Horticulture 113
advertisement

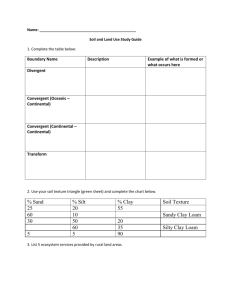
Horticulture 113 Soils and Fertilizers Sample Examination 1. The proportion of sand, silt and clay in a soil refers to a soil's a. structure b. fertility c. horizons d. texture 2. Most soils in Southern Calif. are a. alkaline b. neutral c. acidic 3. In a soil that has been watered and drained, the percentage of total pore space that is filled with air is usually a. 25 b. 50 c. 75 d. l00 4. In collecting a soil sample, it is a good practice to combine the soil from several different depths within the site being sampled. a. T b. F 5. If a soil has 25% clay and 6% OM, what is its approximate CEC? a. 34 b. 24.5 c. l7 d. 68 e. 0 6. Which soil type has the greater bulk density? a. sand b. clay 7. Which of the following soils would be expected to weigh the least? a. loamy clay b. sandy loam c. sandy clay loam d. clay loam 8. The Zone of Leaching is another name for the a. A horizon b. B horizon c. C horizon d. Zone of Leaching e. hardpan 9. Hardpans and claypans form in which horizon? a. A b. B c. C d. D 10. In a "typical" soil, the size of the inorganic fraction is about a. 5% b. 50% c. 25% d. 8% e. 45% 11. Mucks are more decomposed than peaty mucks. a. T b. F 12. Texture alone is a good measure of a soil's CEC a. T b. F 13. Use your soil texture triangle to find the soil classification when there is 10% sand, 47% silt and 43% clay. Write:________________. 14. Which of the following is closest in size to an acre? a. 100' x 100' b. one mile x one mile c. 205' x 205' d. 600' x 200' 16. Which of the following would be the most damaging to the structure of a soil that had good structure to begin with? a. spading b. rototilling c. spreading and watering in fertilizer d. adding gypsum e. adding OM 17. When a plant is at permanent wilting point, the type of water remaining in the soil is a. gravitational b. capillary c. hydroscopic d. transpirational 18. An extreme accumulation of clay (not accompanied by mineral deposits) located in the B horizon would be a. hardpan b. claypan c. the C horizon d. the zone of leaching e. zone of accumulation. 19. The formation of a long ribbon in determining soil texture by feel is an indication of the presence of a. sand b. silt c. clay d. OM. 20. If an oven-dry sample of soil weight 120.0 grams initially, and 114.0 grams after being heated at high temperature for l hour, what was its OM content? a. 1.8% b. 3.0% c. 3.6% d. 6.0% e. 12%. F. 5.0% 21. The majority of plants prefer a soil with a pH range of a. 4.5-5.5 b. 5.5-6.5 c. 6.5-7.5 d. 7.5-8.5 22. How many cubic yards of compost would be needed to cover an area of 2000 sq. ft. to a depth of l inch? a. 1 b. 3 c. 6 d. 9 e. 18 23. Adding OM to a soil cannot change a soil’s a. ability to hold water b. pH c. bulk density d. texture e. structure 24. Rockiness refers only to the amount of exposed bedrock. a. T b. F 25. The micelle is the smallest functional unit of soils and has a net negative charge. a. T b. F 26. Structure in the B horizon is important for good root growth. a. T b. F 27. The addition of iron sulfate to soils causes them to have a lower pH. a. T b. F 28. The PWP is a influenced not only by a soil's texture class, but also the type of crop or vegetation that is to be grown. a. true b. false 29. Adding OM to a mineral soil will always increase its CEC. a. T b. F 30. The addition of sodium to a soil will improve its structure. a. T b. F 31. A sandy soil with l0% OM could be classified as an organic soil. a. T b. F 32. Removing all the stones from a clay soil would be recommended. a. T b. F 33. The first soil horizon to form is the B horizon. a. T b. F 34. When dissolved in the soil solution, all of the following are present as cations: magnesium, calcium, sodium, potassium, hydrogen a. T b. F 35. It is proper to add a 3” layer of OM to the ground in preparing it for planting to a lawn. a. T b. F 36. The mineral that is primarily responsible for structure in soils is a. calcium b. potassium c. sodium d. manganese e. sulfur 37. If plot A has a pH of 5.0 and plot B is 1000 times more alkaline, the pH of plot B would be a. 4.0 b. 7.0 c. 8.0 d. 9.0 38. If a soil has 3% OM, about how many pounds of OM would be needed for an area of 1500 sq. ft. to bring the OM up to 6%? a. 1800# b. 2050# c. 5000# c. 900# e. 3600# 39. After watering and draining, a soil is at a. field capacity b. saturation c. permanent wilting point d. hydroscopic coefficient 40. Structureless soils can be massive or single-grained. a. T b. F 41. How many cubic yards of compost are needed to adequately cover l500 sq. ft. in the preparation of ground for the planting of a lawn? a. l b. 3 c. 6 d. 9 e. 13.5 42. Which of the following has the highest nitrogen content? a. ammonium phosphate b. ammonium sulfate c. calcium nitrate d. ammonium nitrate 43. Hardpan that is deeper than 3' can be ignored for planting purposes. a. T b. F 44. A tensiometer is used to measure a. soil structure b. soil texture c. soil depth d. the relative amount of capillary water in a soil e. soil organic matter content. 45. A CEC of 55 MEq/l00 grams soils would be considered a. low b. about right c. high 46. In horticulture, we generally try to achieve an OM content of 8%. a. T b. F 47. Organic soils are generally managed at a pH of 5.5. a. T b. F 48. Nitrogen is not held strongly by the micelle and is very subject to leaching out. a. T b. F 49. An acre furrow slice weighs how many pounds? a. l,000 c. 2,000,000 d. 5,000,000 b. l,000,000 50. Macropores are located a. within peds b. between peds c. within micelles 51. Which of the following would be the most damaging to the structure of a soil that had good structure to begin with? a. spading b. rototilling c. raking or hoeing in organic matter d. spreading and watering in fertilizer 52. What is the bulk density of a soil if 30 cc of it weighed 45 grams? a. 0.66 g/cc b. l.0 g/cc c. 1.25 g/cc d. 1.5 g/cc 53. Very sandy soils and adobe soils are both considered to be structureless. a. true b. false 54. Which of the following soil types would require the greatest amount of sulfur to change its pH? (assume all have the same initial pH). a. silt loam b. clay loam c. sandy clay loam d. loamy sand e. loam 55. When a soil is exactly at field capacity, the type of water remaining in the soil is called a. capillary b. gravitational c. hydroscopic 56. What is the bulk density of a soil if 30 cc of it weighed 45 grams? a. 0.66 g/cc b. l.0 g/cc c. 1.25 g/cc d. 1.5 g/cc 57. Once we have brought our soils up to 8% organic matter, they are organic soils. a. T b. F 58. Which of the following statements is false? a. clay soils retain fertilizers well against leaching. b. clay soils often have higher mineral contents. c. clay soils are less subject to compaction d. clay soils need watering less frequently. e. clay soils are higher in organic matter content than sandy soils, in general 59. Southern California soils are typically rich in nitrogen. a. true b. false 60. Use your soil triangle to find a CLAY LOAM. Now pick any point in this area and give it’s % Sand, % Silt and %Clay. There are many possible correct answers. Fill in the blanks. %SAND ______ %SILT _______ %CLAY ______ Briefly define each of the following terms: TEXTURE: STRUCTURE: HUMUS: ACRE FURROW SLICE: GRAVITATIONAL WATER: SOIL PROFILE: TENSIOMETER: CHEMICAL ACTIVITY: PED: MICELLE: A sample of soil has the following properties: 40 g 30cc 4% 66% dry weight bulk volume OM clay What is its BULK DENSITY? _______1.33g/cc________ What is its CEC?__________41 Meq______________ What is its TEXTURE CLASS?________clay_______ In the space before each carrier below, write in the letter of the matching recipe: 84. _____ ammonium sulfate a. 0-20-0 85. _____ superphosphate b. 20-0-0 86. _____ urea c. 33-0-0 87. _____ bonemeal d. 18-0-0 88. _____ ammonium nitrate e. 1-18-0 89. _____ potassium sulfate f. 46-0-0 90. _____ calcium nitrate g. 15-45-0 h. 0-0-50 i. 15-0-45 j. 12-0-0