BEng Software Engineering
advertisement

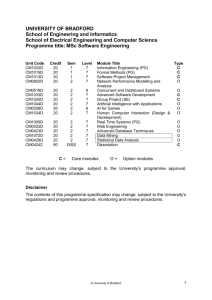
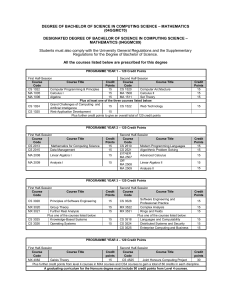
UNIVERSITY OF BRADFORD School of Computing Informatics and Media Department of Computing Programme/course title: Software Engineering Awarding and teaching institution University of Bradford Final award: BEng (Honours) [Framework for Higher Education Qualifications level H] Programme title: Software Engineering Programme accredited by: British Computer Society Duration: BEng: 3 years full time; 4 years sandwich; 6 years part-time UCAS code: G601 BEng/SE (3-year) G602 BEng/SE4 (4- year), Subject benchmark statement: Computing, Engineering Date produced: April 2003 Last updated: July 2011 Programme Aims Software Engineering is concerned with building computer systems that are error free and totally reliable, such as the safety critical systems in aircraft or industrial plant. The general principles of engineering are applied to the production of software that meets these stringent requirements. The early part of the course concentrates on the theoretical foundations of computation and computer technology. It incorporates ideas from many other disciplines, including mathematics, engineering, psychology and graphical design and has a close affinity with electronic communications as illustrated by the Internet and World Wide Web. The term ‘convergence’ is often used to describe how these two disciplines are coming together. Later the emphasis moves to the design and implementation of large software engineering projects. The aims of the course are to provide you with a sound grounding in the fundamentals of computer software development (programming) and the tools and applications used by software engineers, and to provide the skills needed to enable you to practice as a professional software engineer. These aims will be achieved by: Providing you with a core of fundamental modules, in stages 1 and 2 that are essential to all computer scientists, plus a wide range of options, particularly in the final stage, so that you may choose the particular area in which you are strong or wish to specialize, building on the knowledge and understanding gained earlier. Providing the support in the form of lectures, labs and tutorials that will enable you to develop your personal portfolio of skills. The School of Computing, Informatics and Media is committed to providing a very high standard of up-todate computing facilities to support the practical hardware and programming requirements of the courses. Developing discipline skills and personal transferable skills so that on graduation you may move directly into responsible positions in industry or commerce, or may pursue further programmes of study. Promoting educational opportunities for ethnic minorities, women, mature and alternatively qualified students, as well as for school-leavers and traditionally qualified students. 1 The BEng Software Engineering is offered by the Department of Computing, part of the School of Computing, Informatics and Media (SCIM) in the University of Bradford, which includes a large number of undergraduate and postgraduate courses concerned with the understanding, design, and exploitation of computation and computer technology. The Department places great emphasis on both teaching and research, and there are opportunities for you to join one of our research teams and progress on to postgraduate taught courses or research degrees on completion of your first degree. Note that the British Computer Society (BCS) for computing professionals, the route to further professional qualifications, accredits undergraduate and postgraduate courses offered by the Department. Its accreditation of our courses, including the BEng Software Engineering, also means that successful honours graduates are exempted from further examinations for BCS membership. Employment prospects for graduates of the BEng Software Engineering should be excellent. Our current BCS-accredited courses currently enjoy a 91% graduate employment rate, and we expect similar success for the BEng Software Engineering. Learning outcomes Learning outcomes indicate what you should know, understand and be able to do on successful completion of your course. Software Engineering is a subject where current practices in the field are changing rapidly as technologies evolve and new programming languages emerge. However the underlying theory and principles do not change rapidly. You will study these fundamentals and learn how to apply them to the analysis of problems and how to plan, implement and evaluate the solutions. You will learn about new technologies and languages required to implement solutions. In order to achieve the learning outcomes you will develop the following: Knowledge and Understanding: a systematic understanding of the fundamental concepts and theories of computer science including detailed knowledge of hardware, computer architecture, information and communication technologies; a firm grasp of the mathematical foundations of computing and how they underpin the formal specification and design of commercial applications; knowledge of the engineering principles associated with large software projects; an awareness of and concern for the need for software reliability, correctness and safety, such concern being the hallmark of a professional software engineer; ability to comment on aspects of current research in the discipline. Discipline Specific Skills including; how to analyse problems and develop solutions using leading edge ideas and techniques; how to develop computer programs using object oriented programming languages; how to choose which programming languages to use for specific applications; ability to manage and/or contribute to a team approach to software engineering projects; an ability to read and make use of research articles in journals and research literature; the ability to complete a major individual software engineering project; competence in the use of major software application packages. Personal and Transferable Skills: exercise of initiative in information management, interpretation and presentation; ability to make decisions in a variety of contexts; application of IT and communications skills to management problems; report writing and presentation skills; creative and systematic problem solving; teamwork and leadership; project management; and personal management. The Curriculum The map of your studies is detailed below showing core(C) and optional (O) modules. Each year, or stage, of an Honours course comprises two semesters with 60 credits being studied 2 in each semester. For 10 credit modules and 20 credit double modules (last character in module code is a ‘D’) all of the teaching and assessment is undertaken in the same semester. For 20 credit linked modules (last character in the module code is an ‘L’) and the 30 credit project there is teaching and assessment in both semesters. Although the University does not recruit directly to Ordinary degrees this route is available to students for whom a less intense course of study is appropriate. Ordinary degrees comprise 100 credits in stage 1 and 80 credits in stages 2 and 3. For entrants 2011/12 onwards placed on ORDINARY after level 1, in addition to meeting the requirements for Stage 1, students must study units amounting to 100 credits in stages 2 and 3 respectively. Diploma of Industrial Studies Diploma of International Studies You have the option to undertake an industrial placement, or of studying or working abroad for a year between stages 2 and 3; this option is strongly encouraged. SCIM has an industrial training tutor who has contacts with a large number of outside organizations and who assists in helping you find a placement. Successful completion of the industrial year qualifies you for the award of the Diploma of Industrial Studies in addition to your degree. The university’s International Office provides a wide range of opportunities and support for students to gain international experience. Successful completion of the international year qualifies you for the award of the Diploma of International Studies in addition to your degree. Both options provide the opportunity to gain valuable experience, and are viewed favourably by prospective employers. Unit Code Cr Se m L e v e l Module Title H o n s O rd Stage 1 CM0113L 20 CM0107L 20 CM0111L 20 CM0211M CM0116D CM0202M CM0117D 10 20 10 20 1, 2 1, 2 1, 2 1 1 2 2 1 Developing Professional Skills C 1 Computer Architecture and Systems Software C 1 Formal Foundations C 1 1 1 1 Introduction to Web Technologies Software Development (Part 1) Foundations of Human Computer Interaction Software Development (Part 2) C C C C 2 2 2 User Interface Development Database Systems Software Engineering with Group Project C C C 2 Data Structures and Algorithms C 2 Computer Communications and Networks C O 2 Information Systems Analysis and Design C O 2 2 Network Business/Distributed Information Management OR Computer Architecture and System Software 2 C C 3 Final Year Project C 3 3 3 W:Mobile Systems (after CM0315L and CM0414L) X: Information Systems (after CM0305L and CM0414L) Y: Internet Systems (after CM0315L and CM0414L) Z: Real Time Systems (after CM0315L and CM0415L) Information Engineering Formal Methods Decision Support Systems Stage 2 CM0312M CM0307M CM0304D 10 10 20 CM0316L 20 CM0315L 20 CM0305L 20 CM0414L OR CM0415L 20 20 1 1 2 1, 2 1, 2 1, 2 1, 2 1, 2 C C C Stage 3 CM0347K 40 1, 2 Honours and Ordinary CM0504D CM0332D CM0606D 20 20 20 1 1 1 3 W X Y Z C O O O O O C O CM0616D EM0359D CM0602D CM0615D CM0328D EM0361D CM0518D CM0348D CM0331D CM0506D CM0333D 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 M 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Deploying Web Technologies Design for Mobile Content Networks Performance Modelling and Analysis Advanced Database Systems AI for Games Multimedia Systems Concurrent and Distributed Systems Foundations of Cryptography Human Computer Interaction (Design and Development) Real Time Systems Web Engineering O C O O C O O O C O C C C O O O C O O C Please note that, while every effort will be made to accommodate your choices, it may not be possible to permit every possible combination of optional modules, due to timetabling constraints. The curriculum may change, subject to the University's course approval, monitoring and review procedures. Teaching, learning and assessment strategies You will experience a wide range of teaching and learning environments. Concepts, principles and theories are generally explored in formal lectures, practiced in associated tutorials and seminars, and demonstrated in laboratory classes. Practical skills are developed in laboratory sessions. Professional and personal skills are developed through the Developing Professional Skills module which involves communications skills, library skills, group work and presentations. The Software Engineering Group Project develops an appreciation of how to manage group dynamics in whilst working on a substantial software engineering exercise. Honours students undertake a major individual project in their final year, drawing together the knowledge and experience gained throughout the course. The project provides the opportunity for you to demonstrate your ability to solve problems using current ideas and techniques that are at the forefront of computing and information systems disciplines. Students who achieve an Ordinary degree may be given the opportunity to ‘top-up’ to a classified Honours degree at a later stage at which time they will undertake the individual project. Each 10-credit module on the course requires you to commit 100 hours of study. Some of these hours will be formally timetabled - lectures, laboratories, seminars and tutorials – and others will involve you in carrying out private study. The balance between these forms of study changes as you pass through the three years of the course. There are a lot of “contact hours” (time spent with tutors) in the earlier stages of the course; in the final year you will be expected to manage your own learning, under the general guidance of your tutors. Methods of assessment are similarly varied and your progress will be assessed using a mix of formal examinations, presentations and seminar papers, reports, laboratory tests, essays, coursework assignments, and projects. The appropriate method is chosen so that you may demonstrate the particular learning outcomes of each module. Admissions Criteria In addition to a degree, successful completion of the Honours degree course will give candidates a qualification that is recognized by the British Computer Society. Offers are made following detailed consideration of each individual application. Most important in the decision to offer a place is our assessment of a candidate’s potential to benefit from their studies and of their ability to succeed on this particular course. Entrance requirements will vary but are set after consideration of each applicant’s 4 academic background and achievements and all other relevant experience. A typical offer to someone seeking entry through the UCAS scheme would be CCC or 240 UCAS tariff points. Applications are welcome from candidates with non-standard qualifications or who, lacking academic qualifications, have significant relevant experience. Progression Criteria and Exit Points To pass and proceed from each stage to the next, and also to be eligible for a classified Honours award, you must achieve at least 40% in 100 credits and 35% in the other 20 credits. The class and division of the Honours degree that you are awarded is based on the overall weighted marks that you receive for each stage. Stage 2 contributes 30% and stage 3 70%. The classes and divisions of the Honours degree are awarded on the basis of the following minimum final overall weighted average marks: 70.0% or above: 60.0% or above: 50.0% or above: otherwise: First Class Honours Second Class Honours – First Division Second Class Honours – Second Division Third Class Honours If you complete Stage 1 successfully, you are eligible for a Certificate of Higher Education; if you complete stage 2 successfully, you are eligible for a Diploma of Higher Education. The learning outcomes for these awards and the final award are consistent with those of the national qualifications framework for England. The progression and award regulations for Ordinary courses are similar to those for the Honours courses except 40% must be achieved in 80 credits at Stage 1 and 60 credits at subsequent Stages. Regulations Summary Comprehensive information on the University’s Regulation Governing Undergraduate Awards is at http://www.brad.ac.uk/admin/acsec/QA_Hbk/Undergrad_Regs_.html Student Support Arrangements All students admitted to SCIM go through a process of induction that includes detailed talks by the Dean and Head of Department. Afterwards, ongoing support for students is provided in the form of one-stop facilities located at the SCIM Student Support Office (SSO) in Horton Building, open all day during term time, with limited daily opening hours during non-term time. Support for registered students also is provided 24/7 via the SCIM intranet. This includes the SSO website at http://www.inf.brad.ac.uk/internal/sso/ which contains the following information: SCIM Student Handbook SCIM Learning & Behaviour Agreement Course Timetable Examination timetable Answers to Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Coursework submission record E-mail Archives 5 The SCIM intranet also includes the Computing department website at http://www.inf.brad.ac.uk/internal/computing/ which offers further information to support students and includes the following: Student Staff Liaison Minutes Courses and modules Course Tutors contact information Equipment Loans Service The SCIM intranet includes the Technical Support website at http://ts.inf.brad.ac.uk/ which supports students by offering detailed information on all the technical and services offered by the School, including: Equipment Loans Service IT suites Hosting All students on the BEng Software Engineering are allocated a personal tutor who will provide both academic and pastoral support. There are also a number of named individuals within Computing who have specialist responsibilities, and are able to deal with specific issues relating to factors such as disability, equal opportunities and gender. The Staff Student Liaison Committee gives the opportunity for students to give formal feedback to the Course Tutor and/or Department about curricular issues and the general running of the programme. The School also uses the University’s Virtual Learning Environment (VLE) Blackboard to support students via their individual modules The University of Bradford provides important facilities such as extended access to library and computing services, counselling and welfare services, and careers advice. The Disability Office provided targeted support for all students with known disabilities and routinely arranges dyslexia assessments and appropriate support (i.e. reasonable adjustment) for disabled students. Further Information For further information, please check the University prospectus or contact Admissions. The Admissions Office The Recruitment and Marketing Office The University of Bradford School of Computing, Informatics and Media Richmond Road The University of Bradford Bradford, BD7 1DP Horton Building UK Richmond Road Bradford, BD7 1DP UK +44 (0)1274 233054 +44 (0)1274 235963 http://www.brad.ac.uk/courses/ ugadmissions@scim.brad.ac.uk http://scim.brad.ac.uk/courses/ug/ Disclaimer The details of this Programme Specification and information contained therein are subject to change in accordance with the University of Bradford’s course approval, monitoring and review procedures. 6 7