Elements, Rocks, Minerals and
advertisement

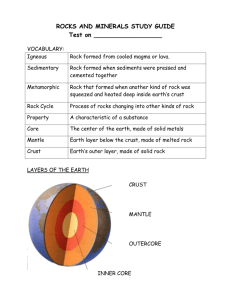
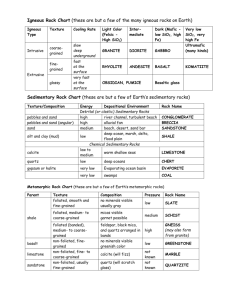
Elements, Rocks, Minerals and The Structure of the Earth The Lithosphere is made up of elements, minerals, and rocks. Elements – cannot be broken apart by chemical or physical means. Of the 92 elements found in nature only 8 of them form most of the Earth’s crust (i.e. carbon, Silicon) Minerals – inorganic compounds of one or more elements found naturally in the lithosphere. Minerals are formed as a result of naturally occurring geologic processes. Minerals are usually 2 or more elements combined: (Si Silicon) and (O Oxygen) combined make Silicon Dioxide or Quartz in the crust Rocks – several minerals combined together. Granite = Quartz + Mica + Feldspar. Rock Types 1) Igneous Rock – created from molten rock. Magma is beneath the surface and lava flows on top of the surface. Extrusive Igneous Rocks – formed from volcanic eruptions. Obsidian resembles black glass and is formed when lava cools very fast so that no crystals form. Intrusive Igneous Rocks – Molten rock that cools and solidifies deep within the lithosphere. They are called plutonic rocks and they reach the surface through millions of years of erosion. ***Igneous Rocks can be classified by how quickly they are formed: Rapid Cooling – Fine Texture Slow Cooling – Coarse Texture 2) Sedimentary Rocks – Rocks that form in layers from eroded material. There are 3 types of sedimentary rocks. (1) Clastic Sedimentary – Formed when accumulations of stones and smaller pieces of weathered rock are cemented, through pressure, together (eg. Sandstone) (2) Chemical Sedimentary – The formation of rock through natural chemical reactions and cementing. (eg. Gypsum – Water evaporates leaving behind salt to combine with other rock) (3) Biogenetic Sedimentary – Formed from living organisms and sea creatures cementing as rock. eg. Limestone CaCO3 (Former Sea Shells), Coal (C) (Accumulation of dead plant matter) 3) Metamorphic Rocks – Rocks that have undergone change in the form of composition, structure, and texture as a result of extreme heat and pressure in crust. (eg. Limestone becomes marble, shale to slate)