm air) and will _______ due to cooler, denser air pushing on it. This upward and downward movement of air is called _______________ _______________. The horizontal, side to side, movement of air at Earth’s surface is called ___________. Winds that result from a local difference in temperature are called _________ ___________. These winds often occur near large bodies of water. If you were at the beach, during the day you would feel _______ ________________, wind coming from the ocean, and at night you would feel a _________ _______________, or wind blowing toward the water. A ______________ _________ is a global wind that almost always blows in the same direction. These winds are caused by the ____________ heating of the Earth’s surface. Areas closer to the ____________ are warmer than areas farther from the ______________ due to the amount of direct sunlight received throughout the year. The cold, dense air above the poles moves toward the equator because warmer, less dense air is rising from these areas near the equator. But this doesn’t work out as a direct line from the equator toward the poles. Some of the warm air rising from the equator ________ and sinks back to Earth before reaching the poles. Also, the Earth’s __________________ causes these winds to move in a curved path. Winds moving north curve to the _________ and winds moving south curve to the __________. This is because our planet rotates from _________ to ___________ (This is not directly in the book, but it give it a try). Our weather systems in the United States move from west to east due to the ______________ _________________. Divide the space below in half. In one half, draw a picture of winds at the beach during the day, and in the other half winds at the beach during the night. Use these terms to label your pictures: warm, less dense air, cooler, denser air, solar energy, ocean, land, sea breeze, land breeze, and arrows to show direction.