Writing Curricula: Vertical Articulation
advertisement
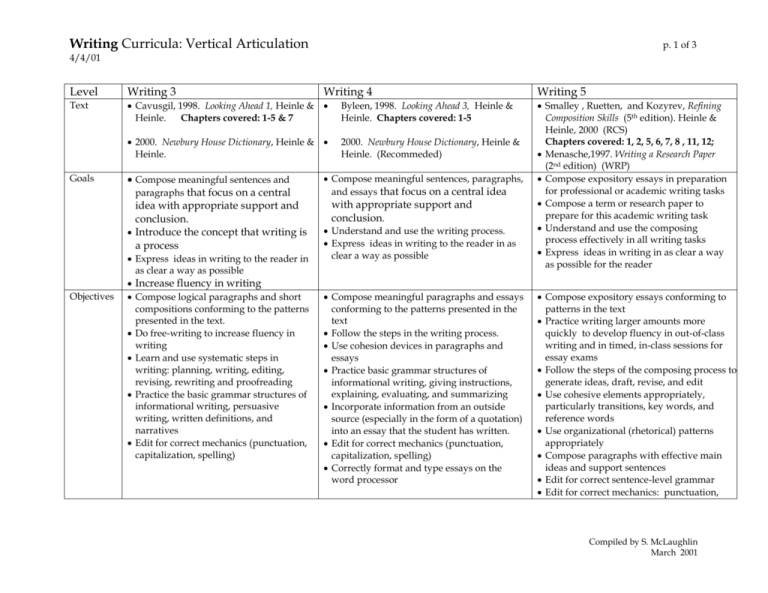
Writing Curricula: Vertical Articulation p. 1 of 3 4/4/01 Level Writing 3 Text Cavusgil, 1998. Looking Ahead 1, Heinle & Heinle. Chapters covered: 1-5 & 7 Byleen, 1998. Looking Ahead 3, Heinle & Heinle. Chapters covered: 1-5 2000. Newbury House Dictionary, Heinle & Heinle. 2000. Newbury House Dictionary, Heinle & Heinle. (Recommeded) Goals Objectives Compose meaningful sentences and paragraphs that focus on a central idea with appropriate support and conclusion. Introduce the concept that writing is a process Express ideas in writing to the reader in as clear a way as possible Increase fluency in writing Compose logical paragraphs and short compositions conforming to the patterns presented in the text. Do free-writing to increase fluency in writing Learn and use systematic steps in writing: planning, writing, editing, revising, rewriting and proofreading Practice the basic grammar structures of informational writing, persuasive writing, written definitions, and narratives Edit for correct mechanics (punctuation, capitalization, spelling) Writing 4 Compose meaningful sentences, paragraphs, and essays that focus on a central idea with appropriate support and conclusion. Understand and use the writing process. Express ideas in writing to the reader in as clear a way as possible Compose meaningful paragraphs and essays conforming to the patterns presented in the text Follow the steps in the writing process. Use cohesion devices in paragraphs and essays Practice basic grammar structures of informational writing, giving instructions, explaining, evaluating, and summarizing Incorporate information from an outside source (especially in the form of a quotation) into an essay that the student has written. Edit for correct mechanics (punctuation, capitalization, spelling) Correctly format and type essays on the word processor Writing 5 Smalley , Ruetten, and Kozyrev, Refining Composition Skills (5th edition). Heinle & Heinle, 2000 (RCS) Chapters covered: 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8 , 11, 12; Menasche,1997. Writing a Research Paper (2nd edition) (WRP) Compose expository essays in preparation for professional or academic writing tasks Compose a term or research paper to prepare for this academic writing task Understand and use the composing process effectively in all writing tasks Express ideas in writing in as clear a way as possible for the reader Compose expository essays conforming to patterns in the text Practice writing larger amounts more quickly to develop fluency in out-of-class writing and in timed, in-class sessions for essay exams Follow the steps of the composing process to generate ideas, draft, revise, and edit Use cohesive elements appropriately, particularly transitions, key words, and reference words Use organizational (rhetorical) patterns appropriately Compose paragraphs with effective main ideas and support sentences Edit for correct sentence-level grammar Edit for correct mechanics: punctuation, Compiled by S. McLaughlin March 2001 Writing Curricula: Vertical Articulation p. 2 of 3 4/4/01 Exit criteria capitalization, spelling, indentation Practice academic writing conventions for a term paper or research paper Exit criteria are not applicable at this level. Students must pass the course with a grade of C- or better. Students must pass the course with a grade of C- or better. Students with grades below C- may exit into level 4 at the discretion of the student advisor in consultation with their writing 3 teacher & supervisor and/or a Michigan test score and writing sample at the level 4 placement level. 50% Compositions and revisions outside of class 40% Other writing assignments 10% Class participation Students with grades below C- may exit into level 5 at the discretion of the student advisor in consultation with their writing 4 teacher & supervisor and/or a Michigan test score and writing sample at the level 5 placement level. 60% Longer paragraphs and compositions 20% Shorter written assignments done-in class 10% Shorter homework assignments 10% Class participation 40% Research Paper 40% Compositions (homework and inclass writing) 10% Journal and other writing, grammar, and mechanics exercises 10% Class participation Writing Skills covered in the text chapters assigned Organizing ideas from general to specific Supporting generalizations with examples from personal experience Extended comparison and contrast Cohesion devices Writing a definition Supporting a definition with examples, comparisons, and opinions Past time narratives Chronological organizers Description Using details for support Writing a survey Summarizing information Grammar Intro to parts of complete sentences Practice four basic sentence structures Review paragraph organization and cohesion devices Write clear, organized instructions Essay organization Write a memo Write detailed explanations of ideas and concepts Make an evaluation based on accepted criteria Use a variety of types of evidence to support your evaluation Summarize and respond to reading passages Distinguish main ideas from supporting details and examples Identifying cohesion devices Grading policy Some students will ask the student advisor to write a letter of recommendation for academic programs. Academic readiness is determined by Michigan Test and TOEFL scores, teacher assessment, and class grades. Writing process General paragraph structure Expository paragraphs Expository essay structure Essays developed according to particular organizational patterns Examples Comparison and Contrast Cause and effect essay Argumentative essay Classification essay (optional) Process analysis essay (optional) Review some grammar patterns, at Compiled by S. McLaughlin March 2001 Writing Curricula: Vertical Articulation p. 3 of 3 4/4/01 Structures Covered in text chapters assigned Punctuation following logical connectors Opinion structures Adverbs of frequency Modals – may & might in generalizations Expressions of quantity Connecting clauses with and, but, so Comparison structures Contrastive connectors Conditional Sentences (real) Present tense verbs Generic articles and nouns Adjective clauses (subject relatives in restrictive relative clauses) Past tense verbs Prepositional phrases in descriptions Pronouns of interactive communication (we vs. you ) Indirect speech Simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences Commands Conditional sentences (present real) Modals in instructions Definition structures Cause and effect sentences Punctuation of direct speech Modals to control the strength of generalizations Punctuation of in-text and end-of-text citations Passive sentences in informational writing Using comparatives and superlatives to give evidence in an evaluation Using a variety of verb tense to show effects over a period of time Subject-verb agreement teacher’s discretion, based on observed students’ needs in particular classes Compiled by S. McLaughlin March 2001