File
advertisement

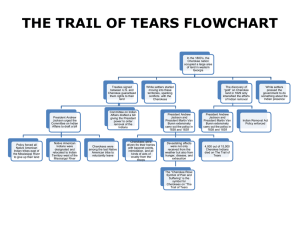
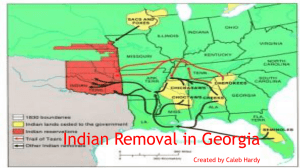
Conflict Over Indian Lands Chapter 10 Outline I. The Creeks (pp. 140 – 144) A. The Creeks were a loose _______________________, and sometimes referred to as ___________________. B. There were two distinct groups: 1. The Upper Creeks: 2. The Lower Creeks: C. During the Revolutionary War, the Creeks sided with the ________________. 1. Georgians demanded land between the _______________ and _____________ rivers. D. The Lower Creeks agreed, but the Upper Creeks, led by chief ____________ ___________________, refused. E. After the Yazoo Land Fraud, the national government promised to remove all Indians from the state: 1. At the same time, the U.S. promised to: F. In 1803, Georgia built a “permanent” state capital named ____________________ on the Oconee River. (See graphic on pg. 126). G. In 1812, the U.S. went to war with Great Britain again because of: a. b. 1. The Upper Creeks, known as _______ ____________, were supplied with British arms and fought to get their land back. 2. General Andrew Jackson defeated the Red Sticks at _______________ ________ in Alabama with the Cherokees and the Lower Creeks led by Chief _____________ ______________. 3. After the war, the U.S. government encouraged the Native Americans to go west to ________________ and __________________. 4. The Creeks were persuaded to cede their lands westward to the ___________ River. 5. On February 12, 1825, Chief McIntosh signed a treaty ceding all Creek lands to the ___________ ____________. 6. As this was done without the support of the Creek people, McIntosh was condemned to ____________. H. The __________________ allowed escaped slaves from Georgia and South Carolina to live on their lands in freedom. 1. By encouraging this practice, the Seminoles threatened the existence of ___________. 2. During the War of 1812, Britain encouraged the Seminoles to harass Georgia and Alabama ____________________. 3. U.S. military forces led by General Jackson were victorious in the __________ Seminole War. 4. In 1830, Congress passed the _________ _____________ Act. 5. The Seminoles resisted, and were forced to move to _________ & _________ after the Second Seminole War. II. The Cherokees (pp. 145 – 152) A. The Cherokees lived in the southern ranges of the _________________ Mountains. B. The Cherokees sided with the ___________ ___________ during the Creek War. C. The Cherokees lived in 80 or so towns and __________ them as a nation by the end of the 1700’s. D. The Cherokees were the most “ ________________” Indians because the adopted much of white culture. 1. Sequoyah created a _______________, a set of written symbols to represent spoken syllables. 2. ______ _____________ became the Cherokee capital. 3. They wrote a _______________________ patterned after the United States. 4. New Echota also served as the home of the _______________ ____________, a bilingual newspaper. 5. Missionaries operated churches and schools, and the Cherokees accepted ______________________. 6. The U.S. approved of the Cherokee nation, but Georgia declared Cherokee laws “ ________ and _________”. 7. In 1829, Cherokee representatives went to Washington and presented a _______________, or a statement of objections to Congress. (See pp. 148-149.) 8. In 1829, ___________ _____________ became president, and asked Congress to pass an Indian removal bill. E. In 1828, _______ was discovered in Dahlonega on Cherokee lands. 1. Georgia was upset that the U.S. sent ___________ to drive the miners off Indian lands, interfering in state affairs. 2. Jackson pulled out the soldiers, since the state claimed the Cherokees were part of Georgia and subject to its ________. 3. Missionaries were forced to take an _______ of _______________, but several refused, and were put in prison. 4. In Worcester v. Georgia, the U.S. ___________ __________ led by Chief Justice ________ _______________ ruled that Georgia laws did not apply in the Cherokee nation. 5. Georgia ignored the ruling, and President Jackson would not _________ it. F. President Jackson stated “The only relief for the Cherokees is by ______________ to the West.” 1. Most Cherokees followed Chief ________ ________ and resisted. 2. Others, such as Major Ridge, his son John, and Elias Boudinot, believed it would be ___________ to move west. a. In 1835, at New Echota, the ____________ faction signed a treaty to give up their lands. b. The majority of the nation, led by John Ross, __________ this treaty. 3. In 1838, U.S. army troops rounded up the Cherokees and were forced to march to the west on foot in the dead of __________. 4. The Cherokee’s suffering was so great the route they took became known as the “____________ of ____________”.