epicenter and magnitude activity
advertisement

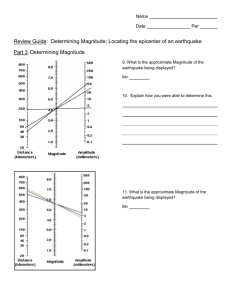
Name: Period: Date: Epicenter and Magnitude Background: In this activity, you will determine the location of an earthquake's epicenter and estimate its Richter magnitude. You will be working with seismograms, which are the records of earthquake waves. In order to accurately record earthquake waves at a seismic station at least three seismographs are needed: one each for E-W, N-S, and vertical motion. By examining seismograms at 3 different recording stations, it is possible to "triangulate" the epicenter of an earthquake. Objective: To locate the epicenter of an earthquake and estimate its Richter magnitude. 1. Start by going to: http://www.sciencecourseware.com/eec/Earthquake/. Under Main Activities, click on “Epicenter and Magnitude”. Make sure you allow pop-ups. Click on “Start Activity” in the pop-up window to begin. Click on “Trigger the Earthquake” to begin! 2. In order to find the epicenter of the earthquake, seismologists need data from 3 different seismic stations. 3. Measure S-P Lag Times for 3 stations. Do this by measuring the distance from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the S wave on seismograms at the 3 seismic stations to determine the S-P lag time. The S-P Lag Time is the time between the arrivals of P and S waves on a seismogram. Seismographs farther from the epicenter have longer S-P lag times. Record all of your data in the table below. Epicenter Data Table Station # S-P Interval (sec) Epicenter Latitude: Amplitude (mm) __° __ ‘ (N or S?) Distance (km) Longitude: Richter Magnitude __° __ ‘ (E or W?) 4. Find the distances of your 3 seismic stations from the epicenter. Use the Travel-Time Curve, a graph of the distance to epicenter as a function of S-P lag time. The distance (km) for Station #1 is shown below: 5. Measure the maximum S-wave amplitude on the seismograms for each of the 3 stations. The Swave amplitude is the height of the tallest wave on the graph, as measured from the x-axis. 6. Draw circles on the map to triangulate to the epicenter. 7. Locate the epicenter on the map. The epicenter is where the 3 circles intersect. 8. Estimate the latitude and longitude of your earthquake’s epicenter. 9. Estimate your earthquake’s magnitude by drawing a line between the values for the known distance and amplitude. The line will pass through the value of the Richter Magnitude. Sample Data Table for Epicenter Location and Determination Station 1 7 8 S-P Interval (sec) 33.7 22.2 13.4 Epicenter Latitude: Longitude: 34°50‘ N 115°50‘ W Amplitude (mm) 1.4 4.5 12 Distance (km) 329 216 130 Magnitude 4.2 4.2 3.8