Topic 3 - Gouverneur Central School District
advertisement

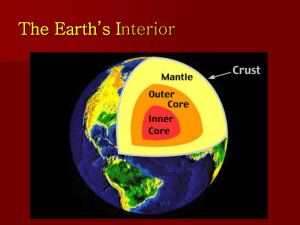
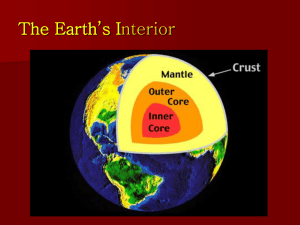
Earthquake – violent shaking of the ground Fault- break in the rock where movement (displacement) occurs Focus – where EQ occurs under the ground Epicenter – where EQ occurs on the surface, directly above the focus intensity – how powerful the EQ is based on damage or destruction, Mercalli scale seismograph – measures EQ magnitude magnitude – force or energy from the EQ, Richter scale p-waves – primary waves, compressional waves, 1st to arrive, fastest, travel in push-pull motion, travel through s-l-g s-waves – secondary waves, shear waves, slower, DO NOT travel through liquids, travel in up & down motion seismologist – scientist that studies EQ’s origin time - time on the clock that the EQ occurs crust – solid outer shell of the Earth, lithosphere continental crust – granitic, less dense, thicker oceanic crust – basaltic, more dense, thinner Moho – interface between more dense and less dense mantle and crust mantle – layer below crust that plates move across, where convection occurs meteorite – same composition as the inner core of the Earth outer core – liquid layer of the Earth inner core – solid inner-most layer of the Earth shadow zone - area on the surface where no p or s-waves are recorded from an EQ Ring of Fire – area around the Pacific Ocean where EQ and volcanoes occur Tsunamis – tidal waves caused by displacement of water continental drift – theory of continents moving across the upper mantle convergent boundary – where plates collide/ come together/ move toward each other trench – feature from a type of convergent boundary, the deepest part of the ocean transform boundary – where plates slide past each other, lateral motion, ex. San Andreas Fault in California Divergent boundary – plates move away from each other, move apart rift – splitting of a continent, rips it apart radiation – form of energy transfer through waves conduction – form of energy transfer through solids by touching, atom to atom convection – form of energy transfer in fluids (liquid or gas), by density differences convection cell – area of convection that causes movement of the fluid, in upper mantle cause plate tectonics (plate motion) lithosphere – same as crust asthenosphere - upper part of mantle where there is convection, what plates move across hot spot – stationary super-heated location in the mantle, Yellowstone and Hawaii