Do you need encryption
advertisement

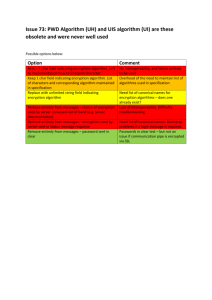
Do you need encryption? By Dr. Francisco Eduardo Rivera Federal Aviation Administration ATO-E (AUA-6) 800 Independence Ave. SW Washington DC, 20591 (202) 385-8309 Francisco.rivera@faa.gov SALT Washington Interactive Technologies 2004 Arlington, Virginia – August 18-20, 2004 ABSTRACT In the information society we live in, everybody needs to record confidential information. The quantity of confidential information depends on the assets you have and your job. Particularly, many web sites require you to have a login name and a password to enter in to the site and require you to change them often. In fact, some of the web sites even let you make transactions. To keep confidential information on paper is not a viable solution because, it is easier to lose, hard to recover, clumsy to store, and changes frequently. Lastly, once found, anybody can see it and use it. The solution is to store this information in a computer, on a disk or in a Personal Digital Assistant (PDA); and of course to encode it secretly, that makes the information encrypted. The need to protect confidential information is becoming a priority due not only to direct hackers but also because of the latest phenomenon -- identity theft. In this article we examine the meaning of encryption and its relevance for a common user. We review the different techniques for encryption and how secure they are, in a non-mathematical language. We also review different strategies to manage this confidential information using some common commercial software. STRUCTURE We want to write this article in a non-technical language and of course far to use mathematics, although we can just say that Cryptology is a Mathematical based Computer Science and when we say Mathematics is with Upper case and can be very complex. In fact is a speciality that is offered in some PhD programs such as University of Maryland, or the Central European University. There are many research centers, companies and gubernamental organisms such Department of defense, National Security Agency, or Homeland Security dedicated to the study of Cryptology. So we are not going to enter into the many complexitities of this field and try just to answer if for a normal user like you or me is Encryption a need and a suitable tool. Cryptography has a long history by which humans transmitted secretly messages from Romans to Aztecs, but probably Cryptography acquiers its fame during the Second World War. In this War the information (and misinformation) acquiered a special value to win the battles and finally the war, with plenty of stories of spies and machines to decipher. Today thanks to the Internet as a public, open network of data, it is the normal way in which we communicate us, but the Internet is intrinsecally open not only in its standards but in its contents too. It is a network of networks in which you do not know a priori where your messages are going to pass through and these messages are needed to be repeated from one node to another in this super-network. There is no direct way to keep secret something. What is Cryptography or Encryption? We must first attempt to define what are we undestand for Crypotography. Cryptography is the Science and the process is called Encryption. Cryptography is undestood mainly as the science (or the art) of “converting data into a secret code for transmission over a public network.” (Techencyclopedia 2004). Thus Encryption is “the reversible transformation of data from the original (the plaintext) to a difficult-to-interpret format (the ciphertext) as a mechanism for protecting its confidentiality, integrity and sometimes its authenticity. Encryption uses an encryption algorithm and one or more encryption keys.” (Techencyclopedia, 2004) Encryption is transforming the data into an ureadable format and by definition it needs to be reversivble in the sense that at the other end of the communication line (or network) it can be decipher to obtain the message into plaintext again. The process is based on an algorithm in order to repeat the process or to send other messages using the same process. The algorithm can be very complex composed of several steps, combinations, compressions, permutations, but in the last it can be described as a mathematical transformation. We assume that only those who know the algorithm can decipher the encrypted message. So the algorithm must be secret by definition. But if the algorithm is secret how it can be studied? The only way is to create an algorithm that can be public and can be customized to each user that is modified but not in its structure and only in the way in which it is applied. This is why it was invented the “key” which is a secret “small”code that applied to the general algorithm can transform the algorithm in an unique way such that the results of applying the same algorith with different key produce different results and that cannot be deducted. In the modern cryptography is thus always associated the encryption algorith with a key. Nevertheless “encrypted messages can sometimes be broken by cryptanalysis, also called codebreaking” (Webopedia, 2004) that helps to decipher the message. This is the main problem of Cryptography how to avoid with a reasonable small (fast, finite, etc.) algorithm to produce an encryption that is unbreakable. Anyway, modern encryption techniques can be reasonable unbreakable. And although you can invent your own algorithm that for you is very difficult, very probably it is not difficult for many computer techniques to break code; including the intelligent trial and error that repeated many times using a fast computer can decode your secret in a reasonable short time. So do no try to re-invet the wheel, use one of the many well proofed algorithms. The Clinton Administration enouraged “the use of strong encryption techniques in commerce and private communication while protecting the public safety and national security. It would be developed by industry and will be availbale for both domestic and international use.” (Electronic Privacy Information Center, 1996) Phishing is a technique that is currently being used by spammers, or more appropriately “scammers”, to obtain, or “fish” for, private information of email consumers, particularly taking advantage of home email users who do not have elaborate firewalls protecting them. Phishers are most commonly mining for bank account numbers, social security numbers, and credit card information. Security is the issue, Privacy in general and confidentiality, integrity and sometimes its authenticity Confidentiality is Integrity is Authenticity is It is a Growing problem Are there other alternatives to Encryption? Password access Password protecting files Use a Vault. PGP Pretty Good Privacy EFS Ipsec PPTP encryption Do we need Encryption? Encryption may be very complex. Ypou still need to manage keys secretly. If you want to keep your procedures private, probably nobody can help you to retrieve your information. What to do next? References Techencyclopedia, TechWeb a service of CMP, The Business Technology Network, www.techweb.com, 2004. Webopedia, a service of Jupitermedia Corporation. www.webopedia.com, 2004. Electronic Privacy InformationCenter, Administration Statement on Commercial Encryption Policy”, http://www.epic.org/crypto/key_escrow/wh_cke_796.html July 12, 1996.