Big Maths - Bellfield Primary School
advertisement
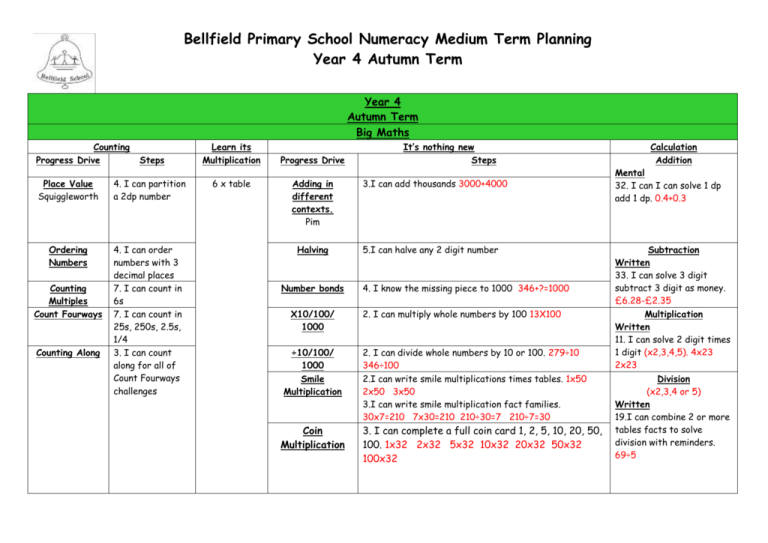
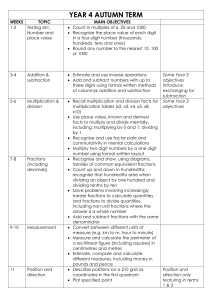
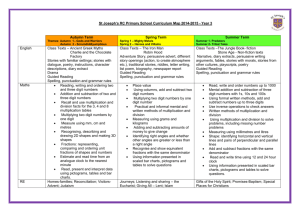
Bellfield Primary School Numeracy Medium Term Planning Year 4 Autumn Term Year 4 Autumn Term Big Maths Counting Progress Drive Steps Place Value Squiggleworth 4. I can partition a 2dp number Ordering Numbers 4. I can order numbers with 3 decimal places 7. I can count in 6s 7. I can count in 25s, 250s, 2.5s, 1/4 3. I can count along for all of Count Fourways challenges Counting Multiples Count Fourways Counting Along Learn its Multiplication 6 x table Progress Drive Adding in different contexts. Pim Halving Number bonds X10/100/ 1000 ÷10/100/ 1000 Smile Multiplication Coin Multiplication It’s nothing new Steps 3.I can add thousands 3000+4000 5.I can halve any 2 digit number 4. I know the missing piece to 1000 346+?=1000 2. I can multiply whole numbers by 100 13X100 2. I can divide whole numbers by 10 or 100. 279÷10 346÷100 2.I can write smile multiplications times tables. 1x50 2x50 3x50 3.I can write smile multiplication fact families. 30x7=210 7x30=210 210÷30=7 210÷7=30 3. I can complete a full coin card 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100. 1x32 2x32 5x32 10x32 20x32 50x32 100x32 Calculation Addition Mental 32. I can I can solve 1 dp add 1 dp. 0.4+0.3 Subtraction Written 33. I can solve 3 digit subtract 3 digit as money. £6.28-£2.35 Multiplication Written 11. I can solve 2 digit times 1 digit (x2,3,4,5). 4x23 2x23 Division (x2,3,4 or 5) Written 19.I can combine 2 or more tables facts to solve division with reminders. 69÷5 Outline of main topics Week Main Topic Title 1 Objectives To count in multiples of 6, 25 and 1000 Count Fourways 1, 7 I can count in multiples of 6, 25 and 1000 To find 1000 more or less than a given number Number I can find 1000 more than any number I can find 1000 less than any number To recognise the place value of each digit in a four-digit number (thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones) Place value 3 (1) Locate 3- and 4-digit numbers on land-marked lines, 100s or 1000s labelled, and on empty number lines Counting along 1-2 I recognise the value of each digit in a 4 digit number I can partition a 4 digit number I understand that 0 is used as a place holder To order and compare numbers beyond 1000. Ordering numbers 3 Compare using < and > I can order and compare numbers in context e.g. temperature, measures and money Solve number and practical problems that involve all of the above and with increasingly large positive numbers I can use 4 digit numbers in different ways to solve one and two step number problems, through the use of column method. I can use a variety of representations to solve problems including fractions and measure. Links with Hamilton, NRICH and NCETM Hamilton Trust Week 1 NCETM Activities https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42476 NRICH Activities 1. Some Games That May Be Nice or Nasty The Deca Tree Addition and Subtraction (Another week later in the term) 2/3 Measurement 4 Revise mental calculation strategies for addition and subtraction Adding pairs of two digits Addition22-25 Complements to 10 Jigsaw Numbers 1-2 Addition and subtraction facts to 20 Add numbers with 3 digits using the informal written methods (expanded) of addition Addition 26-29 I can use columnar addition to add numbers with 3 digits I can use columnar subtraction to subtract numbers with up to 3 digits Subtract three digit numbers using a number line (finding the difference) Subtraction 29-32 To estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to a calculation I can estimate answers to a calculation. I can use inverse operations to check answers to a calculation. Solve addition and subtraction two-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why. (1) Hamilton Trust Week 2 and 3 NCETM Activities https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42543 NRICH Activities 1. The Puzzling Sweet Shop Money Bags Amy’s Dominoes Escape from the Castle Fifteen Cards Sealed Solution Roll These Dice I can identify the operation(s) to use when solving problems. I can solve two-step addition and subtraction problems within a context (extending to decimal units of measure) I can justify the methods I have used to solve a problem. Convert between different units of measure (e.g. kilometre to metre; ) Link this to multiplying and dividing by 10 and 100 ITS NOTHING NEW. (Only do measures that link to these calculations at this stage no x1000.) X10, 100, 100, -1-2. ÷10, 100, 100, -1-2 Measure and calculate the perimeter of a rectilinear figure (including squares) in centimetres and metres (straight lines) (1) I can measure a perimeter of a rectilinear figure in centimetres I can measure a perimeter of a rectilinear figure in metres Estimate, compare and calculate different measures (2) I can estimate different measures I can compare different measures I can calculate different measures NCETM Activities https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42733 NRICH Activities 1. Torn Shapes 2. Discuss and Choose 5 Recognise and show, using diagrams, families of common equivalent fractions Count Fourways 1-8 I can understand the relationship between denominators and their divisors. I can recognise equivalent fractions I can show equivalent fractions using diagrams or shapes I can find common equivalent fractions Solve problems involving increasingly harder fractions to calculate quantities, and fractions to divide quantities, (1) Fractions Quantities involved – ½ ¼ 1/10 1/5 Of shapes and quantities 1 1 3 Recognise and write decimal equivalents to /4; /2; /4 Count Fourways 1-8 I can recognise decimal equivalents to 1/4; 1/2; ¾ I can write decimal equivalents to 1/4; 1/2; ¾ To find the effect of dividing a one- or two-digit number by 10 and 100, identifying the value of the digits in the answer as units, tenths and hundredths . X10, 100, 100, -1-2. ÷10, 100, 100, -1-2 I can recognise when a 1 or 2 digit number has been divided by 10 or 100. I can explain when a 1 or 2 digit number has been divided by 10 or 100. I can read and identify the value of the digits within an answer as units, tenths or hundredths. I can use language such as decimal point when describing differing values of a digit. Solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals to one decimal place. Adding with Pim 1-4 I can solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions. I can solve simple measure and money problems involving two decimals. I can solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals. NCETM Activities https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42648 NRICH Activities 1. Fractions in a Box Chocolate To read, write and convert time between analogue and digital 12 and 24-hour clocks Statistics and Measure (Time) 6 I can read the time on a 12 hour analogue clock. I can read the time on a 12 hour digital clock. I can read the time on a 24 hour digital clock. I can write the time on a 12 hour analogue clock. I can write the time on a 12 hour digital clock. I can write the time on a 24 hour digital clock. I can convert time between analogue and digital to 12 hours. I can convert time between analogue and digital to 24 hours To solve problems involving converting from hours to minutes; minutes to seconds; years to months; weeks to days. I can convert between hours and minutes in real life situations (eg. TV listings). I can convert between minutes and seconds in real life situations (eg. bus timetables). I can convert between years and months in real life situations (eg. calendars). I can convert between weeks and days in real life situations To interpret and present discrete data using bar charts and continuous data using bar charts I can interpret discrete data using bar charts with scales beyond 2, 5, 10. I can interpret continuous data using bar charts with scales beyond 2, 5, 10. I can present discrete data using bar charts To solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information presented in bar charts (1) I can solve comparison problems using information presented in bar charts, pictograms and other graphs I can solve sum and difference problems using information presented in bar charts, pictograms and other graphs. Assess and Review 7 Assessment against big maths trackers and progress drives Assessment against each objective on the emergent, expectant and exceeding. Collins Assess and review lessons Testbase NCETM NRICH Big Maths Assessment grids Hamilton Trust Week 9 NCETM Activities Stat https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42962 Time https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42733 NRICH Activities 1. Venn Diagrams More Carroll Diagrams Plants Half Term 1 To count in multiples of 6, 25 and 1000 Count Fourways 1, 7 I can count in multiples of 6, 25 and 1000 To find 1000 more or less than a given number I can find 1000 more than any number I can find 1000 less than any number Number To recognise the place value of each digit in a four-digit number (thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones) Place value 3 (1) Locate 3- and 4-digit numbers on land-marked lines, 100s or 1000s labelled, and on empty number lines Counting along 1-2 (1) I recognise the value of each digit in a 4 digit number I can partition a 4 digit number I understand that 0 is used as a place holder To order and compare numbers beyond 1000. Ordering numbers 3 Compare using < and > I can order and compare numbers in context e.g. temperature, measures and money Solve number and practical problems that involve all of the above and with increasingly large positive numbers I can use 4 digit numbers in different ways to solve one and two step number problems, through the use of column method. I can use a variety of representations to solve problems including fractions and measure. Read Roman numerals to 100 (I to C) and know that over time, the numeral system changed to include the concept of zero and place value. I can read Roman numerals to 100 (I to C) I can understand concepts of how the numeral system changed to include the concept of zero and place value. I can identify the different ways to write Whole numbers in historical context e.g. Roman Numerals Hamilton Trust Week 6 NCETM Activities https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42476 NRICH Activities Some Games That May Be Nice or Nasty The Deca Tree Recall multiplication and division facts for multiplication tables up to 12 × 12 Autumn Term – 2,3,4,5,6,9,10,11 (1) 2/3 I can recall I can recall I can recall I can recall I can recall I can recall all all all all all all the multiplication facts to 12 x 6 of the division facts to 72 ÷ 6 the multiplication facts to 12 x 7 of the division facts to 84 ÷ 7 the multiplication facts to 12 x 9 of the division facts to 108 ÷ 9 Multiplication and Division Use place value to multiply and divide by 10 and 100. X10, 100, 100, -1-2. ÷10, 100, 100, -1-2 To use place value, known and derived facts to multiply and divide mentally, including: multiplying by 0 and 1; dividing by 1; (2) I can multiply any number by 0 I can divide any number by 0 I can multiply any number by 1 I can divide any number by 1 Multiply two-digit by a one-digit number using formal written layout (grid multiplication – see calculation policy. Multiplication 11-12. I can use an informal written method to calculate 2 digit x 1 digit statements Smile Multiplication 1-2 Solve problems involving multiplying and adding. I know whether to use multiplication or division to solve a problem I can solve problems involving multiplication I can solve problems involving division I can solve problems involving multiplication and addition. I can work out intervals on a scale using my times table facts (Y4) I can use my multiplication and related division facts to solve problems involving objects with remainders I can use repeated addition to solve 2 digit number x 1 digit number calculations I can mentally calculate 3 digit x 1 digit statements using my tables facts I can mentally calculate 3 digit x 1 digit statements and their related division facts. I can use multiplication to solve two-step problems I can use division to solve two-step problems. Begin to decide whether to round up or down after division Choose appropriate number operations and calculation methods to solve money and ‘real life’ word problems with one or more steps. Explain and record methods. Check with equivalent calculation Hamilton Trust Week 5, 10 and 11 NCETM Activities https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42598 NRICH Activities 1. Multiplication Square Jigsaw Shape Times Shape Table Patterns Go Wild! Let’s Divide Up! That Number Square! Carrying Cards Light the Lights Again Multiples Grid Zios and Zepts 2. Trebling All the Digits 4 To compare and classify geometric shapes, including quadrilaterals and triangles, based on their properties and sizes (1) Geometry I can compare and classify the properties and sizes of quadrilaterals for example: parallelogram, rhombus, trapezium I can compare and classify the properties and sizes triangles for example: isosceles, equilateral, scalene To identify lines of symmetry in 2-D shapes presented in different orientations (2) I can identify lines of symmetry in 2D shapes in different orientations To complete a simple symmetric figure with respect to a specific line of symmetry.(3) I can draw symmetrical patterns I can complete a simple symmetric figure with one line of symmetry I can recognise line symmetry in a variety of diagrams including where the line of symmetry does not dissect the original shape Hamilton Trust Week 4 NCETM Activities https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42842 NRICH Activities 1. Nine-pin Triangles Cut it Out 2. Let’s Reflect National Flags Stringy Quads 3. A Cartesian Puzzle Symmetry Challenge Coordinate Challenge 5 Recognise and show, using diagrams, families of common equivalent fractions Count Fourways 1-8 I can understand the relationship between denominators and their divisors. I can recognise equivalent fractions I can show equivalent fractions using diagrams or shapes I can find common equivalent fractions I can simplify fractions in order to calculate equivalences using factors and multiples. Fractions Solve problems involving increasingly harder fractions to calculate quantities, and fractions to divide quantities, (1) Begin to relate finding unit fractions to division and use to find ½, 1/3, ¼, 1/5 or 1/10 of multiples of 2, 3, 4, 5 or 10 moving onto non unit fractions of the fractions above with whole number answers. Of shapes and quantities 1 1 3 Recognise and write decimal equivalents to /4; /2; /4 Count Fourways 1-8 I can recognise decimal equivalents to 1/4; 1/2; ¾ I can write decimal equivalents to 1/4; 1/2; ¾ To find the effect of dividing a one- or two-digit number by 10 and 100, identifying the value of the digits in the answer as units, tenths and hundredths . X10, 100, 100, -1-2. ÷10, 100, 100, -1-2 I can recognise when a 1 or 2 digit number has been divided by 10 or 100. I can explain when a 1 or 2 digit number has been divided by 10 or 100. I can read and identify the value of the digits within an answer as units, tenths or hundredths. I can use language such as decimal point when describing differing values of a digit. Solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals to one decimal place. Adding with Pim 1-4 I can solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions. I can solve simple measure and money problems involving two decimals. I can solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals. I can find a fraction which is several parts of a whole. NCETM Activities https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42648 NRICH Activities Fractions in a Box Chocolate Addition and Subtraction 6 Revise mental calculation strategies for addition and subtraction Adding pairs of two digits Addition22-25 Complements to 10 Jigsaw Numbers 1-2 Addition and subtraction facts to 20 Add numbers with 3 digits using the informal written methods (expanded) of addition Addition 26-29 I can use columnar addition to add numbers with 3 digits I can use columnar subtraction to subtract numbers with up to 3 digits Subtract three digit numbers using a number line (finding the difference) Subtraction 29-32 To estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to a calculation I can estimate answers to a calculation. I can use inverse operations to check answers to a calculation. Solve addition and subtraction two-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why. (1) 7 Assess and Review I can identify the operation(s) to use when solving problems. I can solve two-step addition and subtraction problems within a context (extending to decimal units of measure) I can justify the methods I have used to solve a problem. Assessment against big maths trackers and progress drives Assessment against each objective on the emergent, expectant and exceeding. Collins Assess and review lessons Testbase NCETM NRICH Big Maths Assessment grids Hamilton Trust Week 7 and 8 NCETM Activities https://www.ncet m.org.uk/resource s/42543 NRICH Activities 2. The Puzzling Sweet Shop Money Bags Amy’s Dominoes Escape from the Castle Fifteen Cards Sealed Solution Roll These Dice