Fall 05 exam
advertisement
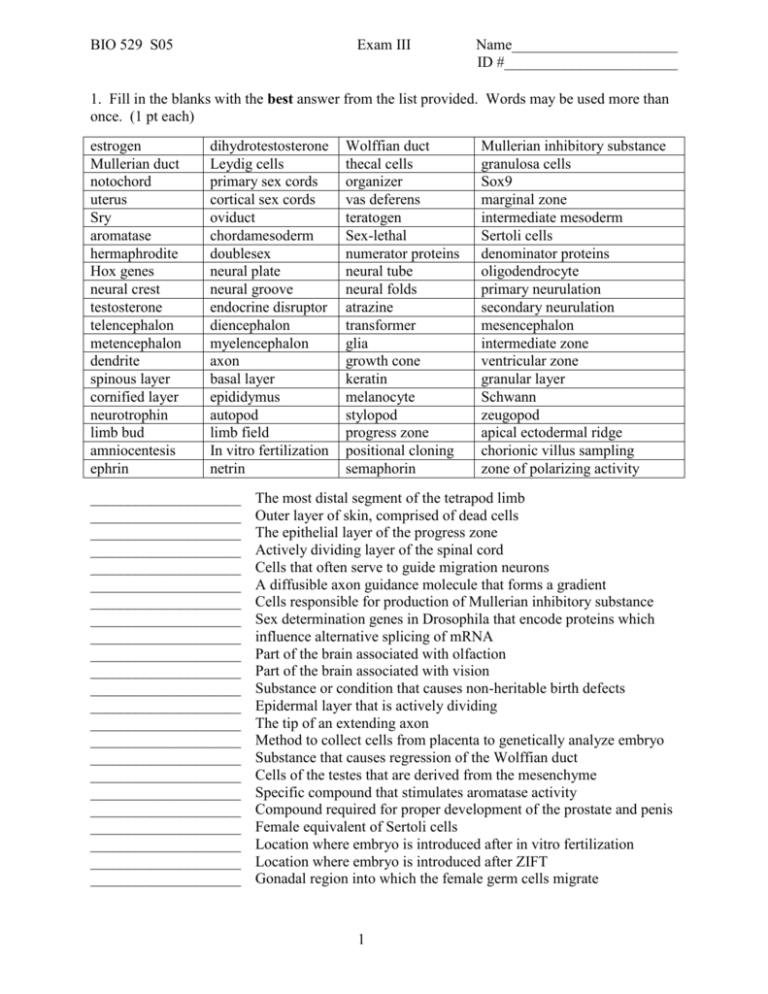
BIO 529 S05 Exam III Name______________________ ID #_______________________ 1. Fill in the blanks with the best answer from the list provided. Words may be used more than once. (1 pt each) estrogen Mullerian duct notochord uterus Sry aromatase hermaphrodite Hox genes neural crest testosterone telencephalon metencephalon dendrite spinous layer cornified layer neurotrophin limb bud amniocentesis ephrin dihydrotestosterone Leydig cells primary sex cords cortical sex cords oviduct chordamesoderm doublesex neural plate neural groove endocrine disruptor diencephalon myelencephalon axon basal layer epididymus autopod limb field In vitro fertilization netrin ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ Wolffian duct thecal cells organizer vas deferens teratogen Sex-lethal numerator proteins neural tube neural folds atrazine transformer glia growth cone keratin melanocyte stylopod progress zone positional cloning semaphorin Mullerian inhibitory substance granulosa cells Sox9 marginal zone intermediate mesoderm Sertoli cells denominator proteins oligodendrocyte primary neurulation secondary neurulation mesencephalon intermediate zone ventricular zone granular layer Schwann zeugopod apical ectodermal ridge chorionic villus sampling zone of polarizing activity The most distal segment of the tetrapod limb Outer layer of skin, comprised of dead cells The epithelial layer of the progress zone Actively dividing layer of the spinal cord Cells that often serve to guide migration neurons A diffusible axon guidance molecule that forms a gradient Cells responsible for production of Mullerian inhibitory substance Sex determination genes in Drosophila that encode proteins which influence alternative splicing of mRNA Part of the brain associated with olfaction Part of the brain associated with vision Substance or condition that causes non-heritable birth defects Epidermal layer that is actively dividing The tip of an extending axon Method to collect cells from placenta to genetically analyze embryo Substance that causes regression of the Wolffian duct Cells of the testes that are derived from the mesenchyme Specific compound that stimulates aromatase activity Compound required for proper development of the prostate and penis Female equivalent of Sertoli cells Location where embryo is introduced after in vitro fertilization Location where embryo is introduced after ZIFT Gonadal region into which the female germ cells migrate 1 BIO 529 S05 Exam III Name______________________ ID #_______________________ For all remaining questions, you must show your work or explain your reasoning to receive any partial credit. 2a. Name two different types of viruses that have been utilized for human gene therapy trials. (3 pts) b. Explain at least two problems that have been encountered using these viral vectors. (4 pts) 3a. Label each layer or structure indicated by a box in the diagram of epidermis below. (8 pts) b. What cell type would you find directly under the basal lamina? (2 pts) 2 BIO 529 S05 Exam III Name______________________ ID #_______________________ 4a. Name the two actively dividing layers of neuronal stem cells in the cerebellum. (3 pts) b. What is the signaling molecule that maintains the outer proliferative layer of the cerebellum and what cell layer produces that molecule? (4 pts) 5. Name the four populations of neural crest cells and one tissue that comes from each (8 pts) 6. Based on your knowledge of sex determination in flies and mammals, fill in the table below to indicate the expected outward sexual appearance (phenotype) for each situation indicated. Phenotypes you may choose are: male, female, or intersex. (15 pts) Genotype XY with constitutively activated Sex lethal gene XXY human XXY fly XXY fly triploid for all autosomes XXY with deletion of Sry gene XXY with normal Sry gene XX with homozygous deletion of transformer gene XY fly with deletion of several numerator genes XY fly with deletion of several denominator genes XX with homozygous deletion of androgen receptor XY with homozygous deletion of androgen receptor XX with constitutively active FGF9 gene XX with duplication of Sox9 gene XX with homozygous deletion of Sox9 gene XY with homozygous deletion of Sf1 gene 3 Phenotype BIO 529 S05 Exam III Name______________________ ID #_______________________ 7a. In the assigned reading from Riddle et al. (Cell paper from 1993), the authors used misexpression of Shh to suggest that it could be the molecule responsible for the properties of the ZPA. This was most clearly demonstrated by the implantation of cells expressing Shh into the developing limb. Where in the limb were the cells implanted and what was the outcome of the experiment? (4 pts) b. Based on the results described above and the model presented by the authors, what would have been the expected result from loss of Shh in the developing limb? (2 pts) c. In the second assigned reading (Litingtung et al., from Nature 2002), the actual results of the loss of Shh in the limb were reported. What was the phenotype? (2 pts) d. In the Nature paper, they also looked at loss of the Ci homologue, Gli3. What was the expected phenotype of loss of Gli3 in the developing limb? What was the actual phenotype? How are these results explained? (6 pts) 4 BIO 529 S05 Exam III Name______________________ ID #_______________________ 8. Based on your knowledge of tissue interactions during limb development, predict the outcome of the following surgical experiments in chick embryos. For each, be sure to indicate all limb segments that would be produced, whether each is wing or leg, and indicate any altered polarities of the tissue. (14 pts) a. The mesoderm underlying the early wing bud is transplanted to replace the mesoderm of the leg bud after production of the stylopod. b. The ectoderm of the early wing bud is transplanted to replace the ectoderm of the leg bud after production of the stylopod. c. The tissue at the posterior of the early wing bud is removed and replaced with tissue from the anterior of a different early wing bud. d. The tissue at the anterior of the early wing bud is removed and replaced with tissue from the posterior of a different early wing bud. e. The mesoderm and ectoderm at the tip of a wing bud after production of the zeugopod is transplanted to replace the mesoderm and ectoderm at the tip of a leg bud after production of the stylopod. f. The ectoderm tip of a wing bud after production of the zeugopod is added to the tip of a leg bud after production of the stylopod. g. The mesooderm underlying the wing bud is removed after production of the stylopod and replaced with mesoderm from a leg bud after production of the zeugopod. 5 BIO 529 S05 Exam III Name______________________ ID #_______________________ 9. Explain how the X:A ratio in Drosophila leads to the differential activation of a target gene that will distinguish male from female. Be sure to include a description of the molecular “measurement” of X:A ratio, how this molecularly initiates sex determination, the identity of the target of X:A ratio regulation, and how that gene then distinguishes male from female. If in doubt, provide more information rather than less. (10 pts) 6