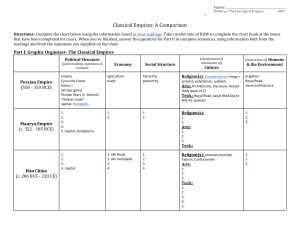
Conrad-Demarest Chart
advertisement
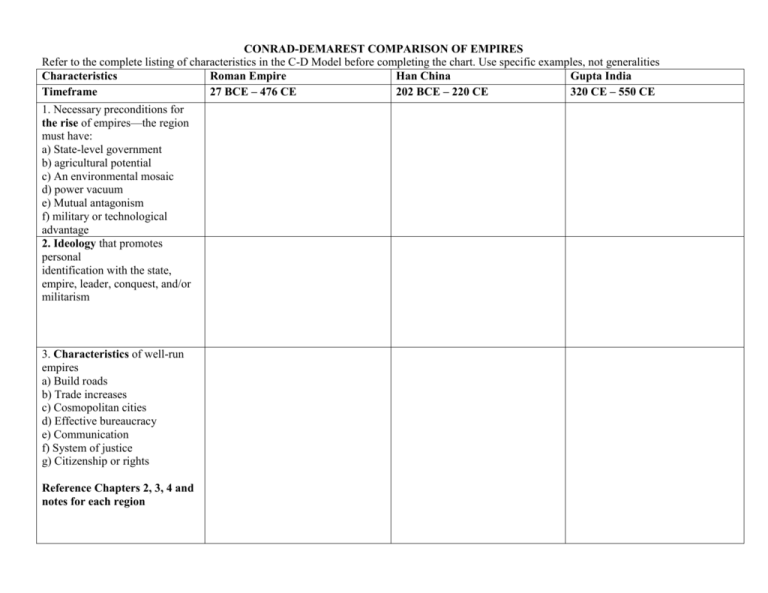
CONRAD-DEMAREST COMPARISON OF EMPIRES Refer to the complete listing of characteristics in the C-D Model before completing the chart. Use specific examples, not generalities Characteristics Roman Empire Han China Gupta India Timeframe 27 BCE – 476 CE 202 BCE – 220 CE 320 CE – 550 CE 1. Necessary preconditions for the rise of empires—the region must have: a) State-level government b) agricultural potential c) An environmental mosaic d) power vacuum e) Mutual antagonism f) military or technological advantage 2. Ideology that promotes personal identification with the state, empire, leader, conquest, and/or militarism 3. Characteristics of well-run empires a) Build roads b) Trade increases c) Cosmopolitan cities d) Effective bureaucracy e) Communication f) System of justice g) Citizenship or rights Reference Chapters 2, 3, 4 and notes for each region Characteristics Roman Empire Han China Gupta India Timeframe 4. Major results of empire: a) Economic rewards b) Relative stability and prosperity c) Population increase 27 BCE – 476 CE 202 BCE – 220 CE 320 CE – 550 CE 5. Empires fall because: a) Failure of leadership b) Expansion beyond a practical limit: c) Lack of new conquests erodes economic base and lessens faith in ideology that supported the empire d) Rebellions from within/ challenges from without Pages to Reference for the Fall of Empires: a. Rome – handout (Fall of Rome); textbook p. 107111 b. Han China – textbook p. 106 c. Gupta India – textbook p. 107