RATES OF REACTION - GENERAL
advertisement

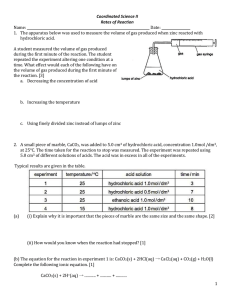
RATES OF REACTION - GENERAL 1. Part A Name three factors that effect the rate of a reaction, and describe the effect of changing each factor. 1. [6] Part B Suggest a reason for each of the following observations: a. Magnesium powder reacts faster than magnesium ribbon, with dilute sulphuric acid. [1] b. Hydrogen peroxide decomposes much faster in the presence of the enzyme catalase. [1] c. The reaction between manganese carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid speeds up when some concentrated hydrochloric acid is added. [1] d. Zinc powder burns much more vigorously in oxygen than zinc foil does. [1] e. The reaction between sodium thiosulphate and hydrochloric acid takes a very long time if carried out in an ice bath. f [1] Zinc and dilute sulphuric acid react much more quickly when a few drops of copper(II) sulphate solution are added. [1] g. Drenching with water prevents too much damage from spilt acid. [1] h. A car's exhaust pipe will rust faster if the car is used a lot. [1] i In fireworks, powdered magnesium is used rather than magnesium ribbon. [1] j. In this country, dead animals decay quite quickly. But in Siberia, bodies of mammoths that died 30000 years ago have been found fully preserved in ice. [1] k. The more sweet things you eat, the faster your teeth decay. [1] 1. Food cooks much faster in a pressure cooker than in an ordinary saucepan. [1] m. Water at sea-level boils at 100oC, on the top of Mount Everest water boils at 75oC. [1] n. Iron wool reacts faster in air than does an iron bar. [1] o. Catalyic converters work best over a long, rather than a short journey. [1] p. When alcohol is made by the process of fermentation the maximum yield of alcohol occurs at 40oC [1] 2A). The rate of the reaction between magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid could be measured using this apparatus: a What is the purpose of: (i ) the test tube? [1] (ii) the gas syringe? [1] b. How would you get the reaction to start? [1] B). Some magnesium and an excess of dilute hydrochloric acid were reacted together. The volume of hydrogen produced was recorded every minute, as shown in the table: Time/mins 1 Volume of hydrogen /cm3 0 1 14 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 23 31 38 39 40 40 40 40 40 a What does an excess of acid mean? b Plot a graph of the results, with the vertical; axis being volume of hydrogen / cm3 and the horizontal axis labelled Time / mins. [1] [4] c i. ii. iii. iv v How much hydrogen was produced in the : first minute? second minute? third minute? fourth minute? fifth minute? [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] d What is the total volume of hydrogen produced in the reaction? [1] e How many minutes pass before the reaction finishes? [1] f What is the average rate of the reaction? [1] g A similar reaction had a rate of 15 cm3 of hydrogen in the first minute. Is this a slower or reaction than the one above (in f)? [1] h 6. How could you make the above reaction go slower, while still using the same quantities of metal and acid? When 10 cm3 of nitric acid is added to a lump of limestone (calcium carbonate) [1] a colourless gas is given off. After 2 minutes the reaction stops. a) Give a reason why the reaction stops. b) If powdered calcium carbonate was used instead of a lump of calcium carbonate: (i) would the reaction be faster or slower? (1) (ii) Explain your answer. (1) c) Nita does the experiment but decides to use hot acid (at 80oC ) rather than using cold acid (at 20oC). (i) Would this reaction be faster or slower. (ii) Explain your answer. (1) (1) d) (i) (ii) (1) (1) e) When Nita clears up she manages to spill some acid on the bench. What should she do to remove the acid ? In these experiments what is the name of the gas given off ? If a lit splint were put into this gas what would you expect to see? (1) (1)