Bradford Reading Record
advertisement

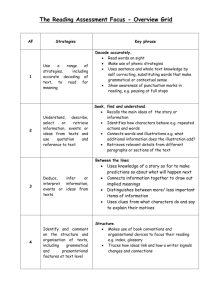
Bradford Reading Record Reading progression document linked to the new national curriculum Y1 – Y6 AP/February, 2015 Word reading Year 1 Decoding Reads on sight 100 HF words Reads on sight irregular high frequency words, other familiar and important words Identifies syllables in order to read polysyllabic words Recognises and reads alternative spellings for vowel phonemes Recognises and reads alternative spellings for consonant phonemes Identifies and reads words with common plurals Identifies and reads words with ‘ed’ and ‘ing’ endings Reads for meaning – expects the text to make sense and self-corrects Becoming more fluent Reads on sight irregular high frequency words from Phases 4 and 5 Reads other familiar and important words Consistently blends CVC and CCVC/CVCC words Makes 1 to 1 correspondence between written and spoken words Reads on sight irregular high frequency words from Phases 2, 3 and 4 Blends phonemes, in order in the word, to read CVC and words containing consonant clusters Recognises and blends consonant clusters Recognises and blends consonant digraphs Identifies syllables in order to read polysyllabic words Confidently blends all known phonemes identifying alternative graphemes Reads on sight irregular words and other familiar and important words Recognises full range of vowel digraphs and trigraphs Reads fluently and for meaning Year 1 Comprehension Retrieval Inference Sequences a simple story or event recalling main points Uses structure of a simple story when reacting or retelling Talks about the themes of simple texts Answers literal retrieval questions about a text Can discuss the significance of a book title and events Begins to retell simple stories accurately Can recite some poems by heart Shows reasonable inference at basic level, e.g. identifying who is speaking in a story Comments/questions about meaning of parts of text, e.g. details of illustrations, opening and impact of cover Makes simple deductions with support from prompts Begins to make predictions about characters Uses information from the text to predict events and talk about the character traits Relates incidents from reading to own experience and that of others Structure Language Understands and uses correctly terms referring to conventions of print: book, cover, beginning, end, page, word, letter, line Identifies print effects, e.g. bold, italics and capitalisation Use patterns and structures of text to support retelling/reciting Understands the sequence of a story Understands the difference between fiction and non-fiction Understands the way non-fiction texts are organised and uses this when reading Understands difference in how fiction and non-fictions texts are organised Uses organisational features to support reading Begins to comment on particular words, phrases and sentences Year 2 Comprehension Word reading Decoding Retrieval Inference Begins to take account of a wider range of punctuation when reading, e.g. exclamation marks, question marks Can blend syllables silently and out loud Recognises and reads simple and continuous past tense Recognises and reads a variety of suffixes – ing, ed, er, est, ful, ly and y Reads on sight irregular words and other familiar and important words Confidentially blends alternative spellings of vowels and consonants Reads fluently, taking into account punctuation and text features, e.g. bold or italic print Confidently reads polysyllabic words Recognises common prefixes and suffixes and regular verb endings to construct meaning of words Reads on sight 300 HF words Recognises a full range of alternative spellings of phonemes Can recount main events, themes and information Is able to generate some questions before reading Retells more complex stories clearly with appropriate detail and balance Can discuss with reference to the text Can recite poems by heart with appropriate intonation Can participate in discussion about books, taking turns and listening to what others say Begins to predict more than one event using reading experience of same author/themes or content of non-fiction Makes simple inferences about thoughts and feelings Identifies key themes and discusses reasons for events in stories Makes confident inferences/predictions based on wider reading experience Structure Language Understands and comments on the structure and presentation of narrative and how information is presented in non-fiction texts Makes comparisons between fiction and non-fiction texts noting similarities and differences Offers suggestions for organisational features Begins to identify words, phrases and sentences used for effect Begins to identify voices in stories Begins to discuss the effect of specific word or phrase choices on meaning, e.g. to create humour, images and atmosphere Word reading Year 3 Decoding Comprehension Retrieval Inference Structure Begins to recognise a wider range of prefixes, suffixes and punctuation and responds by using appropriate intonation and expression Confidently decodes digraphs and trigraphs including silent letters Uses a range of strategies independently to establish meaning of words in context Begins to read in different ways for different purposes Shows understanding of main points. Begins to skim and scan whole text to identify relevant pieces of information Provides evidence/information making specific reference to text Can confidently skim and scan to locate information Shows increasing accuracy in information retrieval Makes use of non-fiction features to locate information Prepare poems and play scripts to read aloud Can offer sensible reasons for predictions about plot and character Begins to make connections across a text Justifies ideas and predictions based on knowledge of the text Links ideas and information across texts more confidently Identifies some different genres and key features in fiction and non fiction Can consider and comment on the effect on the reader of the main features of fiction and non fiction texts Language Author Traditions Uses a dictionary to check the meaning of words Understands the use of different voices in stories Identifies languages used to create moods and build up tension, e.g. powerful verbs, adjectives and connectives Begins to identify themes and underlying ideas in texts Can offer opinions about texts and explain personal point of view Can compare different versions of the same story Begins to identify subtle messages in a text Identifies themes & conventions in a wide range of books Makes some simple connections between texts identified, e.g. similarities in plot, topic, or books by same author, about same characters Recognises some features of the context of texts e.g. historical setting, social or cultural background Word reading Year 4 Uses a range of strategies independently to establish meaning of words in context Can use more than one source when researching & recording information Can support understanding and point of view by finding information and begins to text mark Identifies main ideas drawn from more than one paragraph and summarises these Prepares poems and playscripts to read aloud, and to perform, showing understanding through intonation, tone, volume and action Inference Begins to recognise the difference between fact and point of view Structure Begins to identify structural features of a wider range of fiction and non-fiction texts Recognises different forms of poetry (e.g. free verse, narrative poetry) Language Begins to offer reasons for use of voice and language choices Considers the effect of these on the reader Begins to comment on overall effect of a text and how the writer has achieved this, justifying opinions Makes some simple connections between texts identified, e.g. similarities in plot, topic, or books by same author, about same characters Recognises some features of the context of texts, e.g. historical setting, social or cultural background Decoding Comprehension Retrieval Author Traditions Word reading Year 5 Decoding Comprehension Retrieval Inference Structure Language Understands how word order, punctuation, order and connectives can shame the meaning of sentences Uses knowledge of word formation and derivation to construct meaning of words in context Empathises with characters’ viewpoints Begins to text mark and annotate when skimming and scanning to identify main ideas Can retrieve, record and present information from non-fiction Identifies and justifies selection of key points by using wide range of strategies to locate information/ideas across a text Can identify key details in a text and begin to team the skills of summarising Learn a wider range of poetry by heart Can participate in discussions about books, challenging others’ views courteously Can empathise with different points of view Understands main events, characters, ideas and themes. Infers meaning and motives using text and wider experiences Uses clues from action, dialogue and description to interpret meaning Infers and deduces moods, messages, feelings and attitudes Begins to refer to text to support opinions and predictions Begins to identify implicit and explicit points of view Confidently recognises key features of a range of text types and genres Uses structural and organisational features of text types to support understanding, recognising how paragraphs are linked Identifies and comments on use and effect of author’s language including imagery and figurative language when conveying moods, feelings and attitudes Offers suggestions for writer’s choice of technique Author Traditions Begins to show awareness of authorial viewpoint in fiction and non-fiction, e.g. narration, characterisation, time shifts, bias Recognises ways in which writers present issues and viewpoints in fiction and non-fiction Can discuss techniques for development of plot Notes features common to different texts or versions of the same text identified, with simple comment, e.g. characters, settings, presentational features Word reading Year 6 Decoding Retrieval Comprehension Confident in using a wide range of strategies when locating information/ideas across a text Can summarise the main ideas from one paragraph Retrieves and collates essential pieces of information from a range of sources Can explain and discuss their understanding of what they have read, including through formal presentation and debates, maintaining focus on the topic and using notes where necessary Refers to text to support opinions and predictions (point+evidence then point+evidence +explanation then point + evidence -+ explanation+evaluation) Identifies and explains implicit and explicit points of view Compares and contrasts explicit and implicit points of view Understand and uses the structure of a range of text types to support understanding Understands and can comment on the effect of structure and organisation of different text types Sustains understanding over extended texts by using structural and organisational features effectively Can confidently identify and begin to explain viewpoint in texts Can discuss implied and multi-layered meanings Explains and begins to evaluate success of use of imagery and figurative language Identifies and analysis authors techniques and vocabulary when creating moods, messages, feelings and attitudes and can offer reasons for choice considering the effect on the reader Inference Structure Language Reads confidently, using knowledge of grammar and word roots to read for meaning Consolidates knowledge of word roots, derivations and spelling patterns to read unknown words Uses connectives as signposts to indicate a change of tone Secure and confident in use of knowledge of word roots, derivations and spelling patterns to read unknown words Wide ranging and accurate use of morphemic and etymological knowledge Author Traditions Begins to give reasons for adoption of viewpoint in texts Analyses and comments on success of texts and writers in evoking particular responses Can consider how implied and multi-layered meanings are created Can identify similarities and differences between texts, or versions, with some explanation, e.g. narrative conventions in traditional tales or stories from different creatures, ballads, and newspaper reports