Enduring Understandings
advertisement
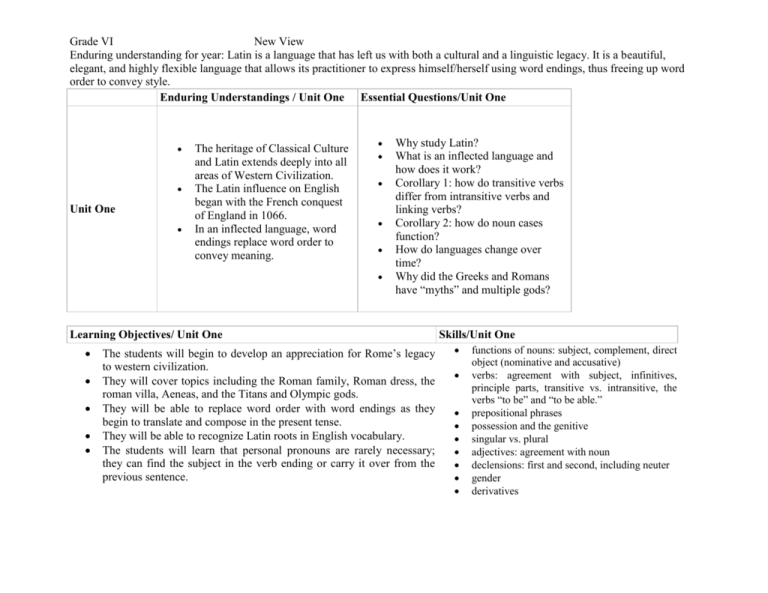
Grade VI New View Enduring understanding for year: Latin is a language that has left us with both a cultural and a linguistic legacy. It is a beautiful, elegant, and highly flexible language that allows its practitioner to express himself/herself using word endings, thus freeing up word order to convey style. Enduring Understandings / Unit One Essential Questions/Unit One Unit One The heritage of Classical Culture and Latin extends deeply into all areas of Western Civilization. The Latin influence on English began with the French conquest of England in 1066. In an inflected language, word endings replace word order to convey meaning. Why study Latin? What is an inflected language and how does it work? Corollary 1: how do transitive verbs differ from intransitive verbs and linking verbs? Corollary 2: how do noun cases function? How do languages change over time? Why did the Greeks and Romans have “myths” and multiple gods? Learning Objectives/ Unit One The students will begin to develop an appreciation for Rome’s legacy to western civilization. They will cover topics including the Roman family, Roman dress, the roman villa, Aeneas, and the Titans and Olympic gods. They will be able to replace word order with word endings as they begin to translate and compose in the present tense. They will be able to recognize Latin roots in English vocabulary. The students will learn that personal pronouns are rarely necessary; they can find the subject in the verb ending or carry it over from the previous sentence. Skills/Unit One functions of nouns: subject, complement, direct object (nominative and accusative) verbs: agreement with subject, infinitives, principle parts, transitive vs. intransitive, the verbs “to be” and “to be able.” prepositional phrases possession and the genitive singular vs. plural adjectives: agreement with noun declensions: first and second, including neuter gender derivatives Grade VI New View Enduring understanding for year: Latin is a language that has left us with both a cultural and a linguistic legacy. It is a beautiful, elegant, and highly flexible language that allows its practitioner to express himself/herself using word endings, thus freeing up word order to convey style. Assessments/Unit One Diagnostic o Quia games for prior knowledge/misconceptions o Survey on basic grammar, terminology, and culture o Personal letters Formative o In-class translations o Language Lab. activities, including “chat’ feature and teacher-generated Quia games, both grammatical and cultural o Student-generated questions, in-class and homework, both for class and for tests o Teacher-generated questions o Student-generated Latin composition demonstrating knowledge and application of concepts o Games, including charades, pictionary, battleship, fleet-of-pen, connect five o Teacher-generated Quia games Summative o Quizzes -- vocabulary for each chapter, with grammar component; often divided into two, vocab then grammar/application o Labeling quiz after Chapter 4 o Review vocabulary test on Chapters 1-8 o Review grammar test o Mythology RAFT (ongoing) o Roman House real estate brochure Grade VI New View Enduring understanding for year: Latin is a language that has left us with both a cultural and a linguistic legacy. It is a beautiful, elegant, and highly flexible language that allows its practitioner to express himself/herself using word endings, thus freeing up word order to convey style. Unit Enduring Understandings/Unit Two Essential Questions/ Unit Two Name Unit Two Greco-Roman mythology shaped the art, music, and literature of the Renaissance and beyond. Inflected languages permit flexibility not allowed in English, which is only mildly inflected. Latin and many languages express verb tenses in two aspects, completed and and ongoing: perfective and imperfective. How does an inflected language offer flexibility (n.b: The two words come from the same root!) How might you use this flexibility? How does Latin convey time? How does the passive voice function and differ from the active voice? Why do we avoid the passive voice in English? How do the gods of Greco-Roman mythology reflect human archetypes? What does verb aspect mean? Learning Objectives/ Unit Two Skills/ Unit Two The students will have an increased understanding of and appreciation for Verbs: conjugation of all six tenses, passive Greek and Roman legend and mythology. They will learn of the legendary and active, of first conjugation verbs. founding of Rome and the Trojan War. nouns and adjectives: multiple uses of all Students will be able to approach translation using all available five cases, including dative of indirect information: case endings, verb agreement, context clues, common sense. object, ablative of means, ablative of agent. They will learn that Latin verbs have six tenses, with endings and principal parts that . serve as tense markers, and that the patterns are consistent and repetitive. They will learn how to go from the active to the passive voice, in all six tenses. Grade VI New View Enduring understanding for year: Latin is a language that has left us with both a cultural and a linguistic legacy. It is a beautiful, elegant, and highly flexible language that allows its practitioner to express himself/herself using word endings, thus freeing up word order to convey style. Assessments/Unit Two Formative o In-class translations o Language Lab. activities, including “chat’ feature and teacher-generated Quia games, both grammatical and cultural o Student-generated questions, in-class and homework, both for class and for tests o Teacher-generated questions o Student-generated Latin composition demonstrating knowledge and application of concepts o Games, including charades, pictionary, battleship, fleet-of-pen, connect five o Teacher-generated Quia games o Conjugation Graphic o Declension Graphic Summative o Quizzes -- vocabulary for each chapter, with grammar/application component; often divided into two o Comprehensive quizzes on the passive voice in all tenses o Verb synopses o Review vocabulary test on Chapters 1-12 o Review grammar test on Chapters 1-12 o Mythology RAFT (ongoing) o Culture Project Grade VI New View Enduring understanding for year: Latin is a language that has left us with both a cultural and a linguistic legacy. It is a beautiful, elegant, and highly flexible language that allows its practitioner to express himself/herself using word endings, thus freeing up word order to convey style. Unit Name Enduring Understandings /Unit Three Essential Questions/ Unit Three Unit Three The passive voice is useful for dodging responsibility. Case endings in Latin can communicate entire phrases in English. Legends serve an historical purpose and sometimes are based on fact, dimly recalled. How can one case be used to communicate different concepts? How do history and legend relate? How do heroes reflect their time and culture? Learning Objectives/ Unit Three The students will solidify their basic knowledge of noun function as it relates to noun case. They will be able to distinguish between and use both the imperfects, or continuous action verbs, and the perfect, or completed verbs. They will be able to give commands using 1st and 2nd conj. They will learn basic numbers and the Roman numeral system. They will study the kings and heroes of early Rome and continue with Greek mythology. Skills/ Unit Three The imperative mood/commands 3rd declension and 3rd i-stem nouns Genitives: partitive, subjective, objective numbers and numerals formation of adverbs noun/adjective agreement, now with 3rd decl. kings of Rome Grade VI New View Enduring understanding for year: Latin is a language that has left us with both a cultural and a linguistic legacy. It is a beautiful, elegant, and highly flexible language that allows its practitioner to express himself/herself using word endings, thus freeing up word order to convey style. Assessments/Unit Three Formative o In-class translations o Language Lab. activities, including “chat’ feature and teacher-generated Quia games, both grammatical and cultural o Student-generated questions, in-class and homework, both for class and for tests o Teacher-generated questions o Student-generated Latin composition demonstrating knowledge and application of concepts o Games, including charades, pictionary, battleship, fleet-of-pen, connect five o Teacher-generated Quia games Summative o “Passifying Machine” o Quizzes -- vocabulary for each chapter, with grammar component; often divided into two o Neuters/numbers/kings quiz o Create-your-own chapter project o Review vocabulary test on Chapters 1- 16 o Review grammar test on Chapters 1-16, student-generated, by and for individual student o Mythology RAFT (due)









