CILOs
advertisement

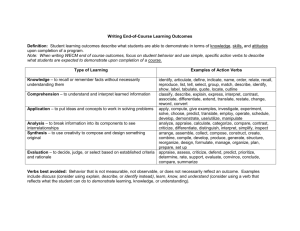
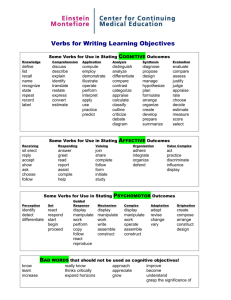
The Hong Kong Institute of Education Outcomes-based Learning Unit Guide to Writing Course Statements (CILOs) Intended Learning Outcomes 1. What are Course Intended Learning Outcomes? Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs) are clear and measurable statements that define what a student is able to DO at the completion of a course or program. Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs) refer to observable and measurable: Knowledge – example: students know basic management principles and concepts. Skills – example: students can locate appropriate sources by searching electronic databases. Attitudes – example: students appreciate the professional code of ethics for business practice. Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs) are NOT statements about what is covered in a course. The following are NOT learning outcome statements: Students will write three papers in the course. The course offers students the opportunity to exercise their critical thinking skills. Student will be exposed to a wide range of theories currently practices in the field. 2. Characteristics of Course Intended Learning Outcomes Statements Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs) should: Reflect essential knowledge, skills or attitudes students should be able to demonstrate at the end of the course; Reflect broad conceptual knowledge; Focus on results of the learning experiences; Reflect the desired end of the learning experience, not the means or the process; Reflect simple, specific action verbs that lend themselves to measurement 1 Verbs (see appendix) are crucial to writing effective learning outcome statements. Concrete verbs are better than vague verbs. “Define” is better than “be familiar with”; “apply” is better than “know.” Aim for goals that are neither too broad nor too specific: Students will demonstrate information literacy skills (too vague). Students will be able to use institutional online services to retrieve information (too specific). Students will locate information and evaluate it critically for its validity and appropriateness (better). Examples of Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs) Statements: Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to: Use theoretical frameworks of history to make independent interpretations of the development of cultural assumptions, values and practices (History). Design, evaluate, and use a variety of instructional media and technology (Education). Accurately use social scientific concepts to describe and analyze what they observe (Sociology). Identify diverse patterns in social life and explain how social, political, economic, and cultural forces contribute to their emergence (Sociology). 3. Developing Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs) Start from the list of objectives on your course outline (the ones that have been there all along). Group these objectives into categories or generalizations to create a shorter set of over-arching LO statements. Focus on what the student can do. Don't address what was taught or presented, but address the observable outcome you expect to see in the student. List the knowledge, skills, attitudes, or values you would like students to possess when they graduate from your course. Use active verbs. Active verbs are easier to measure. Using appropriate action verbs, state what students will be able to do or what they should be able to demonstrate as a result of completing your course. Include an assessable expectation. It helps if you have clearly defined expectations concerning the criteria related to that outcome. Share the outcomes with faculty from other disciplines and within your own discipline. 2 Share the outcomes with your students. Students need to clearly understand what is expected, they are unfamiliar with the discipline specific language. This helps focus the clarity of the statements. Modify as you learn from experience. Use language that is clear and direct. When possible, use language your students can understand. 4. Key Questions to Ask 1. Are you trying to assess what your students are learning as a result of completing your course? 2. Are your Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs) measuring something useful and meaningful? 3. Are the Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs) appropriate and realistic given the level and types of students taking your course? 4. Is the outcome measurable? 5. Do you have too many Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs) listed? 3 APPENDIX Action Verbs and Bloom’s Taxonomy Cognitive Learning Action Verbs Knowledge: to recall or remember facts without necessarily understanding them arrange, articulate, collect, define, describe, duplicate, enumerate, examine, identify, label, list, memorize, name, order, quote, recognize, relate, recall, reproduce, show, tabulate, tell Comprehension: to understand and interpret learned information associate, classify, contrast, describe, differentiate, discuss, distinguish, estimate, explain, express, interpret, locate, paraphrase, predict, recognize, report, restate, review, translate Application: to put ideas and concepts to work in solving problems Analysis: to break information into its components in order to see interrelationships and ideas Synthesis: to use creativity to compose and design something original Evaluation: to judge the value of information based on established criteria apply, calculate, complete, compute, change, choose, deliver, demonstrate, discover, dramatize, employ, establish, examine, experiment, illustrate, interpret, make, modify, operate, practice, relate, schedule, show, sketch, solve, use analyze, appraise, arrange, calculate, categorize, classify, compare, connect, contrast, criticize, differentiate, distinguish, divide, examine, experiment, infer, interpret, investigate, order, question, separate, test arrange, assemble, collect, compose, construct, create, design, formulate, generalize, integrate, manage, organize, plan, prepare, propose, set up, rewrite appraise, argue, assess, attach, conclude, convince, compare, critique, defend, evaluate, judge, predict, question, rate, recommend, review, summarize, support Affective Learning appreciate, accept, attempt, challenge, defend, dispute, join, judge, praise, question, share, support Psychomotor Learning bend, grasp, handle, operate, reach, relax, shorten, stretch, differentiate (by touch), express (facially), perform (skillfully) 4