5th Grade Math Curriculum
advertisement

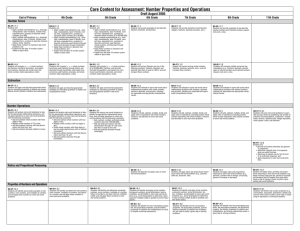
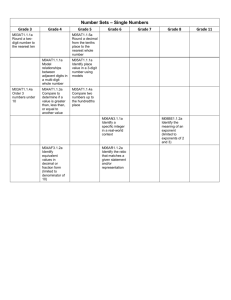
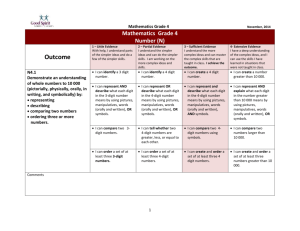
FIFTH GRADE MATH CURRICULUM The primary focus of Math in the Archdiocese of Kansas City in Kansas is to promote in our students their problem solving abilities, which are among God’s many gifts. Standard 1: Number and Computation The student will: 1. Recognize Roman numerals used on dates, clock faces, and in outlines (Used in Bible) 2. ▲Know, explain, and use equivalent representations for a. Whole numbers from 0 through 1,000,000 b. Fractions greater than or equal to zero (Fractions in Exo 29:40) c. Decimals greater than or equal to zero through hundredths place and when used as monetary amounts 3. ◊Compare and order integers, fractions, decimals. 4. Recognize prime and composite numbers 5. ▲Identify, explain, and find the greatest common factor and least common multiple of two or more whole numbers through the basic multiplication facts from 1x1 through 12x12 6. Use the concepts of these properties a. Commutative of addition and multiplication b. Associative of addition and multiplication c. Zero property of addition (additive identity) and property of one for multiplication (multiplicative identity) d. Symmetric property of equality e.g. 35=24+11 is same as 24+11=35 e. Distributive property f. Substitution property e.g. if a=3 and a=b then b=3 7. ▲Use various estimation strategies to estimate whole number quantities from 0 through 100,000; fractions greater than or equal to zero, decimals greater than or equal to zero through hundredths place, and monetary amounts to $10,000 and explains how various strategies are used. 8. ▲Determine if a real-world problem calls for an exact or an approximate answer using whole numbers and performs the appropriate computation using various computational methods including but not limited to mental math and paper/pencil. 9. ▲Solve one and two-step real-world problems using these computational procedures. a. Add and subtract whole numbers 0 through 100,000 b. Multiply through a four-digit number by a two-digit number e.g. 3,042 people attended for $23 each, how much was spent? c. Multiply monetary amounts up to $1,000 by a one or two digit number d. Divide whole numbers through a 2 digit divisor and a 4 digit dividend e. Add and subtract decimals from thousandths place through hundredths place when used as monetary amounts e.g. Peter ran the 100-meter dash in 12.3 seconds and Tanner ran the same race in 12.19 seconds. How much faster was Tanner? 10. Convert improper fractions to mixed numbers and vice versa. 11. ◊Explain the numerical relationship between whole numbers, fractions, and decimals. 12. ◊Estimate to check whether or not the result of a real-world problem is reasonable and make predictions on the information. 13. ◊Divide whole numbers through 2-digit divisor and 4-digit divident. 14. ◊Add and subtract fractions. Standard 2: Algebra The student will: 1. Use attributes to generate patterns e.g. multiples or perfect squares, geometric shapes, measurements, things related to daily life including stained glass Church windows and religious mosaics. 2. Use concrete objects, drawings, and other representations to work with both repeating (9,10,11,12,…) and growing (20,30,40,50,…) patterns. 3. ▲Explain and use variables and symbols to represent unknown whole number quantities from 0 through 1,000 and variable relationships. 4. ▲Solve one-step linear equations with one variable and a whole number solution using addition and subtraction with whole numbers from 0 through 100 and multiplication with the basic facts. e.g. 3y=12, 45=17 + q, r-42=36. 5. ▲Use a function table (input/output machine, T-table) to identify, plot, and label whole number ordered pairs in the first quadrant of a coordinate plane. 6. Plot and locate points for integers (positive and negative) on a horizontal number line and vertical number line. 7. ◊State the rule to find a pattern. 8. ◊Generate a one-step linear equation to solve real-world problem. Standard 3: Geometry Teacher note: The term “geometry” comes from the Greek words meaning, “earth measure.” The process of learning to measure at the early grades focuses on what property (length, width, height) is to be measured and to make comparisons. The student will: 1. Select and use appropriate measurement tools. (Find measurement examples in scripture such as Num 35:5, Job 11:9) 2. Recognize three-dimensional figures from various perspectives. 3. ▲Recognize and describe the solids (cubes, rectangular prisms, cylinders, cones, spheres, triangular prisms, rectangular pyramids, triangular pyramids) using the terms faces, edges, and vertices. 4. Identify rotational symmetry in geometric shapes and real world figures. 5. Identify the properties of congruent figures. 6. Graph coordinates in the 1st quadrant of the coordinate plane. 7. ▲Solve real-world problems by applying properties of plane figures and lines of symmetry. 8. ▲Convert a. Within the customary system: inches and feet, feet and yards, inches and yards, cups and pints, pints and quarts, quarts and gallons, pounds and ounces. b. Within the metric system: centimeters and meters, meters and kilometers, milliliters and liters, and grams and kilograms. 9. ▲Solve real-world problems by applying appropriate measures for a. Length to the nearest inch or centimeter. b. Weight to the nearest whole unit e.g. if you bought 200 bricks that weighed 5 lbs. each, how much total weight? c. Months in a year and minutes in an hour. d. Perimeter of squares, rectangles, and triangles. e. Area of squares and rectangles. 10. ◊Recognize, draw, and describe right, obtuse, and acute angles. 11. ◊Convert within the metric system. 12. ◊Know and use perimeter and area formulas for squares and rectangles. 13. ◊Recognize and perform through two transformations on a two-dimensional figure. Standard 4: Data The student will: 1. Understand that God gave us a gift to interpret data. 2. Interpret and use data to make reasonable inferences, predictions, and decisions from these data displays: a. Graphs using concrete objects, b. Pictographs, c. Frequency tables, d. Bar and line graphs, - use Church attendance and donations to make predictions e. Venn diagrams and other pictorial displays, f. Line plots, g. Charts and tables, h. Circle graphs. 3. ▲Identify, explain, and calculate or find these statistical measures of a whole number data set of up to twenty whole number data points from 0 through 1,000 a. Minimum and maximum values, b. Range, c. Mode (no-, bi-, uni-), d. Median (including answers expressed as a decimal or a fraction without reducing to simplest form), e. Mean (including answers expressed as a decimal or a fraction without reducing to simplest form). 4. Recognize and explain the difference between exact and approximate answers. 5. ◊List all possible outcomes of a simple event in an experiment or simulation in an organized manner including the use of concrete objects. 6. ◊Represent the probability of a simple event in an experiment or simulation using fractions. ◊ Essential prerequisite skill ▲Assessed math indicator for KSDE