Pregnancy Diet

Pregnancy Diet
GENERAL INFORMATION:
What is a healthy diet during pregnancy?
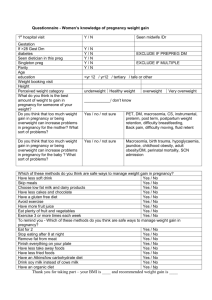
A healthy diet during pregnancy contains a variety of foods that provide the amount of calories and nutrients you need. During pregnancy, your body needs extra calories and nutrients to support your growing baby. Some extra nutrients you need include protein and certain vitamins and minerals. Following a healthy diet can help you to gain the right amount of weight during your pregnancy. It can also decrease your baby's risk of birth defects, low birth weight, and certain health problems. The amount of weight you should gain may depend on your weight before pregnancy, and if you are carrying more than one baby. Your caregiver will tell you how much weight you should gain.
The amount of calories you need depends on your daily activity, your weight before pregnancy, and current weight gain. Your calorie needs also depend on the stage of pregnancy you are in. Caregivers divide pregnancy into three blocks of time called trimesters. In the first trimester, you usually do not need extra calories.
In the second and third trimesters, most women should eat about 300 extra calories each day.
What should I avoid eating and drinking while I am pregnant?
Alcohol: You should not drink beer, wine, liquor (such as whiskey or gin), or any other mixed drinks. Drinking alcohol can increase your risk of having a miscarriage (losing your baby). Your baby may also have health problems such as being born too small and having learning problems.
Caffeine: It is not clear how caffeine affects pregnancy. Limit your intake of caffeine to avoid possible health problems. Caffeine may be found in coffee, tea, cola, sports drinks, and chocolate.
Foods that contain mercury: Mercury is naturally found almost all types of fish and shellfish, and is not harmful to most people. However, some types of fish absorb higher levels of mercury that can be harmful to an unborn baby and young children. During pregnancy it is important to carefully select the kind of fish that you eat. You should avoid certain types of fish, and eat fish and shellfish that are lower in mercury. o Do not eat shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish. o You may eat up to 12 ounces of fish or shellfish that have low levels of mercury each week. These include shrimp, canned light tuna, salmon, pollock, and catfish. Because albacore tuna has more mercury than canned tuna, eat only 6 ounces of albacore (white) tuna per week.
Foods that cause food-borne illness: o Raw and undercooked foods: You should avoid eating undercooked or raw meat, poultry, eggs, fish, or shellfish (shrimp, crab, lobster). You should also avoid eating cooked foods that have been near raw foods.
Cook leftover foods and ready-to-eat foods such as hot dogs until steaming hot. o Unpasteurized food: Unpasteurized foods are foods that have not gone through the heating process (pasteurization) that destroys bacteria. You should not drink unpasteurized milk or juice. Cheese made from unpasteurized milk can also be harmful. This includes Brie, feta,
Camembert and blue, or Mexican cheeses. These cheeses contain bacteria that can harm your growing baby.
What foods can I eat while I am pregnant?
Eat a variety of foods from each of these food groups every day. Your dietitian or nutritionist will tell you how many servings you should have from each food group each day. Each item listed counts as one serving.
Breads and starches:
Whole grains: o One-half of a cup of cooked brown rice. o One-half of a cup of oatmeal. o One slice of 100 percent whole wheat or rye bread. o Three-fourths of a cup (one ounce) of whole-grain dry cereal.
Other breads and starches: o One-half cup of cooked rice or pasta. o One-half of a hot dog or hamburger bun. o One-half of a small bagel. o One six-inch tortilla or pita bread. o One small dinner roll.
Fruits: Eat a variety of fruits each day. Choose fresh, canned, or dried fruit instead of fruit juice as often as possible.
One half-cup (four ounces) of a cup of fruit juice.
One half-cup of chopped, cooked, or canned fruit.
One medium size apple, peach, orange, or banana.
Vegetables: Eat dark green and orange vegetables several times a week.
A serving of vegetables is: o One half-cup of cooked or raw vegetables. o One half-cup of vegetable or tomato juice. o One cup of raw or leafy vegetables (such as a tossed salad).
Dark green vegetables: Broccoli, spinach, romaine lettuce, collard, turnip and mustard greens.
Orange vegetables: Carrots, sweet potatoes, winter squash and pumpkin.
Other vegetables: Tomatoes, lettuce, green beans, and onions.
Starchy vegetables: White potatoes, corn, and green peas.
Dairy Foods: Choose fat-free or low-fat dairy foods.
One and one-half ounces of low-fat cheese.
One cup (eight ounces) of low-fat or fat-free milk or yogurt.
One-half of a cup of low-fat frozen yogurt.
Meat and other protein sources: Choose lean meats and poultry (chicken and turkey).
Bake, broil, and grill meat instead of frying it. Eat a variety of protein foods.
One and one-half ounces (about two tablespoons) of nuts or two tablespoons of peanut butter.
One-half cup of soy tofu or tempeh.
One large egg.
Three-fourths of a cup of cooked dried beans, peas or lentils.
Three to four ounces of any lean meat, fish, or poultry.
Fats:
One-eighth of an avocado.
One teaspoon of oil (canola, olive, corn, safflower, soybean).
One teaspoon of tub, stick or squeeze regular margarine.
One tablespoon of low-fat margarine (30 to 50 percent vegetable oil).
One teaspoon of regular mayonnaise or one tablespoon of low-fat mayonnaise.
One tablespoon of regular salad dressing or one and one-half of a tablespoon of low-fat salad dressing.
How much water do I need to drink each day?
Water makes up a large part of your body, including your blood. During pregnancy, the amount of blood in your body increases up to twice as much as usual. The water you drink makes up part of this fluid.
Water protects and cushions your baby, and controls body temperature. You need about eight to ten (eight-ounce) cups of water each day. This amount includes water, other liquids, and water from foods.
What vitamin and mineral supplements might I need to take?
Most women can get the extra nutrients they need from food if they eat a healthy, well-balanced diet.
However, some women do need vitamin and mineral supplements to meet their extra nutrient needs during pregnancy. Your caregiver will tell you if you need a supplement, and the type you should use. Talk to your caregiver before taking any other kind of drug, including herbal (natural) supplements.
Folic acid: The amount of folic acid you need before you get pregnant is at least
400 micrograms each day. Folic acid helps to form your baby's brain and spinal cord in early pregnancy. During pregnancy, your daily need for folic acid increases to about 600 mcg. Include folic acid in your diet each day by eating citrus fruits and juices, green leafy vegetables, liver, and dried beans. Folic acid is also added to foods such as breakfast cereals, bread products, flour and pasta.
Iron: This mineral is important because it helps the baby's blood and your blood carry oxygen. Good sources of iron are meat, liver, poultry, oysters, and fish.
Other sources are beans, vegetables (spinach, peas, broccoli), and fortified cereals and breads. Your body will absorb iron better from non-meat sources if you have a source of vitamin C at the same time. Drink tea and coffee separately from ironfortified foods and iron supplements. You need about 30 mg of iron during pregnancy.
Prenatal vitamins: Eat a healthy diet, even if you take a prenatal vitamin. You may forget to take your vitamin for a day. If you forget, do not take double the amount the next day.
Calcium and vitamin D: Your need for calcium and vitamin D does not increase during pregnancy. However, women who do not eat milk products may need a calcium and vitamin D supplement. Talk to your caregiver about calcium supplements if you do not regularly eat good sources of calcium. The amount of calcium you need is about 1,300 mg if you are between 14 and 18 years old and
1,000 mg if you are 19 to 50 years old.
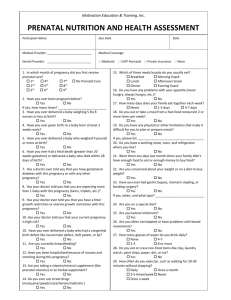
What diet changes may help if I have morning sickness?
Morning sickness is common during the first few months of pregnancy. You might feel nauseated (sick to your stomach) or you could vomit (throw up) many times a day. To improve symptoms of morning sickness, eat small, frequent meals instead of three large meals. Foods high in carbohydrate such as crackers, dry toast, and pasta may be easier to eat for some women.
Drink liquids between meals rather than with meals. Avoid foods that have a strong smell and foods that make you feel sick. Avoid having an empty stomach. Call your caregiver if you have very bad nausea and vomiting with other symptoms. These symtpoms may include constant nausea and vomiting, not eating or drinking, weight loss, and trouble doing daily activities.
What diet changes may decrease the problem of constipation?
Many women have problems with constipation during pregnancy. Being constipated means having hard stools that are difficult to pass. A high fiber diet can improve the symptoms of constipation. Some breakfast cereals, whole grain breads and prune juice are high in fiber. Raw fruits, vegetables and cooked beans are also good fiber sources. Increasing your intake of fluids and getting regular physical activity may also be helpful. Be sure to check with your caregiver before you begin any exercise program.
What diet changes may decrease my heartburn?
Pregnancy hormones cause food to move more slowly through your digestive system, which sometimes causes heartburn. To improve the symptoms of heartburn, avoid lying down right after eating. When you do lie down, sleep with your head slightly elevated. Eat small, frequent meals instead of three large meals. Avoiding caffeine, chocolate, or spicy foods may also be helpful.
How can I get calcium in my diet if I cannot tolerate milk?
Some women cannot eat milk or milk products (milk intolerance). Milk intolerance may cause gas, stomach cramping, bloating, and loose stools (BMs) after eating or drinking milk products. Some people can tolerate at least one cup (8 ounces) of milk with meals. If you cannot drink milk, lactose-free or lactose-reduced milk and calcium-fortified soymilk are good choices. Hard, aged cheeses and yogurt may be easier to digest than milk. Ask your caregiver about pills you can take to help you digest milk products.
What other healthy guidelines should I follow?
Vegetarians and vegans: Vegetarians and vegans need to be careful to include enough protein, vitamin B12, and iron during pregnancy. Some non-meat sources are fortified cereals, nut butters, soy products (tofu and soymilk), nuts, grains, and legumes. These nutrients are also found in eggs and milk products.
Cravings: Many women have cravings for certain foods during pregnancy. They may crave foods such as chocolate, citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits, tangerines), pickles, potato chips, and ice cream. Foods that are high in calories, fat and sugar should not replace healthy food choices. Some women have cravings for unusual substances such as clay, dirt, laundry starch, freezer frost, ice, and chalk. This condition is called pica. Eating these things may lead to health problems such as anemia and cause illness. Tell your caregiver about your cravings. Caregivers can make sure that you are eating the right foods that you need during pregnancy.
Smoking and drug use: Do not smoke cigarettes, marijuana (pot) or use other illegal drugs during pregnancy. These substances are harmful to your baby. For example, smoking increases the chances of your baby being born at a low birth weight or being born too early. It is never too late to quit smoking if you smoke.
Smoking harms your heart, lungs, and blood. You are more likely to have a heart attack, lung disease, and cancer if you smoke. You will help yourself and your baby by not smoking. Your caregiver can give you information on how to stop smoking or using illegal drugs.
Risks: Not eating a healthy diet can cause problems for you and your baby. You may not be able to gain the weight needed for a healthy pregnancy. A healthy weight gain is important for having a baby with a healthy weight. Babies who are born at a healthy weight have a lower risk of having certain health problems at birth and later. Following a healthy diet may help you avoid gaining too much weight during pregnancy. Gaining too much weight can also cause problems during pregnancy and delivery.