Study Guide for EQA#2
advertisement
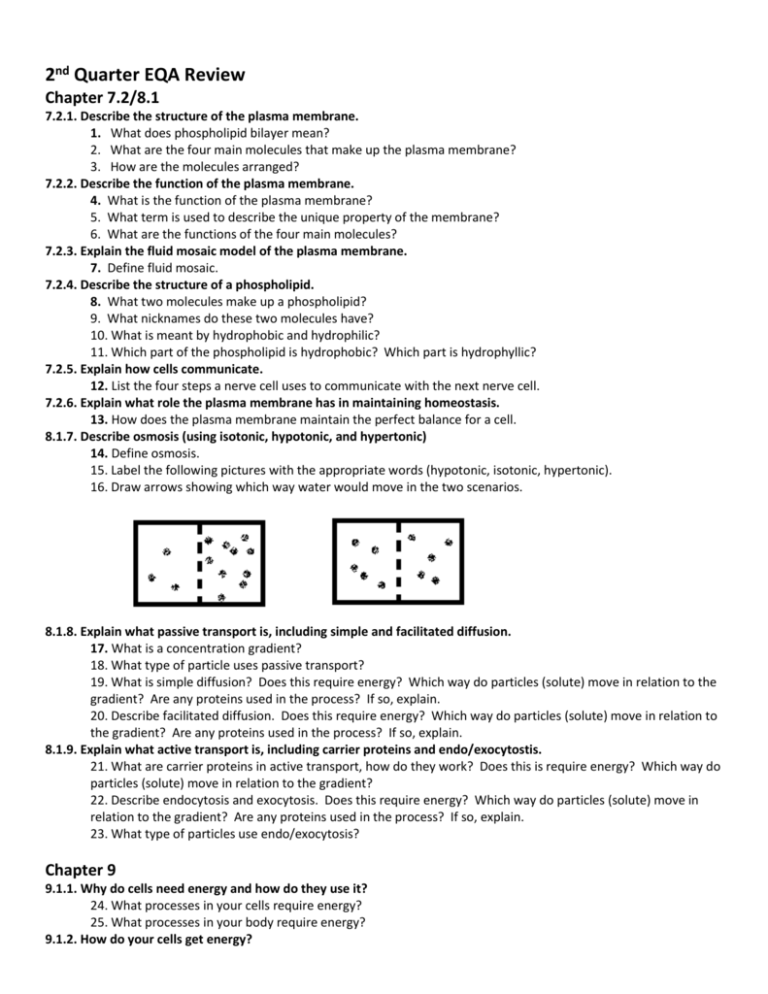
2nd Quarter EQA Review Chapter 7.2/8.1 7.2.1. Describe the structure of the plasma membrane. 1. What does phospholipid bilayer mean? 2. What are the four main molecules that make up the plasma membrane? 3. How are the molecules arranged? 7.2.2. Describe the function of the plasma membrane. 4. What is the function of the plasma membrane? 5. What term is used to describe the unique property of the membrane? 6. What are the functions of the four main molecules? 7.2.3. Explain the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane. 7. Define fluid mosaic. 7.2.4. Describe the structure of a phospholipid. 8. What two molecules make up a phospholipid? 9. What nicknames do these two molecules have? 10. What is meant by hydrophobic and hydrophilic? 11. Which part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic? Which part is hydrophyllic? 7.2.5. Explain how cells communicate. 12. List the four steps a nerve cell uses to communicate with the next nerve cell. 7.2.6. Explain what role the plasma membrane has in maintaining homeostasis. 13. How does the plasma membrane maintain the perfect balance for a cell. 8.1.7. Describe osmosis (using isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic) 14. Define osmosis. 15. Label the following pictures with the appropriate words (hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic). 16. Draw arrows showing which way water would move in the two scenarios. 8.1.8. Explain what passive transport is, including simple and facilitated diffusion. 17. What is a concentration gradient? 18. What type of particle uses passive transport? 19. What is simple diffusion? Does this require energy? Which way do particles (solute) move in relation to the gradient? Are any proteins used in the process? If so, explain. 20. Describe facilitated diffusion. Does this require energy? Which way do particles (solute) move in relation to the gradient? Are any proteins used in the process? If so, explain. 8.1.9. Explain what active transport is, including carrier proteins and endo/exocytostis. 21. What are carrier proteins in active transport, how do they work? Does this is require energy? Which way do particles (solute) move in relation to the gradient? 22. Describe endocytosis and exocytosis. Does this require energy? Which way do particles (solute) move in relation to the gradient? Are any proteins used in the process? If so, explain. 23. What type of particles use endo/exocytosis? Chapter 9 9.1.1. Why do cells need energy and how do they use it? 24. What processes in your cells require energy? 25. What processes in your body require energy? 9.1.2. How do your cells get energy? 26. You eat _____ to get ________ out of it. Then you turn it into _____. 27. What molecule gives your cells energy directly? 9.1.3. How does ATP store and release energy? 28. What three molecules form ATP? 29. Where is the energy stored in ATP? 30. How would you release energy from ATP? 9.1.4. How do your cells get the energy from ATP? 31. How do proteins get the energy from ATP? 9.3.5. What is cellular respiration? 32. What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration? 33. What are the three steps of cellular respiration? 34. Is cellular respiration aerobic or anaerobic? 35. What type of cells use cellular respiration? 36. When would your cells use cellular respiration? 9.3.6. Describe Glycolysis. 37. Is glycolysis aerobic or anaerobic? 38. What molecule goes into glycolysis? 39. What are the products of glycolysis? 40. Where does glycolysis happen? 9.3.7. Describe the Citric Acid Cycle/ Krebs Cycle 41. Is the CAC aerobic or anaerobic? 42. What molecule goes into CAC? 43. What are the products of CAC? 44. Where does CAC happen? 9.3.8. Describe the Electron Transport Chain- ETC 45. Is the ETC aerobic or anaerobic? 46. What molecule goes into ETC? 47. What are the products of ETC? 48. Where does ETC happen? 49. HONORS: Draw out the ETC. 50. HONORS: What is photolysis? 9. 3.9 HONORS: Why is oxygen needed for cellular respiration? 51. Why is oxygen so important to the ETC? 9.3.10. Describe Lactic acid fermentation. 52. Is Lactic acid fermentation aerobic or anaerobic? 53. What type of cells use lactic acid fermentation? 54. Describe the process of lactic acid fermentation. 55. What are the products of lactic acid fermentation? 9.3.11. Describe Alcoholic fermentation. 56. Is Alcoholic fermentation aerobic or anaerobic? 57. What type of cells use Alcoholic fermentation? 58. Describe the process of Alcoholic fermentation. 59. What are the products of Alcoholic fermentation? 9.2.12. What is photosynthesis? 60. What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis? 61. What are the two steps of photosynthesis? 62. What type of cells use photosynthesis? 63. What organelle is responsible for photosynthesis? 64. What molecule absorbs light energy? 9.2.13. Describe the light- dependent reactions? 65. What things are used during the light-dependent reaction? 66. What molecules are made during the light-dependent reaction? 67. HONORS: Where does the light-dependent reaction occur? 68. HONORS: Draw out the steps of the light-dependent reaction. 9.2.14. Describe the light-independent reactions? 69. What things are used during the light-dependent reaction? 70. What molecules are made during the light-dependent reaction? 71. HONORS: Where does the light-dependent reaction occur? 72. HONORS: Draw out the steps of the light-dependent reaction. 9.2.15. Compare photosynthesis and cellular respiration. 73. What are the reactants of each process? 74. What are the products of each process? 75. What type of cells use each process? Chapter 11 11.1.1. What is DNA? 76. What is the function of DNA? 77. What does DNA stand for? 11.1.2. Who are Hershey and Chase? 78. What did they do for science? 79. Explain the experiment that Hershey and Chase conducted. 11.1.3. What is the structure of DNA? 80. What shape is attributed to DNA? 81. How many strands is DNA? 82. What holds the strand(s) together? 11.1.4. What is a nucleotide? 83. What three parts make up a nucleotide? 84. What is complementary base pairing? 11.1.5. What is DNA replication? 85. Define DNA replication. 86. Honors: Describe DNA replication in detail. 11.1.6 Who discovered the structure of DNA? 87. Who is credited? 88. Who should have been recognized? 89. Draw a small DNA molecule of 4 total nucleotides, label all parts (Phosphate, deoxyribose, Nitrogen base, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine, Nucleotide)