UNDERSTANDING YOUR PET`S BLOOD TESTS "CBC, chem 7
advertisement

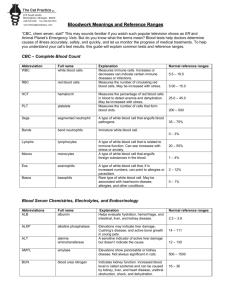
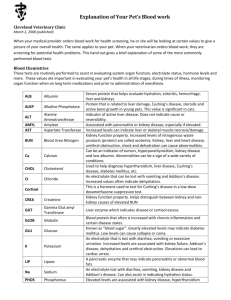
UNDERSTANDING YOUR PET'S BLOOD TESTS "CBC, chem 7, STAT!" This may sound familiar if you watch popular television shows, such as E.R., Chicago Hope, and Emergency Vets. Despite the Hollywood drama these are real tests that give the doctor critical information regarding the internal functions of the patient. The doctor uses these tests to help diagnose disease, assess response to medication and determine anesthetic safety. Identifying potential problems early is "the key" to preventive medicine! To help you understand your pet's blood test results this guide explains some of the common tests. CBC (complete blood count) This is a common tests performed on people and pets. It gives helpful information regarding dehydration, anemia, infection and blood clotting ability. Pets with fevers, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness or loss of appetite may benefit from this test. Pets undergoing surgery are also helped. HCT (hematocrit) measures the percentage of red blood cells. It is helpful to determine blood weakness or dehydration. Hb (hemoglobin) help determine the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood. WBC (white blood cell count) measures the body's immune cells. Increases or decreases indicate certain diseases, infection and one form of cancer. GRANS / LYMPHS are specific types of white blood cells. EOS (eosinophils) are another type of white blood cell that may indicate certain allergies or parasitic infections. PLATELETS measures cells that help in blood clotting function. RETICS (reticulocytes) are immature red blood cells.High levels suggest regenerative anemia. FIBRINOGEN is another blood clotting function test.High levels can also mean pregnancy. CHEM-7 (blood chemistries) These common tests evaluate the function of the internal organs, body salt levels, hormone levels and more. They are important in evaluating older pets, pets with vomiting or diarrhea, poison exposure, pets receiving long term medications and a pet's health prior to anesthesia. ALBUMIN is a blood protein that helps the doct-or evaluate hydration, hemorrhage, intestinal, liver and kidney disease. ALKPHOS (alkaline phosphatase) elevations may indicate liver damage, Cushing's disease, diabetes or low thyroid. ALT (SGPT) is a sensitive indicator of active liver disease but doesn't indicate the cause. AMYLASE elevations suggest pancreas gland infections or kidney disease. BUN (blood urea nitrogen) indicates kidney or liver function, dehydration, shock or urinary obstruction. CALCIUM deviations can indicate many different problems. Over-active parathyroid glands, kidney disease, certain forms of cancer can be detected. CHOLESTEROL is a supplemental test to help reveal thyroid disorders, liver disease, diabetes and Cushing's disease. CORTISOL is a hormone that is measured to detect Cushing's or Addison's disease, both hormone disorders. CREATININE levels reveal kidney function. It helps additionally if the BUN is elevated. GLOBULIN is a blood protein that increases with chronic inflammation and certain diseases. GLUCOSE is a blood sugar. Elevated levels can indicate stress or diabetes. Low levels can cause collapse, seizures or coma. K (potassium) is an electrolyte (body salt) lost with vomiting, diarrhea or excessive urina tion. Increased levels indicate kidney or Addison's disease, dehydration or urethral obstruction. High levels can result in death. LIPASE is an enzyme that measures inflammation of the pancreas (digestive) gland. NA (sodium) is an electrolyte lost due to vomiting, diarrhea, kidney or Addison's disease. PHOSPHORUS elevations are often associated with kidney disease, over active thyroid glands or bleeding disorders. TOTAL BILIRUBIN elevations may indicate liver obstruction or blood destruction. TP (total protein) indicates dehydration, liver, kidney and infectious diseases. T4 (thyroxine) is a thyroid gland hormone. Decreased levels can be problems for dogs and increased levels are common in the older cat.