Kinematics Unit/Introduction to Video Analysis
advertisement

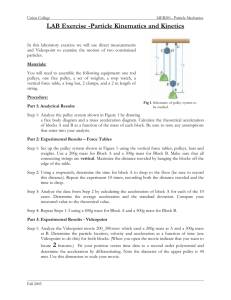
Kinematics Unit/Introduction to Video Analysis Name______________ Introduction: There are many tools that are available to the scientist to analyze the motion of an object. You have already used meter sticks and stopwatches, ticker tape timers and PASCO Motion Sensors. In this activity, you will use a computer software based analysis tool called “Videopoint” to analyze the motion of two objects. Objectives:1) To analyze uniform motion and uniform acceleration of two objects using Videopoint Software. 2) To become familiar with the use of the Videopoint software to allow the use of this tool in later activities and projects. Procedures: 1) Go to the Introduction to Videopoint under “Programs”, run through the tutorial for “projectiles”. The purpose of this is to familiarize you with the basics of data marking and analysis using this program. Leave this window open in the background as you work to allow for quick reference if you run into difficulties. 2) Open the Videopoint program. For this exercise you will be using two video clips that were made previously, in the future you will be creating your own video to analyze. 3) Go to File: “Open Movie”, From the desktop, open the file called “kinematics”, in this file open the file “uniformcart”. 4) When asked how many points to consider choose “1”. 5) Play the video clip, then rewind it. 6) Under “movie” select “set step size”, choose “frames” and “ 3” in the dialog box, click OK. 7) Scale the video using the scale button and the meter stick as a reference point. 8) Click on the dot in the center of the cart in frame 1, the video will advance 1 frame, continue to click on the dot until you reach the last frame. Click the button that highlights each point that you have clicked on. 9) Click on the graph wizard button, select “position” then “add”; “velocity” then “add”, “acceleration” then OK. 10) On the graphs there is a pink “F” button this will allow the fitting of a graph to your data, choose an appropriate fit. 10) Examine the data chart, the graphs and the video, use this information to answer the questions and to form a conclusion for this lab. Print a hard copy for your report. 11) Repeat steps 2-10 for the video clip titled “fancart” Questions: Part I Uniform Motion 1) Describe the spacing of the data points on the video clip, What is the significance of this spacing ? 2) Compare the slope of the Position vs. time graph with the average value of the velocity vs. time graph. How did these values compare to the velocity column from the data table? 3) Compare the shapes of these graphs to “ideal” graphs for uniform motion? Part II: Uniform Acceleration 1) Describe the spacing of the data points on the video clip, What is the significance of this spacing ? 2) For the Position vs. Time Graph, what type of function did you find fit the best? 3) What is the significance of the slope of the Velocity vs. time graph? 4) What relationship exists between the slope of the velocity time graph and the first term of the polynomial equation for the position vs. time graph? Why is this significant? 5) Compare the slope of the velocity vs. time graph to the acceleration values from the data table, and the “average fit curve” from the acceleration vs. time graph. 6) Compare the shapes of the three graphs from this part of the activity to “ideal” graphs for uniform acceleration. Conclusions: Compare the advantages and disadvantages of this analysis tool with the other tools that you have used for motion analysis, suggest some other possible uses for this process. What changes could have been made to improve the quality of this exercise? What are possible sources of error in analysis, how could they be minimized? (NOT “human error”)