temperate organism
advertisement

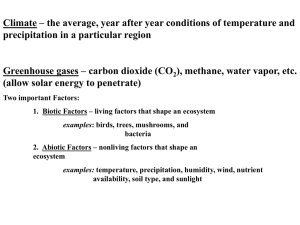
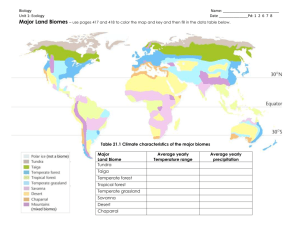
4.3 – Biomes Biomes – a complex of terrestrial communities that covers a large area and is characterized by certain soil and climate conditions and particular groups of plants and animals. Species vary in their adaptations to different conditions associated with their environment. Variations occur in these organisms to give them their best chance of survival and to reproduce. They also permit these organisms to survive in different conditions in different biomes. Too much or too little of any environmental factor can make it difficult for an organism to survive and reproduce in an area. Tolerance – the ability of an organism to survive and reproduce under conditions that differ from their optimal environmental conditions. Microclimate – the climate in a small area that differs from the climate around it. Ex – the weather on top of the hill can differ from what you see near the base of the hill. Climate plays an important factor in determining how and which organisms survives. Climate diagram – a graph that summarizes the temperature and precipitation of a climate over the course of a year. The Major Biomes - ecological variation occurs in the major biomes due to changes in microclimate caused by; o differences in exposure or elevation above sea level o local soil conditions or rock outcroppings o ranges of tolerances of plants and animals for different environmental factors - each biome has characteristic climate and communities of organisms - Tropical Rain Forest o Dense tree tops form a canopy o Second layer of shorter trees are the understory o Hot and wet year round o Thin nutrient poor soils - Tropical Dry Forest o Rainfall is seasonal rather than year round o Contains deciduous trees o Characterized by warm temperatures and alternating wet and dry seasons o Rich soils subject to erosion - Tropical Savanna o Warm temperatures o Seasonal rainfall o Compact soils o Frequent fires set by lightning - Desert o Low precipitation (less that 25 cm per year) o Variable temperature changes (some are extreme heat and cold) o Soils rich in minerals but poor in organic material o Organisms tolerate extreme conditions - Temperate Grassland o Warm to hot summers and cold winters o Moderate seasonal precipitation o Fertile soils and occasional fires o Fires and grazing by large herbivores maintain the characteristic plant community - - - - - - Temperate woodland and shrubland o Hot, dry summers and cool, moist winters o Thin, nutrient poor soils o Periodic fires o A semiarid climate and a mix of shrub communities and open woodlands Temperate Forest o Contain a mixture of coniferous and deciduous trees o Soils are fertile and are rich in humus and other organic material o Cold to moderate winters and warm summers o Year round precipitation Northwest coniferous forest o Mild temperatures o Abundant precipitation during fall, winter and spring o Relatively cool dry summers o Rocky acidic soils o Sometimes called the “emperate rain forest” o Moss often covers tree trunks and the forest floor Boreal Forest o Also called “Taiga” o Long cold winters and short mild summers o Moderate precipitation o High humidity o Acidic nutrient-poor soils o Boreal means north – most of these areas occur in the northern hemisphere Tundra o Characterized by permafrost (permanently frozen subsoil) o Strong winds o Low precipitation o Short and soggy summers and long cold winters o Poorly developed soils due to the constant freezing and thawing of the soils o Permafrost Other land areas o Mountain ranges – abiotic and biotic factors vary from the top to the bottom of the mountain You may pass through a number of biomes on the way to the top such as grasslands, then open woodland of pines, then through a coniferous forest and near the summit go through a tundra like environment o Polar Ice Caps – cold year round and plants and algae are few but do include mosses and lichens Sea ice and ice caps cover most of the area