Carbon Monoxide and Cyanide Poisoning On
advertisement

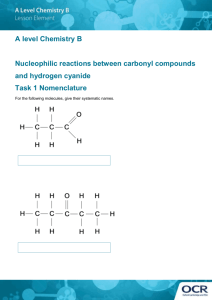
Aurora Health Care EMS Continuing Education 4th Quarter 2014 Quiz Name ___________________________________ Department ______________________________ E-mail address ____________________________ Please highlight or bold your answers and e-mail to david.fladten@aurora.org 1. The leading cause of poisoning in the United States is: a. cyanide from household chemicals. b. food products. c. prescription medicine. d. carbon monoxide (CO). 2. Sources of carbon monoxide include: a. furnaces and gas water heaters. b. structure fires and fireplaces. c. gas engines and automobiles. d. all of the above. 3. You will know when you are in an environment that contains CO because CO has a specific odor and taste. a. true b. false 4. CO poisoning can result in oxygen starvation, cardiac arrhythmias and alteration of judgment because: a. it prevents oxygen from binding to hemoglobin and being transported throughout the body. b. it prevents glucose from entering the cell. c. it allows oxygen to more easily be transported throughout the body, thereby inducing oxygen toxicity. d. it restricts the oxygen that is transported to the heart and brain only. 5. Patients who are complaining of a headache, nausea, dizziness and fatigue might have a SpCO of: a. 10 – 19%. b. 20 – 29%. c. 30 – 39%. d. greater than 60%. 6. CO poisoning is often unrecognized in a person, such as a firefighter because of: a. exhaustion. b. heat stress. c. injury or other illness. d. all of the above. 7. CO poisoning should be treated with 100% oxygen because: a. it decreases the half-life of CO already present in the blood. b. it increases the amount of oxygen that is being delivered. c. it reduces the half-life of CO in the blood by as much as 75%. d. all of the above. 8. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment is important for treating CO poisoning because: a. it reduces the half-life of CO in the blood to 20 - 24 minutes. b. it reduces the half-life of CO in the blood to 5 – 10 minutes. c. we would not survive without it. d. none of the above. 9. You are treating a pregnant female who was in a house during a house fire. You have applied a CO monitor to her and have obtained a reading of 15%. She is complaining of a slight headache but is refusing to go to the hospital. You attempt to talk her into going to the hospital because: a. she has a headache. b. you know that her unborn fetus might have a CO level that is less than hers. c. you know that her unborn fetus might have a CO level that is 10 - 15% higher than hers. d. you should honor her wish and allow her to sign a release without discussing the potential harm to her unborn fetus. 10. Cyanide is a common ingredient in: a. paper. b. plastics. c. metal cleaners. d. all of the above. 11. Routes of administration of cyanide include: a. ingested only. b. inhaled only. c. ingested, inhaled or absorbed. d. absorbed only. 12. The effects of cyanide will be seen more rapidly if: a. the cyanide was swallowed. b. the cyanide was absorbed through the skin. c. the cyanide was inhaled. d. the effects appear at the same rate regardless of how it entered the body. 13. Cyanide works by: a. preventing oxygen from attaching to red blood cells and being transported throughout the body. b. preventing glucose from entering the cell. c. allowing oxygen to more easily be transported throughout the body, thereby inducing oxygen overdose. d. restricting the oxygen that is transported to the heart and brain only. 14. Signs and symptoms of cyanide poisoning include: a. tachypnea, restlessness and dizziness. b. weakness, headache, eye irritation. c. tachycardia, bradycardia, apnea, seizures. d. all of the above. 15. Pre-hospital field treatment for cyanide poisoning includes: a. removing patient from area/source of contamination. b. rinsing affected external body parts with sterile water. c. DO NOT induce vomiting if cyanide has been swallowed. d. all of the above.