HBS Lessons 2-7 Study Guide Mrs. Sheldon 1. Describe how food
advertisement

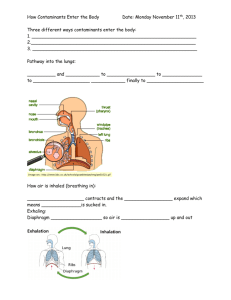
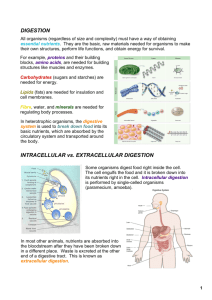
HBS Lessons 2-7 Study Guide Mrs. Sheldon 1. Describe how food moves through the digestive tract. * peristalsis, mucus, mechanical digestion (teeth, tongue..), chemical digestion (enzymes- amylase, gastric juice, .....), sphincters 2. List the steps involved in performing chemical test for sugar and starch. Sugar - include # drops of Benedict's solution, hot pot, color change- yellow, orange, red, and green are positive results Starch- include # drops of Lugosi solution, color change- which color means positive black or dark purple means positive 3. List at least four food sources for proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. * answers can be found in nutrients article on pages 20-23 in textbook 4. Explain why the body needs proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. answers can be found in nutrients read on pages 20-23 in textbook 5. State the function of digestive enzymes. * breakdown specific nutrients, they act on only one type of nutrient 6. How does the mouth get food into a form that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the cells to maintain life? * the teeth tear and grind food into smaller pieces * tongue helps mix and move food * three pairs of salivary glands release saliva, this moistens and softens food and prepares for swallowing * amylase, enzyme in saliva, begins the chemical digestion of starch to simple sugar * when size and consistency of bolus are comfortable, it may be swallowed Mechanical digestion - helps prepare food for chemical digestion * teeth (different types and job of each), tongue, bolus - breakdown food into smaller pieces Chemical digestion- Breaks down the chemical bonds in nutrients and changes them into simple forms to be absorbed *enzyme, amylase breaks down starch 7. Name the digestive enzymes in the mouth and the stomach and explain their specific function. Mouth- Saliva contains salivary amylase- begins chemical digestion of starch Stomach- pepsin- enzyme which breakdown protein, needs the acid environment created by HCL, gastric juice( pepsin and HCl ) both needed for digestion to happen in stomach 8. How does the stomach get food into a form that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the cells to maintain life? Peristalsis- moves food through, 3 layers of muscles churn in different directions Gastric juice( pepsin and HCl ) works together to break down proteins Chyme- a pulpy, paste, mixture of food and gastric juice 9. Explain the function of mucus. * lines stomach wall which protects stomach from gastric juice, if not enough mucus can develop ulcers in stomach lining * help move food through digestive tract 10. Define and give examples of diffusion and indicate why it is also called passive transport. Examples: balloon & anise, tea bags in water, red food coloring in vase... Diffusion- no energy from the cell needed to make it happen, so it is a passive action, molecules move across a membrane from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration 11. Explain the difference between active and passive transport and indicate the importance of both processes in absorption. Active transport- materials are passed across a membrane using energy from the cell Passive transport- no energy needed to cross membrane Absorption- the process of digested nutrients pass through the wall of the small intestine into the bloodstream, not all digested nutrients or membranes are the same size so both active and passive transport are needed to get all nutrients across to be absorbed. 12. How does the small intestine get food into a form that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the cells to maintain life? Chemical digestion- chemical change with help from the pancreas, liver and gallbladder Pancreatic juice breaks down proteins, carbs and fats Liver makes bile which breaks down fats, the bile is stored in the gallbladder until needed. 13. Indicate why the small intestine needs an extensive internal surface area. * amount of nutrients passed into bloodstream and then absorbed depends on amount of surface area available in the small intestine(SI) * for increased surface area SI has 4 features- length, folds in wall, villi ( finger like projections), microvilli (tiny folds in the surface of the individual cells of intestine) * the more surface area, the more absorption 14. Explain the functions of the large intestine. Water, vitamins and minerals are absorbed Undigested food is temporarily stored before it moves to the rectum 15. List in order the organs of the digestive tract, beginning with the mouth. Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum 16. Explain how the digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems help on another do their jobs. Respiratory system- gets oxygen to be used by body Digestive system- breaks down nutrients to be absorbed by body Circulatory system- carries oxygen and nutrients to all cells of the body