Design and Technology Core
advertisement

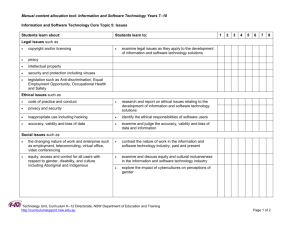
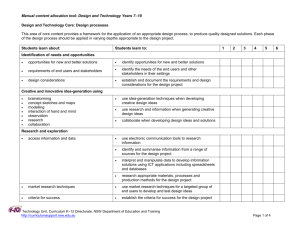
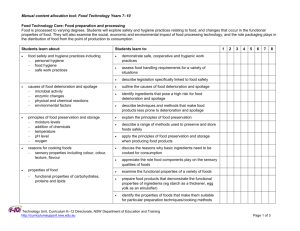
Manual content allocation tool: Design and Technology Years 7–10 Design and Technology Core: A holistic approach A holistic approach to design and technology provides a framework for the understanding of the concepts of design, and for design decisions and reflection. An awareness of the interdisciplinary nature of design gives students a broader perspective of the interrelationship of design with other areas of study. Students learn about: Students learn to: 1 2 3 4 5 6 The concepts of design nature and definitions of design, technology and appropriate technology define design, technology and appropriate technology apply design, technology and appropriate technology principles in the process of developing quality design solutions purposes of design identify the purpose of design across a number of focus areas of design interdisciplinary nature of design which draws on disciplines such as mathematics, sciences, fine art and humanities identify the dependencies of design on other disciplines when designing solutions analyse a case study that demonstrates the interdisciplinary nature of design outline, reflect and apply collaborative methods when developing a design solution interrelationship of design with technology analyse a designed solution and identify how it was affected by the technologies and tools used in its development principles of design when transferred to new situations and contexts reflect on and report the learning of the principles used in design and applied in new situations and contexts document using written communication techniques to provide feedback on their learning Technology Unit, Curriculum K–12 Directorate, NSW Department of Education and Training http://curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au Page 1 of 2 Manual content allocation tool: Design and Technology Years 7–10 Students learn about: Students learn to: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Factors affecting a holistic approach to design and production design purpose and setting factors function form aesthetics end user aspirations and context time factors: historical, contemporary and future considerations quality trends describe factors affecting the design and production of design ideas and solutions from selected focus areas of design analyse and report on the factors that affect the decisions taken in the development of design ideas and solutions apply a holistic approach by considering the factors affecting design and production in a design project human, technical and environmental factors human capital (knowledge, skills and techniques) ergonomics safety, values and ethics industrial and workplace legislation appropriateness of technology choices and design decisions social and environmental sustainability resource choices and availability (tools, materials, time, finance) Technology Unit, Curriculum K–12 Directorate, NSW Department of Education and Training http://curriculumsupport.nsw.edu.au Page 2 of 2