Periodic Table Information
advertisement

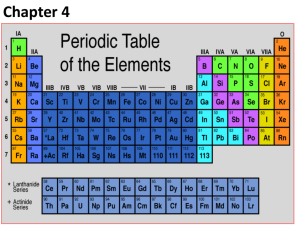
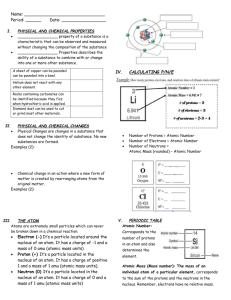
Periodic Table Information Periodic Table of Elements- tool used to help us study the composition of matter. Groups/Families- Vertical Columns 1A-8A= Representative Elements B Elements= Transitional Metals -Elements within the same group have similar physical and chemical properties. Periods- Horizontal Rows -Period number is equal to the number of energy levels (orbitals) within the atom of that element. Metals- left of stair step (excluding H) Nonmetals- right of the stair step Metalloids- have properties of both metals and nonmetals -B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po, At Group 1A- Alkali Metals- most reactive metals, 1 valence electron, readily react with the halogens (explosive in water) Group 2A- Alkaline Earth Metals- very reactive, 2 valence electrons, readily reacts with group 6A metals Group 7A- Halogens- most reactive nonmetals, react readily with the alkali metals, 7 valence electrons Group 8A- Noble Gases- very stable, will not react with other elements, 8 valence electrons (outer energy level is full) Octet Rule Transitional Metals- can change valence counts (B metals) Lanthanide Series- rare heavy earth metals Actinide Series- Synthetic metals, mostly radioactive 14 Si 28.09 14= atomic number Si= chemical symbol 28.09= atomic mass average Atomic number = number of protons in the atom of that element The number of electron equals the number of protons (atoms are always electrically neutral) The number of neutrons equals the atomic mass number (round atomic mass average to whole number) – atomic number. # of neutrons = atomic mass – atomic number Proton- positive charged particle located within the nucleus of the atom. Neutron- particle within nucleus of the atom with no charge. Electron- negatively charged particle located with the electron cloud (orbiting around the nucleus within energy levels (shells)) For representative elements (A’s) the valence electron count is equal to the group number.