Plant Pigment Lab - Blue Valley Schools

PLANT PIGMENTS CHROMATOGRAPHY
LABORATORY EXERCISE
Name: _________________________
Background
In order for plants to absorb the sunlight energy responsible for the creation of carbohydrates, they require specialized proteins called pigments. Pigments have evolved to absorb and reflect particular wavelengths of the visible light spectrum.
In the following exercise, you will learn to segregate the many pigments found in a common plant, and come to learn about their specific function in the plant.
Objective
1. You should be able to identify, and compare and contrast the absorbance of major pigments found in common plants, as well as describe their function in plants.
Materials
Spinach Leaves
Mortar & Pestle
Thin Tip Dropper
Test Tube Rack
Cork
Chromatography Paper
Chromatography Solvent
Test Tube
Paper Clip
Pencil
Scissors
Procedure
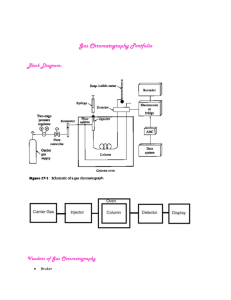
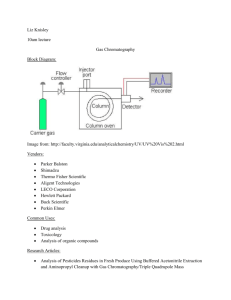
1. Organize yourself in a group of three. One member of the group should acquire a test tube rack, test tube, cork, paper clip, and piece of chromatography paper. Prepare the chromatography apparatus a shown in the figure below.
2. After the chromatography paper is cut to the appropriate width and length to fit in the test tube and has had a tip cut into one end, carefully spot the prepared spinach pigment onto the chromatography paper using the thin tipped dropper provided. Make sure that you apply the pigment a centimeter or so above the tip of the paper (read the next step for the reason).
3. When your apparatus is ready and the chromatography paper has been spotted with spinach pigments, acquire some of the chromatography solvent from the community jar using the dropper provided. It is important that the level of the solvent reach above the tip of the chromatography paper but should not touch the spot of spinach pigments.
4. Immediately after the solvent is placed into the test tube place the chromatography paper, paper clip, cork apparatus into the test tube and carefully sit it in the test tube rack.
5. Let the chromatography setup sit until the solvent front reaches about a centimeter distance from the top of the chromatography paper. Then, remove the chromatography paper and let it air dry. Sketch the results in your question 6 and staple the results to one persons answer sheet in your group.
6. Return all the materials to their appropriate place and answer the remaining questions.
Questions
Read section 8.2 pages 163-165.
1. Electromagnetic energy comes in a variety of forms. Fill out the following table based on information in your textbook.
Electromagnetic
Energy
Gamma Rays
Range of
Wavelengths x-Rays
Ultraviolet Rays
Violet Light
Indigo Light
Blue Light
Green Light
Yellow Light
Orange Light
Red Light
Infrared
Microwaves
Radio Waves
2. Sketch both violet and red wavelengths of light making sure to represent the difference between them. Label each wavelength with their color as well as the level of energy associated with each (high or low).
3. What are pigments?
4. Identify and describe the three things that can happen to light that shines on a pigment.
5. Given the absorbance spectrum for a variety of common plant pigments below: a. identify the colors that chlorophyll a absorbs the best. b. identify the colors that chlorophyll b absorbs the best c. identify the colors that the carotenoids absorb the best
d. Why do the pigments chlorophyll a and b appear green in color? e. Based on the lower graph, which colors result in the highest rate of photosynthesis?
6. Sketch the results of your paper chromatography and use your book to label pigments that you have segregated.