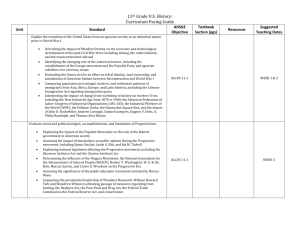
testing and grading procedures
advertisement
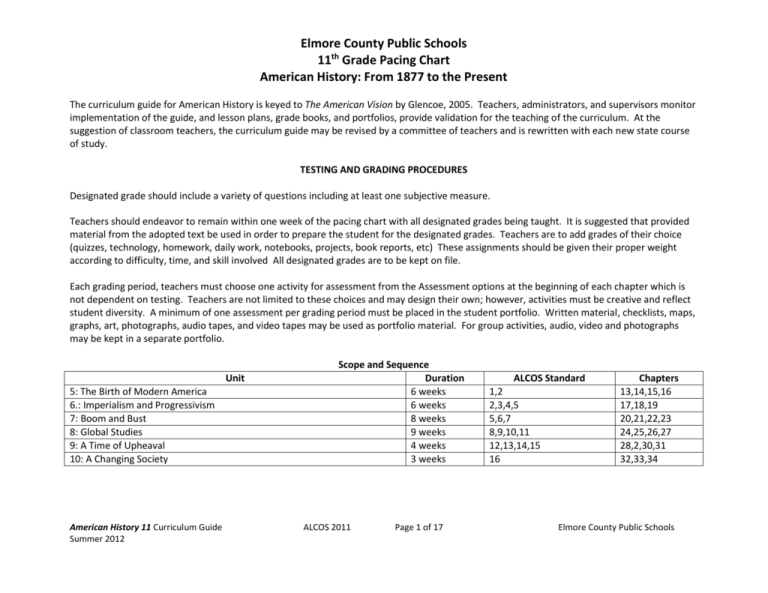
Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present The curriculum guide for American History is keyed to The American Vision by Glencoe, 2005. Teachers, administrators, and supervisors monitor implementation of the guide, and lesson plans, grade books, and portfolios, provide validation for the teaching of the curriculum. At the suggestion of classroom teachers, the curriculum guide may be revised by a committee of teachers and is rewritten with each new state course of study. TESTING AND GRADING PROCEDURES Designated grade should include a variety of questions including at least one subjective measure. Teachers should endeavor to remain within one week of the pacing chart with all designated grades being taught. It is suggested that provided material from the adopted text be used in order to prepare the student for the designated grades. Teachers are to add grades of their choice (quizzes, technology, homework, daily work, notebooks, projects, book reports, etc) These assignments should be given their proper weight according to difficulty, time, and skill involved All designated grades are to be kept on file. Each grading period, teachers must choose one activity for assessment from the Assessment options at the beginning of each chapter which is not dependent on testing. Teachers are not limited to these choices and may design their own; however, activities must be creative and reflect student diversity. A minimum of one assessment per grading period must be placed in the student portfolio. Written material, checklists, maps, graphs, art, photographs, audio tapes, and video tapes may be used as portfolio material. For group activities, audio, video and photographs may be kept in a separate portfolio. Unit 5: The Birth of Modern America 6.: Imperialism and Progressivism 7: Boom and Bust 8: Global Studies 9: A Time of Upheaval 10: A Changing Society American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 Scope and Sequence Duration 6 weeks 6 weeks 8 weeks 9 weeks 4 weeks 3 weeks ALCOS 2011 Page 1 of 17 ALCOS Standard 1,2 2,3,4,5 5,6,7 8,9,10,11 12,13,14,15 16 Chapters 13,14,15,16 17,18,19 20,21,22,23 24,25,26,27 28,2,30,31 32,33,34 Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present What Chapter to Cover Based on the 9 Week System. Pre and Post Tests are determined by these standards. 1st Nine Weeks Settling the West Industrialization Urban America Politics and Reform Becoming a World Power The Progressive Movement Chapters 13,14,15,16,17,18 2nd 9 Weeks World War I The Jazz Age Normalcy and Good Times The Great Depression and the New Deal Roosevelt and the New Deal Chapters 19,20,21,22,23 3rd 9 Weeks A World in Flames America & WWII The Cold War Begins Postwar America Chapters 24,25,26,27,28,29.30,31 4th 9 Weeks The New Frontier and the Great Society The Civil Rights Movement The Vietnam War The Politics of Protest Politics and Economics Resurgences of Conservatism Into a New Century Chapters 32,33,34 American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 2 of 17 Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present Unit 5- The Birth of Modern America (Chapters. 13,14,15,16) - approx. 6 weeks Standard-Based Questions: -How did Manifest Destiny impact the American West in terms of mining, the cattle industry, and the transcontinental railroad. - Discuss how the lives of American farmers were changed by the Grange and eventually the Populist movement. -How were the lives of American Indians changed because of the Dawes Act? -How did the patterns of immigration change during the Industrial Age? -Trace the development of and the successes and failures of the union movement. Standard-Based Conceptual Terms: (Don’t just know the meaning, but describe how that term fits into this era in American History) Agrarian, nomadic, assimilation, quota Unit 6: Imperialism and Progressivism (Chapters 17,18,19) -- approx. 6 weeks Standard Based Questions: - What were the causes of the Spanish American War? - What role did Theodore Roosevelt play in the Spanish American War? - Discuss the consequences of the Spanish American War. - How did the United States imperialize Hawaii? - What contributions did Alabamians make to the United States between Reconstruction and WWI? - How did the Progressive movement impact public opinion and politics? - Analyze how African Americans and other minorities affected the Progressive Era. - How did Horace Mann’s philosophies affect America’s education system? - Compare the presidencies of presidents Theodore Roosevelt, William Howard Taft and Woodrow Wilson. - What is the significance of late 19th century foreign policy, such as Open Door policy, Dollar Diplomacy, Big Stick Diplomacy, and Moral Diplomacy? - What are the underlying or long range causes of World War I? - What are the components of the Treaty of Versailles? How was the Treaty of Versailles received by Americans? - How did the geography of Europe and the Middle East change after WWI? Standard-Based Conceptual Terms: (Don’t just know the meaning, but describe how that term fits into this era in American History) Imperialism, progressivism, diplomacy, militarism, nationalism American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 3 of 17 Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present Unit 7: Boom and Bust (Chapters 20,21,22,23) -- approx. 8 weeks Standard Based Questions: -What type of mass media was used in the 1920s? - Who are some of the major writers and works of the post WWI era? -What did people do with all of their leisure time of the 1920s? -How did the following terms affect the pre Great Depression economy: overproduction, stock market speculation, &restrictive monetary policy? -How did the Hawley -Smoot Tariff Act impact the world wide depression? -How did the Great Depression impact the American family? - What are the three R’s of the New Deal? What are some specific New Deal programs? -What effect did the Dust Bowl have on patterns of migration during the Great Depression? Standard-Based Conceptual Terms: (Don’t just know the meaning, but describe how that term fits into this era in American History) Mass media, overproduction, speculation Unit 8 – The Global Struggle (Chapters 24,25,26,27) -- approx. 9 weeks Standard Based Questions: -What impact did fascism, Nazism, and communism have on the conflicts in Europe leading up to WWII? -Why did many Americans favor isolationism in the years leading up to WWII? -Who were the major WWII leaders and why were they significant? -What is appeasement? Why did it not work ? -Where are the major battles of WWII located on a map? - What were the military strategies of WWII? -Why did the United States use the atom bomb? What were the results? -What war crimes took place during WWII? What were the consequences of the war crimes? -How did WWII change the lives of women, minorities, and other social aspects of American life? -How did Alabama contribute to WWII? -What were the major Cold War policies and issues? -Where were there areas of conflict during the Cold War from 1945 to 1960? Standard-Based Conceptual Terms: (Don’t just know the meaning, but describe how that term fits into this era in American History) Fascism, Nazism, communism, isolationism, appeasement, containment, domino theory American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 4 of 17 Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present Unit 9: A Time of Upheaval (Chapters 28, 29,30 & 31)-- approx. 4 weeks Standard Based Questions: -What were the major initiatives of both the Kennedy and Johnson administrations? -What role did Alabama play in the space race program? -What are the major foreign events and issues of the Kennedy administration? -Where are the major Vietnam battle sites? -How did Alabama (both events & people) contribute to the Civil Rights movement? -Who were some of the major people and organizations associated with the Civil Rights movement? -Who were some of the major people and events involved in the Black Power movement? -What economic impact did African American entrepreneurs have on the modern Civil Rights Movement? Standard-Based Conceptual Terms: (Don’t just know the meaning, but describe how that term fits into this era in American History) Due process, credibility gap, destabilization, Vietnamization Unit 10: A Changing Society (Chapters 32,33 & 34)-- approx. 3 weeks Standard Based Questions: -What were the aspects of Nixon’s policy of détente? -What were the major aspects of the Reagan administration? -What were the major aspects of the George H.W. Bush administration? -What were the major aspects of the Clinton administration? -What were the major aspects of the George W. Bush administration? Standard-Based Conceptual Terms: (Don’t just know the meaning, but describe how that term fits into this era in American History) détente, conservatism, Reaganomics American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 5 of 17 Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present Quarter Unit/Chapter Theme Alabama COS Standards & Objectives Resources 1 American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 6 of 17 Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present 2. Evaluate social and political origins, accomplishments, and limitations of Progressivism. 1 Unit 5 & 6 Explaining the impact of the Populist Movement on the role of the federal government in American society Assessing the impact of muckrakers on public opinion during the Progressive movement, including Upton Sinclair, Jacob A. Riis, and Ida M. Tarbell Explaining national legislation affecting the Progressive movement, including the Sherman Antitrust Act and the Clayton Antitrust Act Determining the influence of the Niagara Movement, the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP), Booker T. Washington, W. E. B. Du Bois, Marcus Garvey, and Carter G. Woodson on the Progressive Era Assessing the significance of the public education movement initiated by Horace Mann Comparing the presidential leadership of Theodore Roosevelt, William Howard Taft, and Woodrow Wilson in obtaining passage of measures regarding trustbusting, the Hepburn Act, the Pure Food and Drug Act, the Federal Trade Commission, the Federal Reserve Act, and conservation The DBQ Project: Progressivism: Where will you put your million dollars? Active Classroom: Backwards Planning PPT: Progressivism and the Age of Reform Active Classroom: How the other half worked and lived – US Readers Active Classroom: Tenement Reform: Analyzing Visual sources Active Classroom: The Jungle: Document Based Activities American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 7 of 17 Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present 3. Explain the United States’ changing role in the early twentieth century as a world power. 1 Unit 5 & 6 Active Classroom: Election of 1912: Decision Making Describing causes of the Spanish-American War, including yellow journalism, the sinking of the Battleship USS Maine, and economic interests in Cuba Identifying the role of the Rough Riders on the iconic status of President Theodore Roosevelt Describing consequences of the Spanish-American War, including the Treaty of Paris of 1898, insurgency in the Philippines, and territorial expansion in the Pacific and Caribbean Analyzing the involvement of the United States in the Hawaiian Islands for economic and imperialistic interests Appraising Alabama’s contributions to the United States between Reconstruction and World War I, including those of William Crawford Gorgas, Joseph Wheeler, and John Tyler Morgan Evaluating the role of the Open Door policy and the Roosevelt Corollary on America’s expanding economic and geographic interests Comparing the executive leadership represented by William Howard Taft’s Dollar Diplomacy, Theodore Roosevelt’s Big Stick Diplomacy, and Woodrow Wilson’s Moral Diplomacy American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 8 of 17 Active Classroom: Progressivism Goes National: History Unfolding Active Classroom: The Election of 1912: Analyzing Visual sources Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present Quarter 2 Unit/Chapter Theme Units 6 & 7 Alabama COS Standards & Objectives Resources 4. Describe causes, events, and the impact of military involvement of the United States in World War I, including mobilization and economic and political changes. Identifying the role of militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism in World War I Explaining controversies over the Treaty of Versailles of 1919, Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points, and the League of Nations Explaining how the Treaty of Versailles led to worsening economic and political conditions in Europe, which provided opportunities for the rise of fascist states in Germany, Italy, and Spain Comparing short- and long-term effects of changing boundaries in pre- and postWorld War I in Europe and the Middle East, leading to the creation of new countries American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 9 of 17 Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present 2 Unit 6 & 7 5. Evaluate the impact of social changes and the influence of key figures in the United States from World War I through the 1920s, including Prohibition, the passage of the Nineteenth Amendment, the Scopes Trial, limits on immigration, Ku Klux Klan activities, the Red Scare, Susan B. Anthony, Margaret Sanger, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, the Harlem Renaissance, the Great Migration, W. C. Handy, the Jazz Age, and Zelda Fitzgerald. Analyzing radio, movies, newspapers, and popular magazines for their impact on the creation of mass culture Analyzing works of major American artists and writers, including F. Scott Fitzgerald, Ernest Hemingway, Langston Hughes, and H. L. Mencken, to characterize the era of the 1920s Determining the relationship between technological innovations and the creation of increased leisure time 6. Describe social and economic conditions from the 1920s through the Great Depression regarding factors leading to a deepening crisis, including the collapse of the farming economy and the stock market crash of 1929. Assessing effects of overproduction, stock market speculation, and restrictive monetary policies on the pending economic crisis Describing the impact of the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act on the global economy and the resulting worldwide depression Identifying notable authors of the 1920s, including John Steinbeck, William Faulkner, and Zora Neale Hurston Analyzing the Great Depression for its impact on the American family American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 10 of 17 Active Classroom: Backward Planning PPT: The 1920s Overview Active Classroom: The First Red Scare: Debating the documents Active Classroom: Prohibition, A Gangster’s Paradise: Debating the documents Active Classroom: The Harlem Renaissance: History Unfolding Active Classroom: The Ku Klux Klan: Debating the documents Active Classroom: What caused the Great Depression: US History Readers Active Classroom: Great Depression: 1929-1939:Digital Atlas Lessons Active Classroom: Hard Times: History Unfolding The DBQ: What Caused the Great Depression? Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present Unit 6 & 7 2 7. Explain strengths and weaknesses of the New Deal in managing problems of the Great Depression through relief, recovery, and reform programs, including the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), the Works Progress Administration (WPA), the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), and the Social Security Act. Analyzing conditions created by the Dust Bowl for their impact on migration patterns during the Great Depression American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 11 of 17 Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present Quarter Unit/Chapter Theme Unit 8 3 Alabama COS Standards & Objectives Resources 8. Summarize events leading to World War II, including the militarization of the Rhineland, Germany’s seizure of Austria and Czechoslovakia, Japan’s invasion of China, and the Rape of Nanjing. The DBQ Project: Why Did Japan Analyzing the impact of fascism, Nazism, and communism on growing conflicts in Europe Explaining the isolationist debate as it evolved from the 1920s to the bombing of Pearl Harbor and the subsequent change in United States’ foreign policy Identifying roles of significant World War II leaders Examples: Franklin D. Roosevelt, Harry S. Truman, Dwight D. Eisenhower, George S. Patton, Sir Winston Churchill, Bernard Montgomery, Joseph Stalin, Benito Mussolini, Emperor Hirohito, Hedeki Tōjō, Erwin Rommel, Adolf Hitler Evaluating the impact of the Munich Pact and the failed British policy of appeasement resulting in the invasion of Poland American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 12 of 17 Bomb Pearl Harbor? The DBQ Project: The Geography of the Cold War: What Was Containment? Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present 3 Unit 8 9. Describe the significance of major battles, events, and consequences of World War II campaigns, including North Africa, Midway, Normandy, Okinawa, the Battle of the Bulge, Iwo Jima, and Yalta and Potsdam Conferences. Active Classrooms “War in Europe” US History Readers Locating on a map or globe the major battles of World War II and the extent of the Allied and Axis territorial expansion Describing military strategies of World War II, including blitzkrieg, islandhopping, and amphibious landings Explaining reasons for and results of dropping atomic bombs on Japan Explaining events and consequences of war crimes committed during World War II, including the Holocaust, the Bataan Death March, the Nuremberg Trials, the post-war Universal Declaration of Human Rights, and the Genocide Convention 10. Describe the impact of World War II on the lives of American citizens, including wartime economic measures, population shifts, growth in the middle class, growth of industrialization, advancements in science and technology, increased wealth in the African American community, racial and ethnic tensions, the G. I. Bill of Rights of 1944, and desegregation of the military. Active Classroom: The Long Road to D-Day: History Unfolding Active Classroom: The War in the Pacific: History Unfolding Active Classroom: Pulling together: Mobilizing the Population: History Unfolding Describing Alabama’s participation in World War II, including the role of the Tuskegee Airmen, the Aliceville Prisoner of War (POW) camp, growth of the Port of Mobile, production of Birmingham steel, and the establishment of military bases American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 13 of 17 Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present 3 Unit 8 11. Describe the international role of the United States from 1945 through 1960 relative to the Truman Doctrine, the Marshall Plan, the Berlin Blockade, and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Active Classroom: The Balance of Power after WWII, 1949-1955:Digital Atlas lesson plans Describing Cold War policies and issues, the domino theory, McCarthyism, and their consequences, including the institution of loyalty oaths under Harry S. Truman, the Alger Hiss case, the House Un-American Activities Committee, and the execution of Julius and Ethel Rosenberg Locating areas of conflict during the Cold War from 1945 to 1960, including East and West Germany, Hungary, Poland, Cuba, Korea, and China American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 14 of 17 Active Classroom: The Korean Crisis: Decision Making Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present Quarter Unit/Chapter Theme Alabama COS Standards & Objectives Resources Active Classroom: Communism, guerillas and falling dominoes US History Readers 12. Describe major initiatives of the John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson Administrations. 4 Units 9 and 10 Describing Alabama’s role in the space program under the New Frontier Describing major foreign events and issues of the John F. Kennedy Administration, including construction of the Berlin Wall, the Bay of Pigs invasion, and the Cuban missile crisis 13. Trace the course of the involvement of the United States in Vietnam from the 1950s to 1975, including the Battle of Dien Bien Phu, the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, the Tet Offensive, destabilization of Laos, secret bombings of Cambodia, and the fall of Saigon. Locating on a map or globe the divisions of Vietnam, the Ho Chi Minh Trail, and major battle sites Describing the creation of North and South Vietnam American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 15 of 17 Active Classroom: Exit Ngo Dinh Dime/The Gulf of Tonkin Incident: US history readers Active Classroom: American Soldiers in Vietnam: analyzing visual sources Active Classroom: The Fall and Aftermath: history unfolding Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present 4 14. Trace events of the modern Civil Rights Movement from post-World War II to 1970 that resulted in social and economic changes, including the Montgomery Bus Boycott, the desegregation of Little Rock Central High School, the March on Washington, Freedom Rides, the Sixteenth Street Baptist Church bombing, and the Selma-to-Montgomery March. The DBQ Project: Martin Luther King and Malcolm X: Whose Philosophy Tracing the federal government’s involvement in the modern Civil Rights Movement, including the abolition of the poll tax, the nationalization of state militias, Brown versus Board of Education in 1954, the Civil Rights Acts of 1957 and 1964, and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 Explaining contributions of individuals and groups to the modern Civil Rights Movement, including Martin Luther King, Jr., James Meredith, Medgar Evers, Thurgood Marshall, the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC), the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC), the Congress of Racial Equality (CORE), the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP), and the civil rights foot soldiers Appraising contributions of persons and events in Alabama that influenced the modern Civil Rights Movement, including Rosa Parks, Autherine Lucy, John Patterson, George C. Wallace, Vivian Malone Jones, Fred Shuttlesworth, the Children’s March, and key local persons and events Describing the development of a Black Power movement, including the change in focus of the SNCC, the rise of Malcolm X, and Stokely Carmichael and the Black Panther movement Describing the economic impact of African-American entrepreneurs on the modern Civil Rights Movement, including S. B. Fuller and A. G. Gaston American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 16 of 17 Made the Most Sense for America in the 1960s? Active Classroom: A New Day Dawning: History Unfolding Active Classroom: The Civil Rights Act of 1964: Document Based Activities Active Classroom: Race: New opportunities, New challenges: History Unfolding Elmore County Public Schools Elmore County Public Schools 11th Grade Pacing Chart American History: From 1877 to the Present 15. Describe changing social and cultural conditions in the United States during the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s. The DBQ 16. Describe significant foreign and domestic issues of presidential administrations from Richard M. Nixon to the present. Was the Equal Examples: Nixon’s policy of détente; Cambodia; Watergate scandal; pardon of Nixon; Iranian hostage situation; Reaganomics; Libyan crisis; end of the Cold War; Persian Gulf War; impeachment trial of William ―Bill‖ Clinton; terrorist attack of September 11, 2001; Operation Iraqi Freedom; war in Afghanistan; election of the first African-American president, Barack Obama Project: Why Rights Amendment Defeated? Additional Resources: Nystrom US History Atlas with desk maps and class sets Video set: 10 Days that Unexpectedly Changed the World History Unfolding Primary Source Kits: African Americans, American Presidents, WWI, WWII, Great Depression, Elections, Vietnam & the Cold War Traveling Trunk: WWII era American History 11 Curriculum Guide Summer 2012 ALCOS 2011 Page 17 of 17 Elmore County Public Schools