final exam outline science 6
advertisement

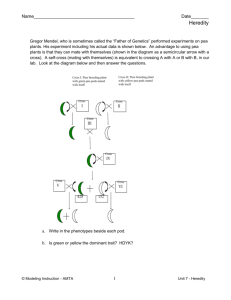
6th Grade Science – Life Science – Final Exam Guide FINAL EXAM DATE: MONDAY, JUNE 8, 2015 Name:__________________________________________________ Class 6.1 or 6.2 OR 6.3 Be diligent about completing the Final Exam Review Pack / Practice Questions Actively participate in class and ask questions in class each day as we go over the material and review for the final. Read / Read / Review Review Review test review packs from the year. Review class tests. Chapter Reviews and Section Review from your textbook. Practice Test Questions Final Exam Pack – separate hand out. Unit 1 – The study of Living Things Chapter 1 – The World of Life Science o Section 1: Asking About Life It All Starts with a Question Life Scientists Why Ask Questions? o Section 2: Scientific Methods The Scientific Method Ask a Question Form a Hypothesis Test the Hypothesis Analyze the Results Draw Conclusions Communicate Results Scientific Knowledge Changes o Section 4: Tools, Measurement and Safety Tools for Seeing Computers Systems of Measurement Safety Rules! o Terms to Know: life science, scientific method, hypothesis, controlled experiment, variable, technology, compound light microscope, electron microscope, area, volume, mass, temperature Chapter 2 – It’s Alive!! Or, Is It? o Section 1: Characteristics of Living Things Living Things Have Cells Living Things Sense and Respond to Change Living Things Reproduce Living Things Have DNA Living Things Grow and Develop Page 1 of 3 o o o Section 2: The Necessities of Life Food Water Air A Place to Live Section 3: The Chemistry of Life – Putting it all Together Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids The Cell’s Fuel - ATP Terms To Know: cell, stimulus, homeostasis, asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction, DNA, heredity, metabolism, producer, consumer, decomposer, protein, carbohydrate, lipid, phospholipid, nucleic acid, ATP. Unit 2 – Cells Chapter 3 – Cells: The Basic Units of Life o Section 1: The Diversity of Life Cells and the Cell Theory All organisms are made of one or more cells The cell is the basic unit of all living things All cells come from existing cells Cell Size Two Kinds of Cells Prokaryotes: Bacteria and Archea Eukaryotes o Section 2: Eukaryotic Cells Cell Wall Cell Membrane Cytoskeleton Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplasts Golgi Complex Lysosomes Vacuoles o Section 3: The Organization of Living Things Tissues: Cells Working in Teams Organs: Teams Working Together Organ Systems: A Great Combination Organisms: Independent Living Population, Community, Ecosystem o Terms to Know: tissue, organ, organ system, organism, unicellular, multicellular, population, community, ecosystem, cell membrane, organelles, cytoplasm, nucleus, prokaryotic, eukaryotic, bacteria, cell wall, ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, chloroplast, Golgi complex, vacuole, lysosome. Page 2 of 3 Chapter 4 – The Cell in Action o Section 1: Exchange with the Environment What is Diffusion? Moving Small Particles Moving Large Particles o Section 2: Cell Energy From Sun to Cell - Photosynthesis Getting Energy from Food – Cellular Respiration o Section 3: The Cell Cycle The Life of a Cell Mitosis and the Cell Cycle o Terms to Know: diffusion, osmosis, passive transport, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, cell cycle, chromosome, binary fission, homologous chromosome, chromatids, centromere, mitosis, cytokinesis, interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase. Unit 3 – Heredity, Evolution, and Classification Chapter 5 – Heredity o Section 1: Mendel and His Peas Gregor Mendel and is Pea Plant Experiment Punnett Square Probability o Section 2: Traits and Inheritance Genes and Alleles Genotype vs. Phenotype Punnett Squares Incomplete Dominance The Importance of the Environment o Terms to Know: heredity, dominant trait, recessive trait, genes alleles, genotype, phenotype, probability. Chapter 9 – Classification o Section 1: Classification: Sorting it All Out Why Classify? How do Scientists Classify Organisms? Taxonomy Levels of Classification Scientific Names Dichotomous Keys o Section 2: Domains and Kingdoms Archae and Bacteria Eukarya Protisita Fungi Plantae Animalia o Terms to Know: classification, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species, taxonomy, dichotomous key, archaea, bacteria, protista, plantae, fungi, animalia. GOOD LUCK Page 3 of 3