香港仔浸信會呂明才書院
advertisement
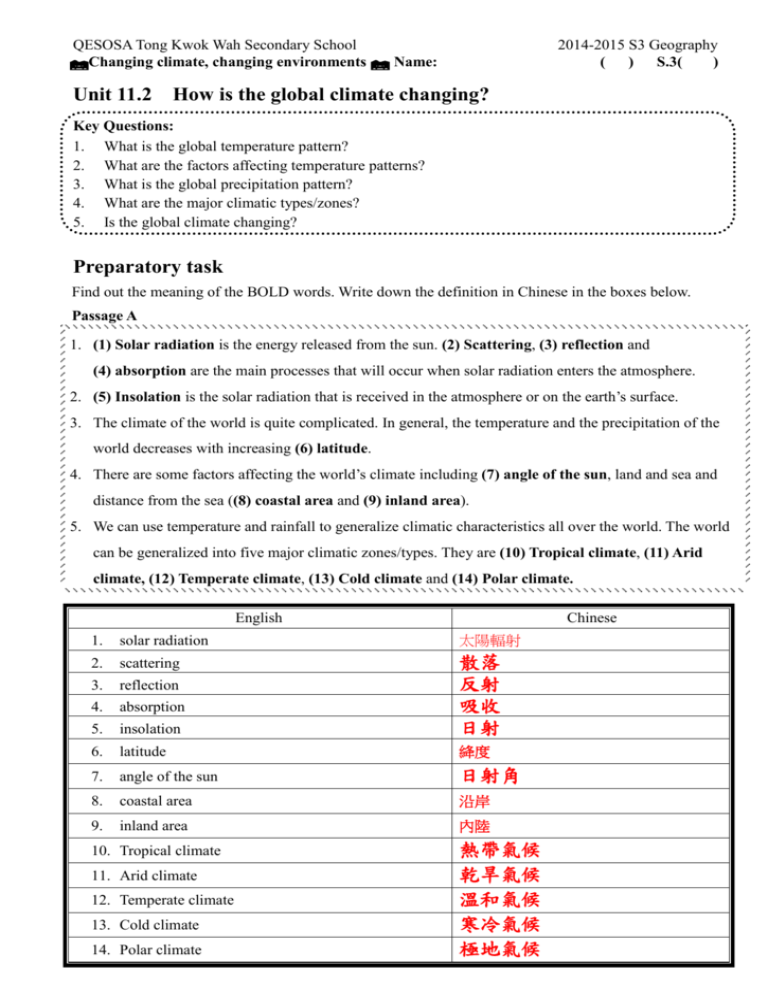
QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments Name: Unit 11.2 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) How is the global climate changing? Key Questions: 1. What is the global temperature pattern? 2. What are the factors affecting temperature patterns? 3. What is the global precipitation pattern? 4. What are the major climatic types/zones? 5. Is the global climate changing? Preparatory task Find out the meaning of the BOLD words. Write down the definition in Chinese in the boxes below. Passage A 1. (1) Solar radiation is the energy released from the sun. (2) Scattering, (3) reflection and (4) absorption are the main processes that will occur when solar radiation enters the atmosphere. 2. (5) Insolation is the solar radiation that is received in the atmosphere or on the earth’s surface. 3. The climate of the world is quite complicated. In general, the temperature and the precipitation of the world decreases with increasing (6) latitude. 4. There are some factors affecting the world’s climate including (7) angle of the sun, land and sea and distance from the sea ((8) coastal area and (9) inland area). 5. We can use temperature and rainfall to generalize climatic characteristics all over the world. The world can be generalized into five major climatic zones/types. They are (10) Tropical climate, (11) Arid climate, (12) Temperate climate, (13) Cold climate and (14) Polar climate. English Chinese 1. solar radiation 太陽輻射 2. scattering 3. reflection 4. absorption 5. insolation 散落 反射 吸收 日射 6. latitude 絳度 7. angle of the sun 日射角 8. coastal area 沿岸 9. inland area 內陸 10. Tropical climate 11. Arid climate 12. Temperate climate 13. Cold climate 14. Polar climate 熱帶氣候 乾旱氣候 溫和氣候 寒冷氣候 極地氣候 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) Name: 1. What is the global temperature pattern? Task 1: Define and identify the composition of solar radiation The following figure shows the composition of solar radiation Definition: Solar radiation is the energy released from the sun. Composition: Solar radiation is mainly composed of (i) ultraviolet (UV) radiation, (ii) visible light (iii) infrared radiation. Task 2: Name the four main processes (P, Q, R and S) occur when solar radiation enters the atmosphere. The following figure shows the condition when solar radiation enters the atmosphere. Solar radiation 100% The edge of the atmosphere P 22% Q R (20%) S P Scattering/Reflection Q Reflection/Scattering R Absorption by the atmosphere S Absorption by the earth’s surface (58%) 2 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments Name: 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) Task 3: Refer to the following figure and answer the questions below. Figure 1a shows the average annual insolation over the earth’s surface. i) Define insolation. Insolation refers to the solar radiation that is received in the atmosphere or on the earth’s surface. ii) How much of the solar radiation becomes insolation? (Hint: According to Task 2) _______________________________________________________________________________ iii) Describe the spatial distribution of average annual insolation on the earth’s surface. Spatial distribution Amount of insolation received Equatorial regions The largest / Large / Less / The least Around 23½N and S The largest / Large / Less / The least 40-50N and S The largest / Large / Less / The least Polar regions. The largest / Large / Less / The least The spatial distribution of insolation on the earth’s surface is (even / uneven). The largest amount of insolation received is located _________________________________ In general, the temperature of the world (decreases / increases) with increasing latitude . 3 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments Name: 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) Task 4: Refer to the following figures and answer the questions below. Figure 1b shows the distribution of temperature pattern of the world. (Low latitude / High latitude) has a higher temperature. Although on the same latitude, the temperature is (different / the same). On the northern hemisphere, the sea has a (higher / lower) temperature than the land. The season in the northern hemisphere is (winter / summer). Figure 1c shows the distribution of temperature pattern of the world. Low latitude / High latitude) has a higher temperature. Although on the same latitude, the temperature is (different / the same). On the northern hemisphere, the sea has a (higher / lower) temperature than that on the land. The season in the northern hemisphere is (winter / summer). 4 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments Name: 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) 2. What are the factors affecting temperature patterns? Factor 1: Angle of the sun (Latitude) In low-latitude regions, more insolation is received. This is because the angle of the sun is ( larger / smaller ) . The amount of insolation concentrates on a ( larger / smaller ) area in these regions. Air temperature is therefore ( higher / lower ). In high-latitude regions, ___________ insolation is received. This is because the angle of the sun is ___________. The same amount of insolation is spread out on a larger area in these regions. Air temperature is therefore ____________. Factor 2: Land and sea The following figures show the temperature of Place A and Place B in summer and winter. ( Place A / Place B ) has a higher temperature in summer. ( Place A / Place B ) has a higher temperature in winter. ( The land / the sea ) absorbs and loses heat quickly. As a result, it is ______ ______ in summer ( The land / the sea ) absorbs and loses heat slowly. As a result, it is ______ _______ in winter and in winter and in summer. 5 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments Name: 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) Factor 3: Distance from the sea The following figures show the temperature of Place C and Place D in summer and winter on a certain day. i) What are the range of temperature of place C and D on a certain day? Complete the table below. Places Summer Winter Range of temperature on a certain day C (Coastal area) D (Inland area) ii) Describe and explain which place has a larger range of temperature. (Place C / Place D) has a larger range of temperature. The land absorbs and loses heat (quickly / slowly). The land will be (cold / hot) in winter and (cold / hot) in summer. (Place C / Place D) is an inland area, there will be (high / low) temperature in summer and (high / low) temperature in winter. The range of temperature should be great. iii) Describe and explain which place has a smaller range of temperature. (Place C / Place D) has a smaller range of temperature. The sea absorbs and loses heat (quickly / slowly). Since (Place C / Place D) is a coastal area, the cool onshore wind in summer will (rise / lower) the temperature while the warm onshore wind in winter will (rise / lower) the temperature there. There will be (hot / cool) temperature in summer and warm temperature in winter. The annual range of temperature should be small 6 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments Name: 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) 3. What is the global precipitation pattern? The following map shows the world distribution of precipitation. i) Describe the spatial distribution of precipitation on the earth’s surface. The spatial distribution Amount of precipitation received Around the equator / Near the poles The larger Inland areas / Coastal areas The larger The spatial distribution of precipitation on the earth’s surface is ( even / uneven ). In general, the precipitation of the world ( decreases / increases ) with increasing latitude . 7 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) Name: 4. What are the major global climatic types/zones? Köppen proposed a classification system of climate in 1918 to generalize climatic characteristics in different places. The following map shows the distribution of the five major climatic types/zones. i) The following table describes the characteristics of each climatic type/zone. Identify the climatic types/zones. Climatic type/zone Tropical climate Letter symbol Characteristics A Hot and wet all year (Average temperature of the coldest month >18C) Aridclimate B Very dry all year (Potential evaporation > Precipitation Temperate climate C Cold winters and mild summers (Average temperature of the coldest month is between 18C and 0C) Cold climate D Very cold all year (Average temperature of the coldest month is ≤0C; the warmest month >10C) Polar climate E Very cold and dry all year (average temperature of the warmest month <10C) 8 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments 5. Name: 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) Is the global climate changing? Figure 5a shows the global average temperature from 1880 to 2011. Figure 5b shows the changes in global precipitation. i) Refer to Figure 5a and 5b. Complete the chart below which summarizes some major climate changes in the world in recent decades. 9 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments Name: 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) 10 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Changing climate, changing environments Name: 2014-2015 S3 Geography ( ) S.3( ) 11