esomeprazole magnesium - Glory Cubed Productions
advertisement

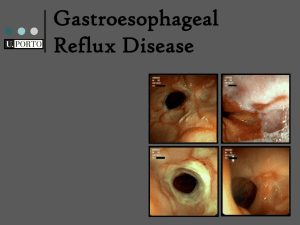
esomeprazole magnesium (perprazole, S-omeprazole) (ess oh me' pray zol) Nexium Pregnancy Category C Drug classes Antisecretory agent Proton pump inhibitor Therapeutic actions Gastric acid-pump inhibitor: Suppresses gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the hydrogen–potassium ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cells; blocks the final step of acid production; is broken down less in the first pass through the liver than the parent compound omeprazole, allowing for increased serum levels. Indications GERD—treatment of heartburn and other related symptoms Erosive esophagitis—short-term (4–8 wk) treatment for healing and symptom relief. Also used for maintenance therapy following healing of erosive esophagitis As part of combination therapy for the treatment of duodenal ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori Reduction in occurrence of gastric ulcers associated with continuous NSAID use in patients at risk (> 60 yr, history of gastric ulcers) for developing gastric ulcers Contraindications and cautions Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to omeprazole, esomeprazole, or other proton pump inhibitor. Use cautiously with hepatic dysfunction, pregnancy, lactation. Pharmacokinetics Route Oral Onset 1–2 hr Peak 1.5 hr Duration 17 hr Metabolism: Hepatic; T1/2: 1–1.5 hr Distribution: Crosses placenta; may enter breast milk Excretion: Urine and bile Adverse effects CNS: Headache, dizziness, asthenia, vertigo, insomnia, apathy, anxiety, paresthesias, dream abnormalities Dermatologic: Rash, inflammation, urticaria, pruritus, alopecia, dry skin GI: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, dry mouth, tongue atrophy, flatulence Respiratory: URI symptoms, sinusitis, cough, epistaxis Interactions Drug-drug Increased serum levels and potential increase in toxicity of benzodiazepines and phenytoin when taken concurrently May interfere with absorption of drugs dependent upon presence of acidic environment (eg ketoconazole, iron salts, digoxin) Nursing considerations CLINICAL ALERT! Potential for name confusion exists between esomeprazole and omeprazole; use caution. Assessment History: Hypersensitivity to any proton pump inhibitor; hepatic dysfunction; pregnancy, lactation Physical: Skin lesions; T; reflexes, affect; urinary output, abdominal examination; respiratory auscultation, liver function tests Interventions WARNING: Arrange for further evaluation of patient after 4 wk of therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disorders. Symptomatic improvement does not rule out gastric cancer. If administering antacids, they may be administered concomitantly with esomeprazole. Ensure that the patient swallows capsule whole; do not crush, or chew; patients having difficulty swallowing may open capsule and sprinkle in applesauce or disperse in tap water, orange or apple juice, or yogurt; do not crush or chew pellets. Obtain baseline liver function tests and monitor periodically during therapy. Maintain supportive treatment as appropriate for underlying problem. Provide additional comfort measures to alleviate discomfort from GI effects and headache. Establish safety precautions if dizziness or other CNS effects occur (use side rails, accompany patient). Teaching points Take the drug at least 1 hr before meals. Swallow the capsules whole; do not chew or crush. If you cannot swallow the capsule, it can be opened and sprinkled in applesauce or mixed in tap water, orange or apple juice, or yogurt; do not crush or chew the pellets. This drug will need to be taken for 4–8 wk, at which time your condition will be reevaluated. Arrange to have regular medical follow-up while you are using this drug. Maintain all of the usual activities and restrictions that apply to your condition. If this becomes difficult, consult with your nurse or physician. You may experience these side effects: Dizziness (avoid driving a car or performing hazardous tasks); headaches (consult with your health care provider if these become bothersome, medications may be available to help); nausea, vomiting, diarrhea (proper nutrition is important, consult with your dietitian to maintain nutrition; ensure ready access to bathroom facilities); symptoms of URI, cough (it may help to know that this is a drug effect, do not self-medicate, consult with your health care provider if this becomes uncomfortable). Report severe headache, worsening of symptoms, fever, chills, darkening of the skin, changes in color of urine or stool. Adverse effects in Italic are most common; those in Bold are life-threatening.