Eukaryotic Cell Structure
advertisement

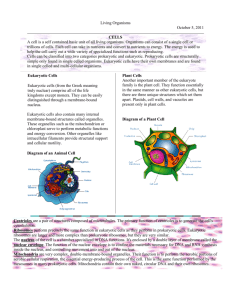
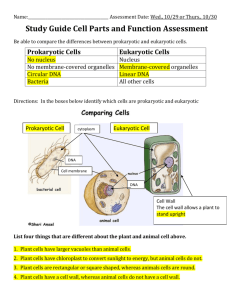
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Discuss the possible origin of eukaryotic cell structures, referring to the theory of endosymbiosis. · One cell took in others · In vacuoles by endosymbiosis · Kept them alive instead of digesting them · One became the mitochondrion, and another the chloroplast · Original cell respired anaerobically · (prokaryotic) cell that respired aerobically became mitochondrion · (prokaryotic) cell that photosynthesized became the chloroplast · Symbiosis/mutualism benefits both/all cells involved · Ribozome sizes of mitochondria and chloroplasts evidence for symbiosis · Presence/type of DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts evidence for endosymbiosis · Presence of two membranes is evidence for symbiosis. Draw a diagram to show the ultra-structure of a generalized animal cell as seen in electron micrographs State one function of each of these organelles: Ribosome, RER, Lysosome, Golgoi Apparatus, Mitochondrion, Nucleus, Chloroplast, Nucleus, 1. Ribosome a. Synthesizes proteins 2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum a. Transports proteins from Ribosomes to other parts of the cell (such as Golgi) 3. Lysosome a. Responsible for the cell's digestion/destruction of macromolecules, old cell parts, and microorganisms 4. Golgi Apparatus a. The Golgi complex is the site of the modification, completion, and export of secretory proteins and glycoproteins b. Forms vesicles to export contents 5. Mitochondrion a. Site of second stage of aerobic respiration (ATP synthesis and Kreb’s Cycle) 6. Nucleus a. Chromosomes contain DNA b. DNA arranged as genes which control all cell activities 7. Chloroplast a. Two stages of photosynthesis State two similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 1. Cell Membranes 2. Ribosomes 3. Cytoplasm 4. Nucleic Acids State two differences between eukaryotic nucleus and prokaryotic nuclear material 1. Eukaryotic – Nuclear Membrane exclusively in nucleus 2. Prokaryotic – No Membrane cytoplasm DNA in Chromosomes DNA DNA Loop Describe three differences between animal and plant cells DNA & RNA in 1. Plant Cellulose Cell Wall Vacuole in Cell Sap 2. Animal- No CCW Chlorophyll in Chloroplasts No CIC Vesicles State the composition and function of the plant cell wall 1. Provide support (as water enters the cell osmotically the cell wall resists expansion and an internal pressure is created which provides turgidity for the plant) 2. To give direct support to the cell and the plant as a whole by providing mechanical strength. 3. To permit the movement of water through and along it and contribute to the movement of water in the plant as a whole in particular the cortex of the root 4. Made of cellulose microfibrils embedded in an amorphous polysaccharide matrix 5. Polymer of 10,000 beta-glucose molecules forming a long unbranched chain 6. Many chains run parallel and have cross-linkages