Sex and Marriage
advertisement

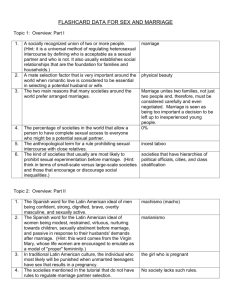
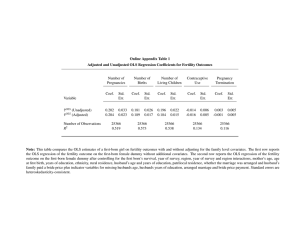
Sex and Marriage Marriage A socially recognized enduring union between two or more adults who publicly acknowledge their rights and obligations and form a new alliance between kin groups. • Purposes of marriage • To legitimize the children (kinship). • To regulate procreation rights to the spouses. • To share in the labor and property of the other spouse. • Establish property for the benefit of the children. • Establish relationship between spouses and relatives. • Case Studies • Cheyenne Two-spirit male/”female” marriage between a male and a two-spirit Why marry a two-spirit? • Nandi of Kenya • Female/”female husband” marriage. • A married woman with no male heir becomes a “female husband”. • The female husband marries a wife. • The son of the wife will have rights to the female husband’s and husband’s lineage. • Why? • Mosuo of China • no marriage and no father investment in own children. • Movie: “A World without Fathers or Husbands” • Economics of Marriage • Bridewealth : gift of money or goods from the groom’s family to the bride’s family. • offset cost of losing economic contributions of bride and children/ solidify marriage • Trobriand Islands Dowry: transfer of goods or money from the bride’s family to the bride. Usually found where women’s economic contribution is minimal (e.g. intensive agriculture) Traditional China Bride service: the groom works for the brides family. Ju’/wasi • • • Universal Incest Taboo All modern cultures prohibit marriage and intercourse between closely related relatives such as parents and children or siblings. • Is it biological? occurs in 38 mammals functions to maintain genetic diversity within a group. • Is it cultural? • The definition of incest differs by culture. • • Yanomamo: cross-cousin marriage preferred but parallel cousin considered incest. • forces people to maintain a wide social network by extending relations with people not in their group. • How many does one marry? • Monogamy: marriage between one man and one woman. Serial monogamy: series of monogamous partners in succession common in the US. • Polygyny: one man with numerous wives. • usually in societies where women are important to economics and/or where there is an excess of available women. • Why Polygyny? • Polyandry: one woman with numerous men. • aids in avoiding resource shortages and limits population growth. • Some Tibetans in Nepal practice polyandry. •