Level 4: HUMANITIES: ABORIGINES AND ASIA/PACIFIC STUDIES
advertisement
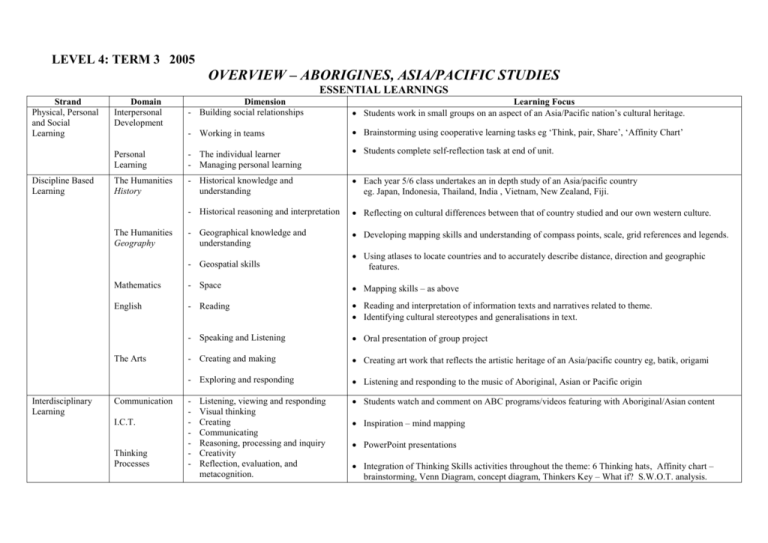
LEVEL 4: TERM 3 2005 OVERVIEW – ABORIGINES, ASIA/PACIFIC STUDIES ESSENTIAL LEARNINGS Strand Physical, Personal and Social Learning Discipline Based Learning Domain Interpersonal Development Learning Focus Students work in small groups on an aspect of an Asia/Pacific nation’s cultural heritage. - Working in teams Brainstorming using cooperative learning tasks eg ‘Think, pair, Share’, ‘Affinity Chart’ Students complete self-reflection task at end of unit. Personal Learning - The individual learner - Managing personal learning The Humanities History - Historical knowledge and understanding Each year 5/6 class undertakes an in depth study of an Asia/pacific country eg. Japan, Indonesia, Thailand, India , Vietnam, New Zealand, Fiji. - Historical reasoning and interpretation Reflecting on cultural differences between that of country studied and our own western culture. - Geographical knowledge and understanding Developing mapping skills and understanding of compass points, scale, grid references and legends. The Humanities Geography - Geospatial skills Using atlases to locate countries and to accurately describe distance, direction and geographic features. Mathematics - Space Mapping skills – as above English - Reading Reading and interpretation of information texts and narratives related to theme. Identifying cultural stereotypes and generalisations in text. - Speaking and Listening Oral presentation of group project - Creating and making Creating art work that reflects the artistic heritage of an Asia/pacific country eg, batik, origami - Exploring and responding Listening and responding to the music of Aboriginal, Asian or Pacific origin - Students watch and comment on ABC programs/videos featuring with Aboriginal/Asian content The Arts Interdisciplinary Learning Dimension - Building social relationships Communication I.C.T. Thinking Processes Listening, viewing and responding Visual thinking Creating Communicating Reasoning, processing and inquiry Creativity Reflection, evaluation, and metacognition. Inspiration – mind mapping PowerPoint presentations Integration of Thinking Skills activities throughout the theme: 6 Thinking hats, Affinity chart – brainstorming, Venn Diagram, concept diagram, Thinkers Key – What if? S.W.O.T. analysis. Level 4: ABORIGINES AND ASIA/PACIFIC STUDIES GLOBAL STATEMENTS: HISTORY: Developing an understanding of the history and culture of other races helps us to understand our own origins and culture and the influences of colonisation and immigration on Australian society today. GEOGRAPHY: Studying basic geographical features of the globe, and our own region in particular, helps us understand and recognise our own global position, landforms and population and provides us with information for comparison. FOCUS QUESTIONS: HISTORY: What is meant by the term ‘culture’? What are some of the important aspects of the culture of ………….(the Aborigines plus an Asian/Pacific nation)? How does the culture of ……………..(as above) compare to our own? How has colonisation affected the indigenous people of Australia? How has immigration impacted on life in Australia today? What is a multicultural society? GEOGRAPHY: What are the continents? What are the main countries within the Asia/ Pacific region and what are their capital cities? What are some of the major landforms within our country? our region? Eg lakes, mountain ranges, major rivers. What are some of the skills we can use when using the atlas as a reference tool? Eg reading longitude/latitude, understanding concept of scale, reading legends, using the compass, identifying time zones. Why do some countries in our region have a dense population, whilst others do not? Where do most Aboriginal people live within Australia? WEEKLY PLANNER – ABORIGINES WEEK 1 TOPIC What are aborigines? When did they arrive in Australia and where did they come from? The Dreamtime Remembering On a map show where the Aborigines came from and indicate the time period. Understanding Read a dreamtime story from the dreaming and answer a series of questions about it. (see ‘Dreaming 2’ worksheet). Daily Life Synthesising In pairs, present a written and/or oral summary for the grade on an aspect of Aboriginal life. Use information provided by the teacher as a basis for the summary. Topics: housing, foods, gathering and hunting, ceremonies, art – colours, artsymbols, music, weapons, language, dreamtime history, dreamtime stories, the Aboriginal flag. The British Invasion Aborigines today Remembering: List the good and bad points about European settlement. YELLOW HAT, BLACK HAT Applying: What if you were setting up a colony? How would you treat the indigenous population? How could you be fair to them? WHAT IF? KEY Justifying Discuss problems associated with colonisation. Put forward arguments from both points of view. Choose your own viewpoint and justify it. Discussion on current issues eg decline in population, Aboriginal rights, issues relating to education, employment, languages, housing, health and isolation followed by a swot analysis on Aborigines. S.W.O.T. ANALYSIS ( strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) 2 3 LEARNING FOCUS – ACTIVITIES AND THINKING SKILLS Applying: * Work on an Aboriginal style dot painting or drawing as the theme progresses. WEEKLY PLANNER – ASIA STUDIES WEEK TOPIC WORLD GEOGRAPHY GEOGRAPHY OF OUR REGION 6/7/8 STUDY OF AN ASIA/PACIFIC COUNTRY - Each grade selects a country to study as a class eg Indonesia, Japan, Vietnam, Thailand, New Zealand, Fiji 9. ASIA STUDIES DISPLAY 10. ‘VISITING’ OTHER COUNTRIES 4/5 LEARNING FOCUS – ACTIVITIES AND THINKING SKILLS Remembering: Following study and discussion of the world map and the Asia-Pacific region particularly, list the continents and the main countries within the Asia/Pacific region. Quiz – capital cities and countries match up. WHITE HAT Understanding: Geography of our region – use your mapping skills to explain and show your understanding of compass points, scale, grid references, legends. Application: Apply mapping, atlas and geospatial skills to plan an itinerary for a holiday overseas. Show the route on a map and accurately describe distance travelled by land, sea or air, direction, and geographical features that you likely to observe on the trip. Analysing: What is culture? Brainstorm what this means as a class and decide on some main headings eg. history, customs, celebrations, music, dance, art, food, dress etc. Work as individuals and in groups to build affinity charts. (see notes) AFFINITY CHART Compare our own western culture with that of an Asian country as individuals and as a class. Investigate aspects of: - Daily life - Geographical features, landforms, size, - Traditions and beliefs population - Customs - Economics – industry, tourism - Governance - Wars and invasions VENN DIAGRAM N/B Any students that have a cultural background in one of the countries studied to be called upon fore assistance in the various grade Synthesising In groups, choose an aspect of the given country’s culture. Plan and create a visual display. Become an expert on the information you have researched and displayed and be prepared to answer questions on it. CONCEPT DIAGRAM Year 5 and 6 students rotate around the different ‘countries’ with a ‘passport’, viewing displays and are encouraged to ask their peers questions about the ‘countries’ they visit.