DT002_1_Power_Electronics_January_2007
advertisement

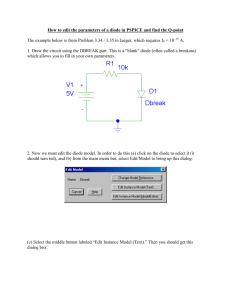
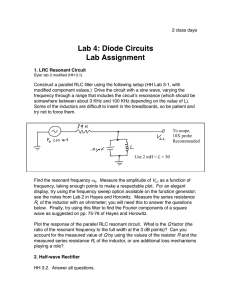
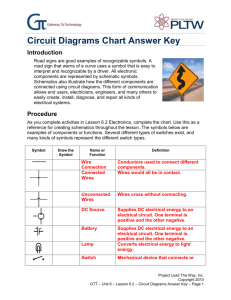
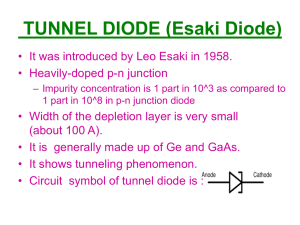
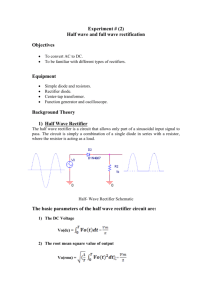
Sketch a graph of a typical voltage-current relationship for a diode. Explain briefly why a diode is sometimes described as a voltage controlled switch Briefly explain the difference between the behaviour of a diode under forward and reverse bias. Sketch simple circuit diagrams to illustrate one example each of forward and reverse bias of a diode. Sketch the circuit symbol used to represent a diode in electrical schematic diagrams and identify the two terminals of a diode by name. A common use for a diode is to perform rectification in power supply circuits. Sketch a schematic diagram for a half-wave rectifier and explain what happens in the circuit. Explain how a smoothing capacitor is used to improve the output voltage from the rectifier and indicate where it should be connected on a schematic diagram. Describe the effect on the output voltage of using a smoothing capacitor that has too little capacitance. State the peak inverse voltage required in a diode if it is to be used in a smoothed rectifier circuit that has an input voltage of 30 volts peak. A diode is specified with a maximum forward current of 1 amp. State the likely consequences of allowing 2 amps of current to flow in the diode for ten seconds. What are the likely consequences of allowing 5 amps to flow in the same diode for 10 milliseconds. What is meant by the terms unregulated and regulated when used in relation to power supply units. Resistors are commonly used in electrical and electronic circuits. Explain the following parameters as they apply to a resistor – Resistance Tolerance Power rating Temperature coefficient of resistance State why resistors are used in electrical circuits and illustrate with a circuit showing a 9 volt battery used to power a Light Emitting Diode that needs 20 mA of current to turn on. State the likely consequences of connecting the battery directly to the LED without using a resistor. A resistor of 10 Ω is used in a circuit where a voltage of 20 volts is connected across it. Calculate the expected amount of current flowing in the resistor and the power dissipated. State the likely consequences of using a resistor rated for 10 watt operation in this application. The circuit diagram shows an output from a logic controller used to turn a motor on and off. Identify each of the components shown in the circuit diagram. Explain the operation of the circuit when the logic controller output switches low Explain the operation of the circuit when the logic controller output switches high