tectonics - geographylwc.org.uk
advertisement
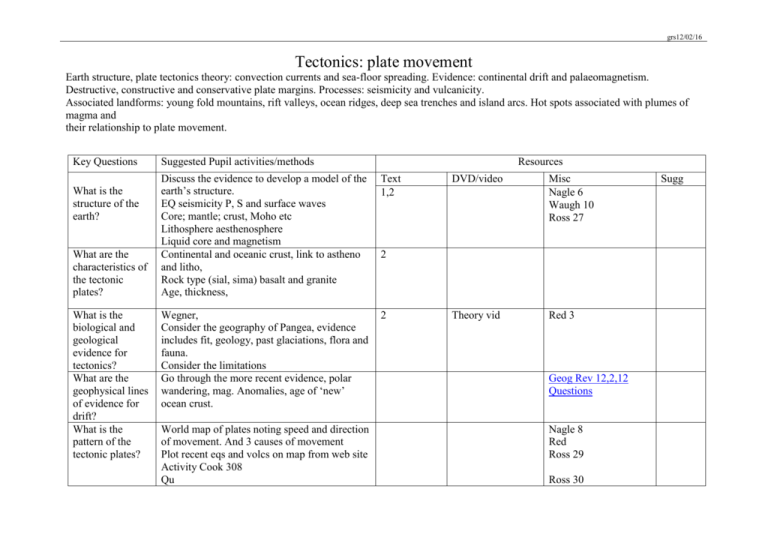
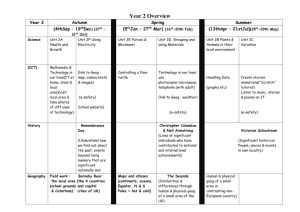
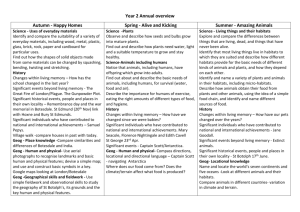
grs12/02/16 Tectonics: plate movement Earth structure, plate tectonics theory: convection currents and sea-floor spreading. Evidence: continental drift and palaeomagnetism. Destructive, constructive and conservative plate margins. Processes: seismicity and vulcanicity. Associated landforms: young fold mountains, rift valleys, ocean ridges, deep sea trenches and island arcs. Hot spots associated with plumes of magma and their relationship to plate movement. Key Questions What is the structure of the earth? What are the characteristics of the tectonic plates? What is the biological and geological evidence for tectonics? What are the geophysical lines of evidence for drift? What is the pattern of the tectonic plates? Suggested Pupil activities/methods Resources Discuss the evidence to develop a model of the earth’s structure. EQ seismicity P, S and surface waves Core; mantle; crust, Moho etc Lithosphere aesthenosphere Liquid core and magnetism Continental and oceanic crust, link to astheno and litho, Rock type (sial, sima) basalt and granite Age, thickness, Text 1,2 Wegner, Consider the geography of Pangea, evidence includes fit, geology, past glaciations, flora and fauna. Consider the limitations Go through the more recent evidence, polar wandering, mag. Anomalies, age of ‘new’ ocean crust. 2 World map of plates noting speed and direction of movement. And 3 causes of movement Plot recent eqs and volcs on map from web site Activity Cook 308 Qu DVD/video Misc Nagle 6 Waugh 10 Ross 27 Theory vid Red 3 2 Geog Rev 12,2,12 Questions Nagle 8 Red Ross 29 Ross 30 Sugg grs12/02/16 What happens at plate boundaries What happens at hot spots? Produce table, identify landforms at margins including, island arcs, trenches, fold mts, ridges, and rift valleys Using Hilton P 15, draw scatter and use Spearman’s to show relationship between eq depth and distance from trench, use Excel file Summary Satellite images Odd one out Loop of plates Discuss processes involved in terms of mantle plumes Hawaii 4 9 Yellowstone Plate move vid Nagle 9 Red 5 Ross 30 Ross 31 Cook TG 183 Geo Fact G90 GeoFile 638 Red 10 Cook 325 Prosser 23 Ross 40 GeoFile 25 526 Geog Rev, 14,2 and 14, 3 Geog Rev 16,3 Vulcanicity Variations in the type and frequency of volcanic activity in relation to types of plate margin and types of lava. Forms of intrusive activity – dykes, sills, batholiths. Minor forms of extrusive activity – geysers, hot springs and boiling mud. Major forms of extrusive activity – types of volcanoes. Two case studies of recent (ideally within the last 30 years) volcanic events should be undertaken from contrasting areas of the world. In each case, the following should be examined: • the nature of the volcanic hazard • the impact of the event • management of the hazard and responses to the event. grs12/02/16 Key Questions Suggested Pupil activities/methods What are the causes of different types of volcanic eruption? Discuss difference between intrusive and extrusive. Identify different types of volcanoes and their geological setting Activity Also type of hazard assoc with each Resources Text 11 DVD/Video 40 79 Misc Red 12 diag 15 Waugh 22 Nagle 14 Cook 327 + TG 184 Geofile 16 327 Geo Fact G30, 164 What are the forms of intrusive activity? What are the minor forms of extrusive activity? What evidence is there within the UK of past tectonic activity? How are we protected against volcano’s eruptions Discuss the formation of dykes, sills, batholiths Go through geysers, hot springs, boiling mud Powerpoint Map extrusive rocks of UK with major faults Distribution and cause PPP Nature; Impact management 12 Red 15 Waugh 23 GeoFile 687 Red 16 Nagle 13 Sugg grs12/02/16 Case study: LEDC Montserrat Causes Impact Management Case study: MEDC Etna Causes Impact Management 27 19 Red 22 Ross 42 GeoFile 19 401 Geog Rev 11,4 GGB5 Jan 05 Frampton 71 Red 20 GeoAct 14290 Geofile20417 Tectonics: seismicity The causes and main characteristics of earthquakes: focus and epicentre; seismic waves and earthquake measurement. Tsunamis – characteristics and causes. Two case studies of recent (ideally within the last 30 years) seismic events should be undertaken from contrasting areas of the world. In each case, the following should be examined: • the nature of the seismic hazard; • the impact of the event; • management of the hazard and responses to the event. Key Questions Suggested Pupil activities/methods Discuss causes of eqs, focus (depth), epicentre, Resources Text DVD/Video Misc Sugg grs12/02/16 What are the causes and distribution of earthquakes? seismic waves. Magnitude and frequency Effects Distribution, global and UK 22 20 Red 24 Cook TG 182 Geo Fact G133 How can the earthquake hazard be managed? Stat test for earthquakes Prediction Protection 26 Ross 46 Cook 338 29 28 Geofile 24510 Geog Rev 19,1 Geo Fact G194, 221 Nagle 24 Stats, mag v deaths, Spearman’s Answers Case study Indonesian tsunami Nature Impact Management Japanese Powerpoint Case study Haiti Nature Impact Management Aftermath, ppt Case study New Zealand Nature Impact Management Geog review 25,1 GeoFile 687 GeoFact 289 34 Clickview, DVD, 89. GeoFile 672 Geog Review 25,1,30 GeoFact 285 Topic Eye Nat Haz 12/13 Geog Review 25,3,34 Worksheet grs12/02/16