Emotional Intelligence
advertisement

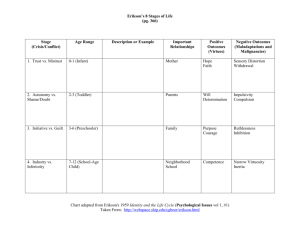
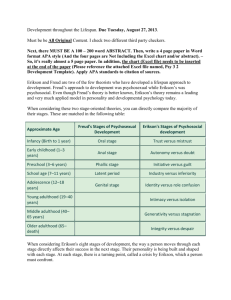
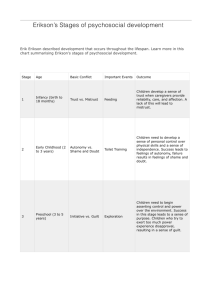
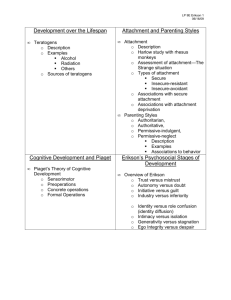
Social, & Emotional Development Overview • • • Erikson: Psychosocial Development Self Concept & Self Esteem Golman’s Emotional intelligence • • Who are you? Who has influenced your career decisions? Who has influenced your value system? • • • • What would make you want to teach Math & Science? More positive experiences with math or science? Close friends who value math or science? More funding for school work? Promise of higher pay? Social Psychology • Eric Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory. How groups influence your sense of self. • The development of personal identity Issues Affecting Adolescents • • • • • Maturation rate Gender & self esteem Suicide Eating disorders Drugs Erikson’s Stages: Infant & Preschool • • • Trust / Mistrust: Birth to 12-18 months Autonomy / Shame & Doubt: 18 months to 3 years Initiative / Guilt: 3 to 6 years Erikson’s Stages : Elementary School Years • Industry / Inferiority: 6 to 12 years Erikson’s Stages : Adolescents • Identity / Role Confusion • “Who am I?” • James Marcia’s work on identity statuses – achievement – foreclosure – diffusion – moratorium • • • Erikson’s Stages : Adult Intimacy / Isolation: Young adulthood Generativity / Stagnation: Middle Adulthood Ego integrity / Despair: Late adulthood • • • • What to do with Erikson Trust: fill the child’s needs consistently Autonomy: Allow to experiment within safe bounds Initiative: Allow limited choices that will often result in success Industry: help students set and achieve realistic goals What to do with Erikson • • • • Identity: – Supply a variety of positive role models – Be tolerant while you maintain sanity Intimacy: listen, then talk Generativity: point out successful service Integrity: compliment on life’s accomplishments Overview of Erikson: Birth Through School Age Overview of Erikson: Adults • • • • Self Concept & Self Esteem Self Concept: What you think of your self. Self Esteem: Do you like what you see in yourself Multiple concepts of self Adolescents & self-esteem Sample Self-Concept Structure Encouraging Self-Esteem • • • • Safe-to-Fail environment Know yourself & your biases Be intellectually honest See Table 3.3, Woolfolk page 85 New Role for Teachers • Affective education • Encouraging personal growth Emotional Intelligence – What is it generally? • Relationship between thought and emotion • Regulation of impulses • Empathy – Marshmallow Study – What are the components of being emotionally intelligent? E.I. Components • Identifying Emotions: seeing your feelings and those of others around you. • Manging Emotions:Thinking before you act. • Using emotions: The ability to include emotion in your reasoning through decisions • Understanding emotions: knowing how emotions are linked together. -Story- Summary • • • Erikson & Psychosocial Development Self Concept & Self Esteem Emotional intelligence Test review • Be able to describe some differences between US and Japanese classroom’s • How might cultural differences in the US effect learning? – Stereotype threat. – Examples of African American, Hawaiian kids. • Know Piaget, Vygotsky, and Erickson’s models in depth. – Be able to explain it – Be able to give their overall design and features -What are some areas where Piaget and Erickson’s models show similar ideas? Where do they differ? • Self Esteem Self & Self concept • What are components of being emotionally intelligent?