Unit 3: Earthquakes Intro Slideshow Notes
advertisement
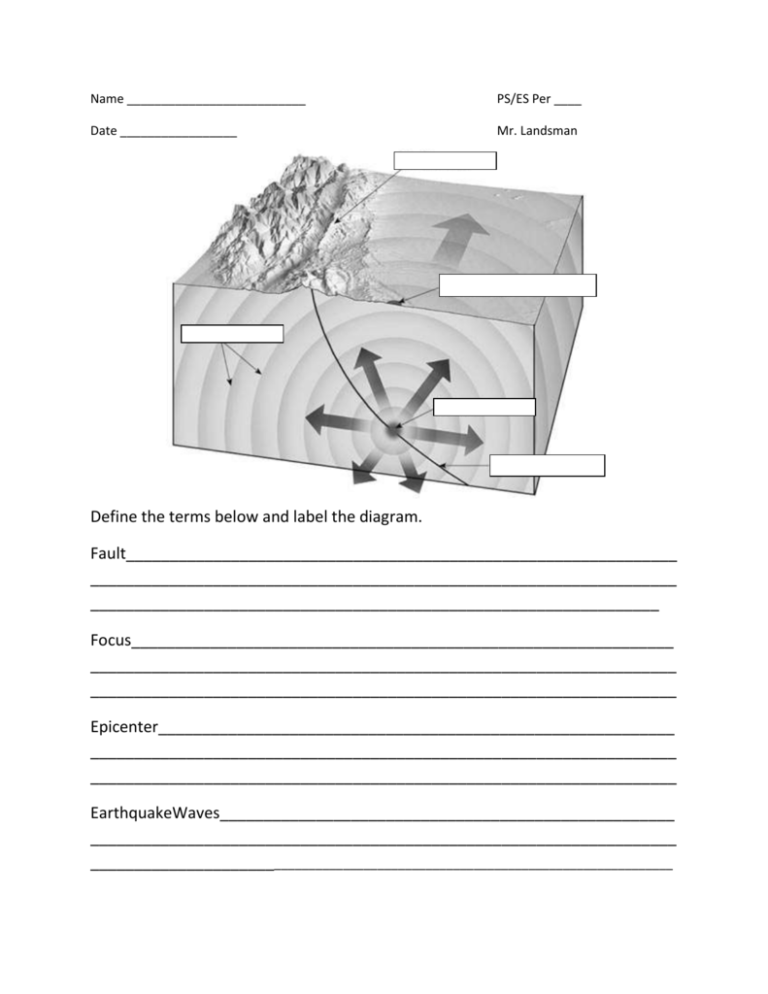
Name __________________________ PS/ES Per ____ Date _________________ Mr. Landsman Define the terms below and label the diagram. Fault_______________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Focus______________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Epicenter___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ EarthquakeWaves____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ What is an Earthquake? • Sudden movement in the Earth’s crust that releases energy in the form of __________________ • Movement occurs along areas of __________________________ in the earth’s crust. How is energy transmitted? • Energy is transmitted through seismic (earthquake) ________________ or vibrations • Types of earthquake waves: • P- waves: Primary waves • Travel fastest, arrive ______________________ • S- waves: Secondary waves • Travel more slowly than P-waves, arrive _______ P-wave Wave Propagation (transmission): Longitudinal waves: • Particles move parallel to the direction the wave travels • Primary wave (p-waves) is a __________________________ wave • They make the ground vibrate _________________________________ • Arrive at seismic recording stations ___________________________ • Can travel through solids, liquids and gases (Solids and Fluids) Transverse waves: • Particles move perpendicular to direction of wave motion • Secondary waves are _____________________________ waves • Travel about ½ as fast as ________________________ • Make the ground vibrate from side to side, up and down • Can only travel through ________________________ ONLY See demo Velocities: – in the same medium, P waves travel at a greater velocity (_________) than S waves. However, the velocities of seismic waves depend upon the physical properties of the material through which the waves travel (medium). Higher density media result in a higher velocity of wave propagation. Summary: Wave Type Relative Velocity It go like dis Transmitted through… P S How are earthquakes detected? Seismograph: • an instrument attached to the Earth designed to detect crustal shifts Seismogram: • recording of the earthquake waves by the seismograph machine Note: this image is an output from a machine. It is NOT what the actual waves look like. How is the strength of an earthquake measured? Mercalli scale (un-scientific): – Based upon _____________________ from people in affected area including damage and what was felt – Also known as Mercalli Intensity Richter________________ Scale: – Measured using the wave size (amplitude) on seismogram – Magnitude scale (ex. An earthquake of 5 has 10 times as much energy released as a 4) Examples: Magnitude 1 = 10 energy units Magnitude 2 = ___________units What happens if an earthquake on the ocean floor displaces a large amount of seawater? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Warning Signs: ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Emergency Preparation Actions: ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale from FEMA I. People do not feel any Earth movement. II. A few people might notice movement if they are at rest and/or on the upper floors of tall buildings. III. Many people indoors feel movement. Hanging objects swing back and forth. People outdoors might not realize that an earthquake is occurring. IV. Most people indoors feel movement. Hanging objects swing. Dishes, windows, and doors rattle. The earthquake feels like a heavy truck hitting the walls. A few people outdoors may feel movement. Parked cars rock. V. Almost everyone feels movement. Sleeping people are awakened. Doors swing open or close. Dishes are broken. Pictures on the wall move. Small objects move or are turned over. Trees might shake. Liquids might spill out of open containers. VI. Everyone feels movement. People have trouble walking. Objects fall from shelves. Pictures fall off walls. Furniture moves. Plaster in walls might crack. Trees and bushes shake. Damage is slight in poorly built buildings. No structural damage. VII. People have difficulty standing. Drivers feel their cars shaking. Some furniture breaks. Loose bricks fall from buildings. Damage is slight to moderate in well-built buildings; considerable in poorly built buildings. VIII. Drivers have trouble steering. Houses that are not bolted down might shift on their foundations. Tall structures such as towers and chimneys might twist and fall. Well-built buildings suffer slight damage. Poorly built structures suffer severe damage. Tree branches break. Hillsides might crack if the ground is wet. Water levels in wells might change. IX. Well-built buildings suffer considerable damage. Houses that are not bolted down move off their foundations. Some underground pipes are broken. The ground cracks. Reservoirs suffer serious damage. X. Most buildings and their foundations are destroyed. Some bridges are destroyed. Dams are seriously damaged. Large landslides occur. Water is thrown on the banks of canals, rivers, lakes. The ground cracks in large areas. Railroad tracks are bent slightly. XI. Most buildings collapse. Some bridges are destroyed. Large cracks appear in the ground. Underground pipelines are destroyed. Railroad tracks are badly bent. XII. Almost everything is destroyed. Objects are thrown into the air. The ground moves in waves or ripples. Large amounts of rock may move. Name____________________ PS/ES Per___ Date_______________ Mr. Landsman The field map below represents Modified Mercalli scale reports from witnesses of an earthquake in New York. Plot isolines on the map at an interval of one ‘Mercalli’. Answer the questions. 1 1 1 1 2 2 4 3 6 4 1 5 1 2 2 1 1 1. Place an X on the likely location of the epicenter. 2. Name one type of damage that may have been observed at the epicenter._____________________________________________________________________________ 3. What caused the earthquake waves? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Citizens in Utica were at the epicenter of the earthquake but did not report any visible faults. Explain how this is possible (use the word “focus” in your answer). _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________